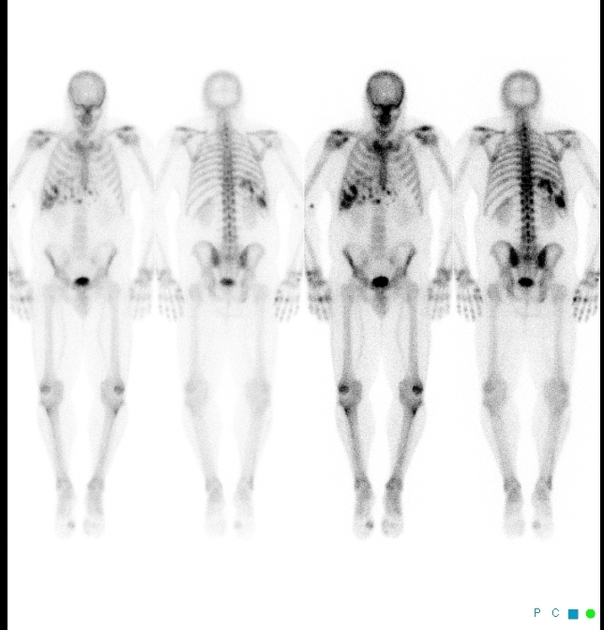
Bone scintigraphy (a.k.a. bone scans) is a nuclear medicine (scintigraphic) study that makes use of technetium-99m (commonly Tc-99m-methylene diphosphonate (MDP)) as the active agent 2. About 50% of the injected dose will be absorbed by the bones after 2 to 6 hours 2.
The study has three phases that follow the intravenous tracer injection. Sometimes a fourth (delayed/delayed) phase is performed.
On this page:
Indications
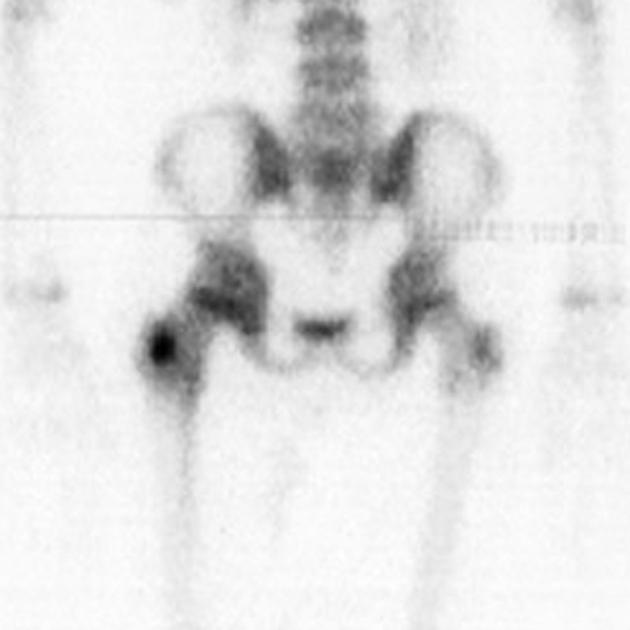
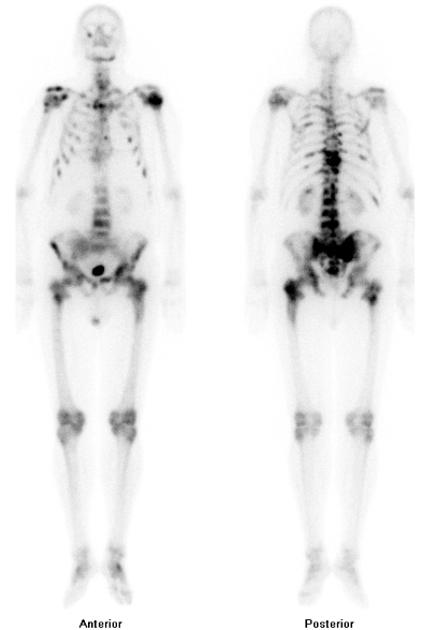
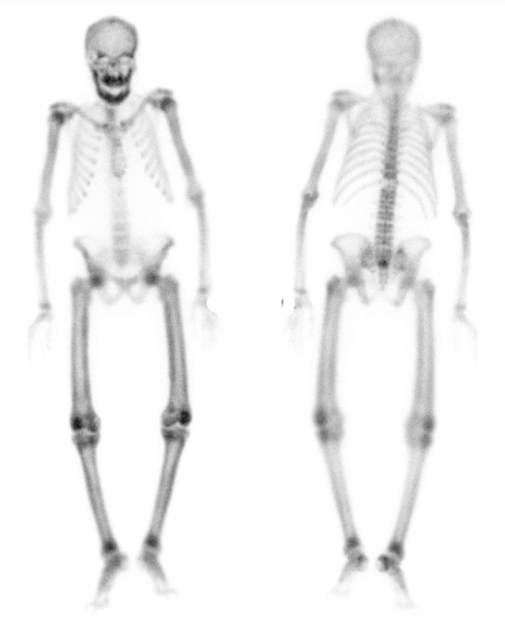
malignancy: detection and follow-up of skeletal metastases 2
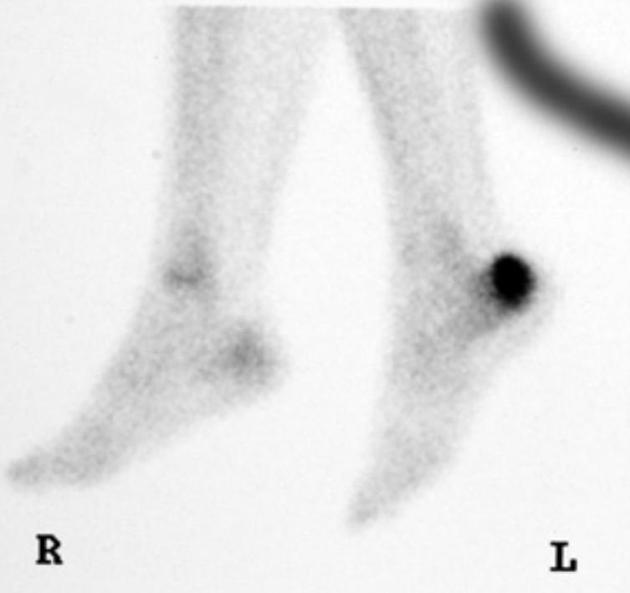
detection of radiographically occult fractures, e.g. stress or insufficiency fractures 2
hip joint prosthesis: evaluation for infection or loosening
Patient preparation
optimal hydration
remove metal objects
void immediately before the study
