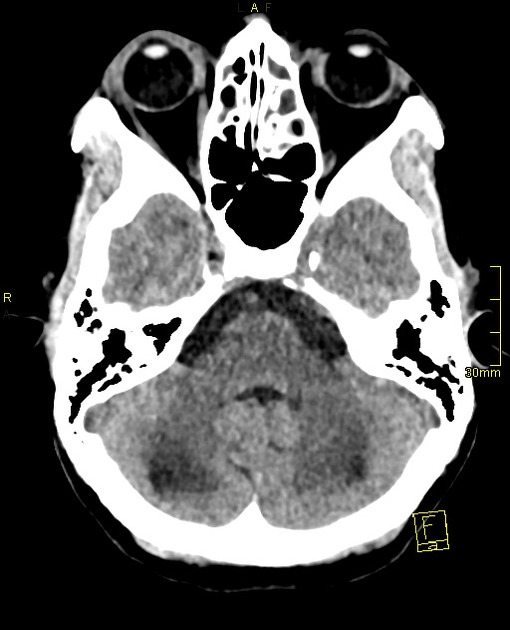
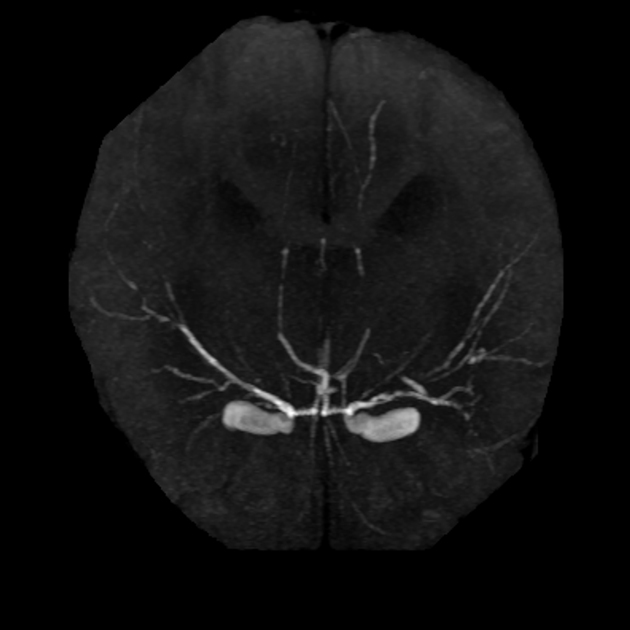
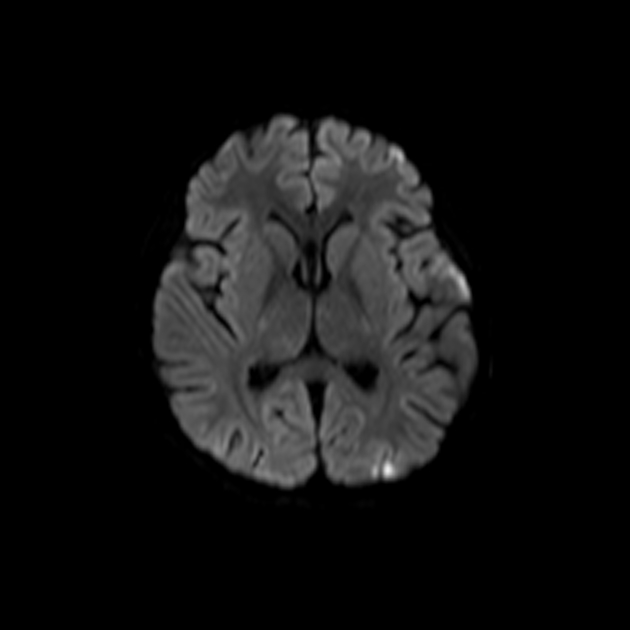
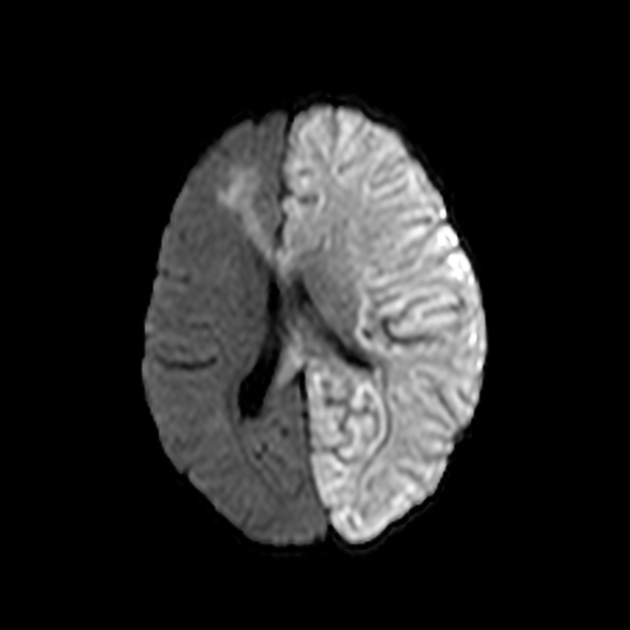
Stroke in children and young adults can result from several causes, which are distinct from the most common causes in adults.
Pathology
Etiology
Arterial ischemic stroke
-
arteriopathies
CADASIL (cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy)
CARASAL (cathepsin A-related arteriopathy with strokes and leukoencephalopathy)
CNS vasculitis (e.g. large vessel childhood primary angiitis of the CNS (cPACNS), systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.)
HANAC syndrome (hereditary angiopathy with nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps syndrome)
MELAS (mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes)
multisystemic smooth muscle dysfunction syndrome (ACTA2 cerebral arteriopathy)
PADMAL (pontine autosomal dominant microangiopathy with leukoencephalopathy)
retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukoencephalopathy and systemic manifestations (RVCL-S)
-
embolic phenomena
-
arterial dissection
-
infection
varicella zoster (postvaricella arteriopathy)
-
thrombophilias
other genetic disorders (e.g. neurofibromatosis type 1 2, Fabry disease)
Hemorrhagic stroke
-
areteriopathies
CNS vasculitis (e.g. large vessel childhood primary angiitis of the CNS (cPACNS), systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.)
-
vascular lesions
arteriovenous malformation
aneurysms
moyamoya disease/syndrome (less commonly causes hemorrhagic stroke than in adults)
-
bleeding diatheses
anticoagulation
inherited coagulopathies
platelet disorders
-
drugs
amphetamines
cocaine
Venous thrombosis
pregnancy
postpartum
combined oral contraceptive pill
thrombophilias (as above)
skull base/intracranial or other proximal venous infection (e.g. Lemierre syndrome)
malignancy (e.g. acute lymphoblastic leukemia)
chemotherapy (e.g. L-asparaginase)
dehydration




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.