Conditions with excessive iron deposition in the body such as Thalassemia major and hemochromatosis causes an increase in radiopharmaceutical uptake in the kidneys and liver while reduces the uptake in the bones 7.
As 99mTc MDP is renally excreted, reduced renal function can result in poor image quality as the tracer is not cleared effectively from the soft tissues. It is therefore important to optimize renal function and ensure adequate patient hydration.
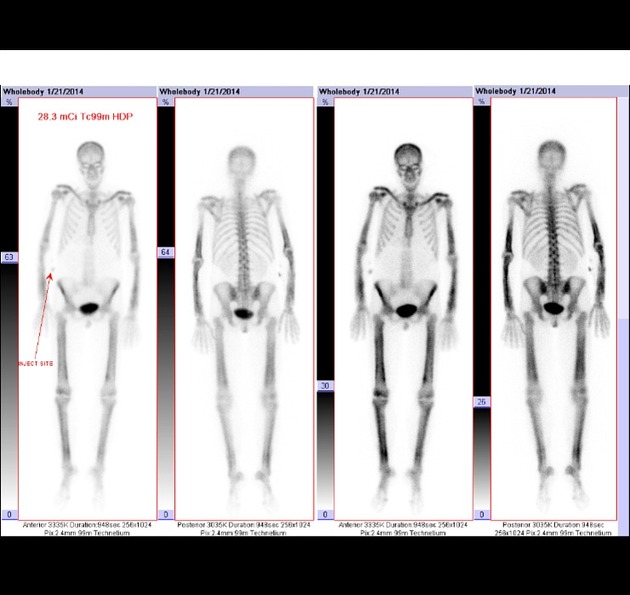
Tracer dose and route of administration
Tc-99m diphosphonate is administered intravenously, at a dose of 740 - 925 Mbq (20 - 25 mCi) in adults 2.
Renal uptake during bone scan is useful in detecting renal abnormalities. The majority of the faint or absent renal uptake is due to renal insufficiency. For those without renal disease, widespread metastatic bone disease is the most common cause for faint or absent renal uptake 6.
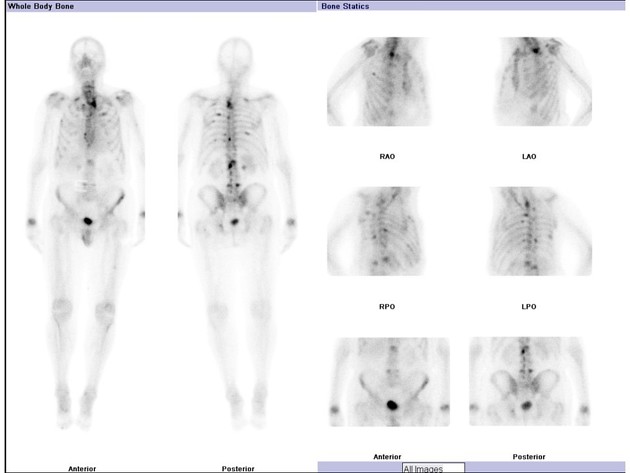
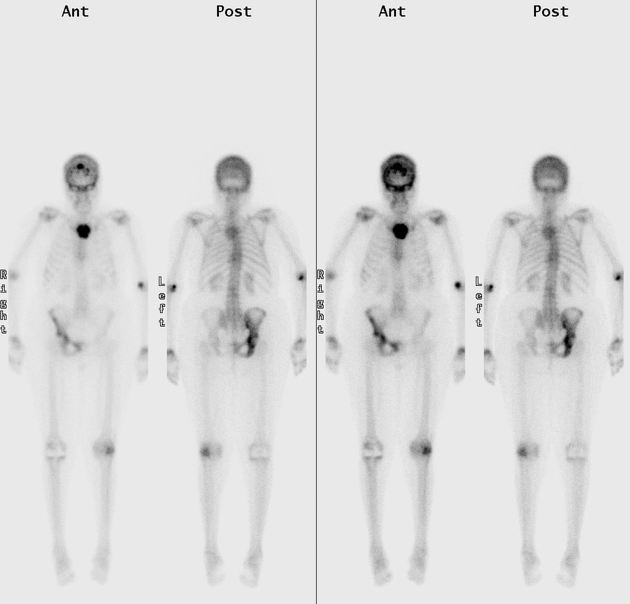
Phases (kinetic modelling)
Flow phase
2-to-5 second images are obtained for 60 seconds after injection
demonstrates perfusion
characterizes blood flow to a particular area
Blood pool phase
obtained 5 minutes after injection
demonstrates the blood pool (balance between plasma and interstitium), not the blood flow
inflammation causes capillary dilatation and increased blood flow
If the study is going to be a triphasic bone scan, a third phase is added.
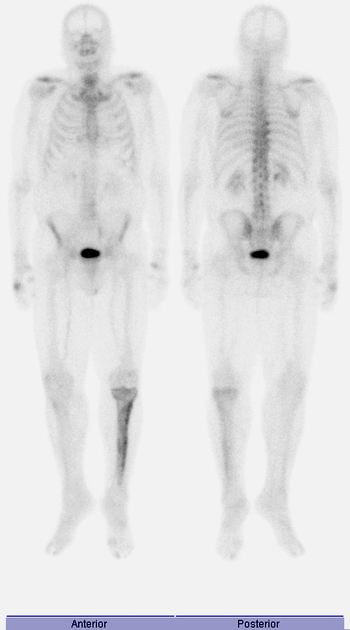
Delayed phase
obtained 2-4 hours later
urinary excretion has decreased the amount of the radionuclide in soft tissue
mechanism of uptake is not known with certainty, although it has been proposed that the radiotracer attaches to hydroxyapatite crystals (chemisorption) 5
degree of uptake depends on blood flow and rate of new bone formation
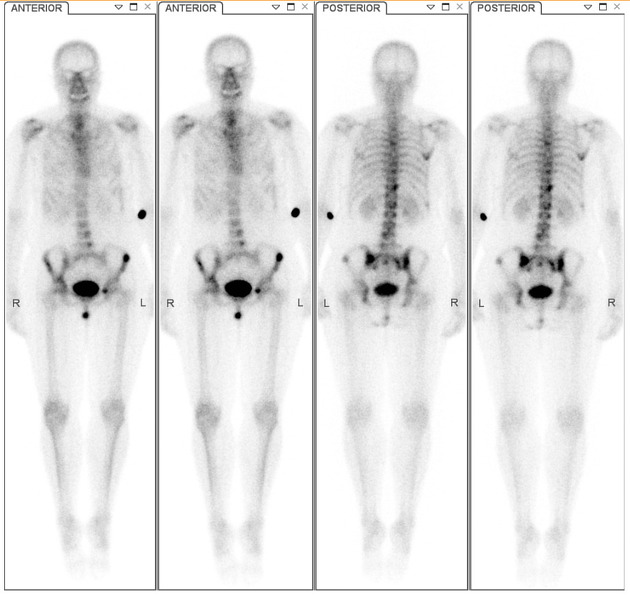
Delayed/delayed
obtained 24 hours after injection as a static image




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.