Small bowel lymphoma is one of the most common small bowel malignancies, accounting for ~25% of all primary small bowel malignancies, and ~40% of all primary gastrointestinal lymphomas.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Small bowel lymphoma is most commonly secondary extranodal involvement in widespread systemic lymphoma. When primary it is seen predominantly in well-defined patient groups, and the demographics, therefore, match those groups. Predisposing conditions include 1:
organ transplant (see post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD))
Helicobacter pylori positive patients
Clinical presentation
The presentation is variable and includes 1:
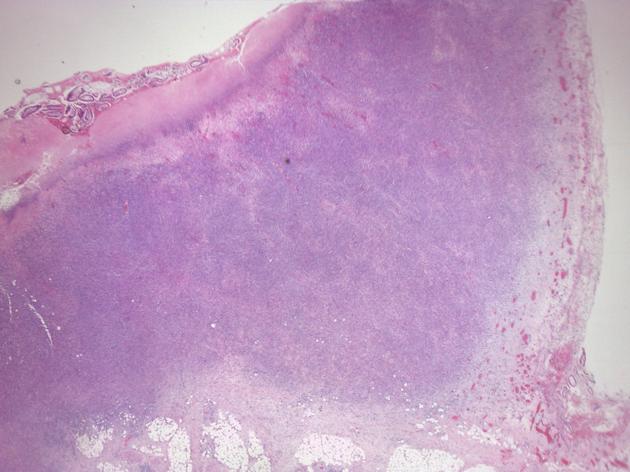
Pathology
The type of lymphoma depends on the underlying predisposing condition.
H. pylori: mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALToma)
PTLD: polyclonal B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (EBV-associated)
HIV: B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma 3, overall most common type
T-cell lymphomas are seen but are uncommon 5; they have a greater tendency to perforate
Location
The most common sites are the ileum (60-65%) and jejunum (20-25%) 7.
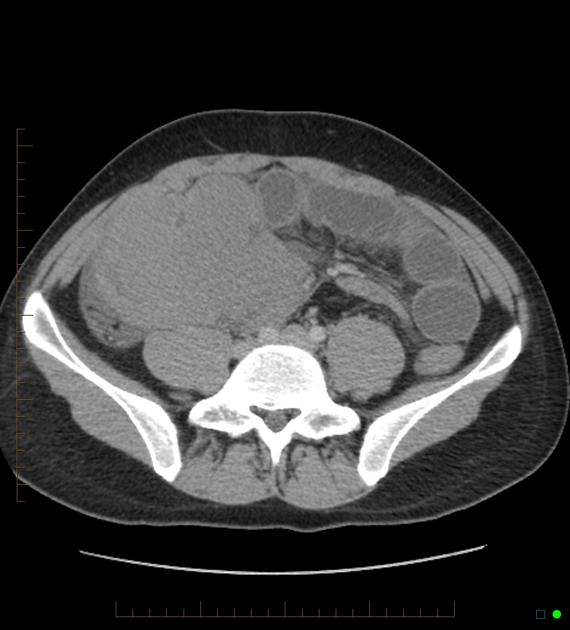
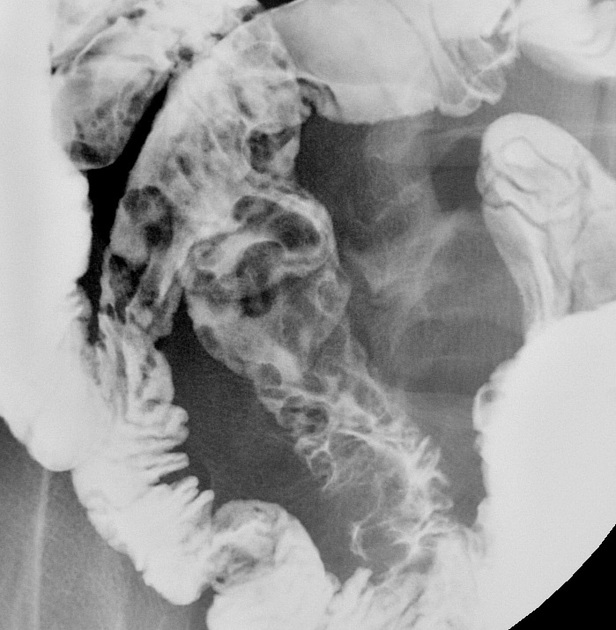
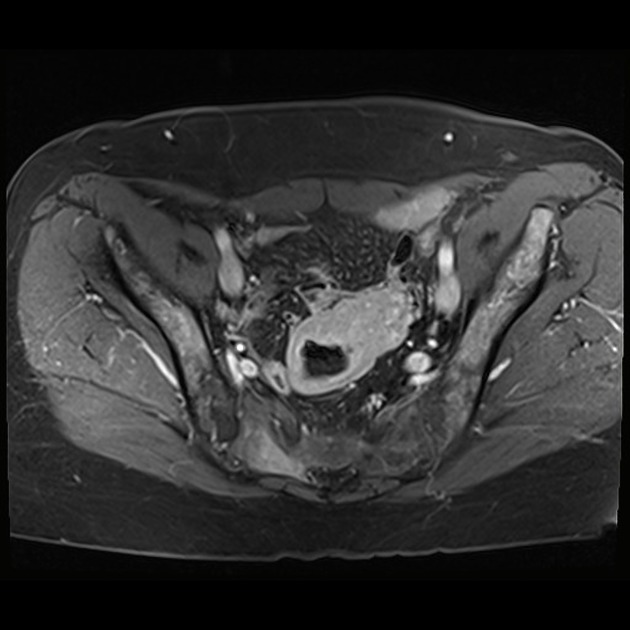
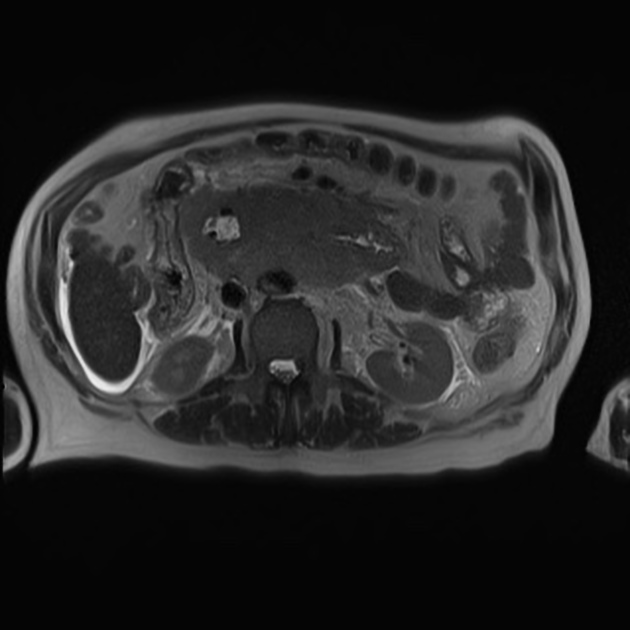
Radiographic features
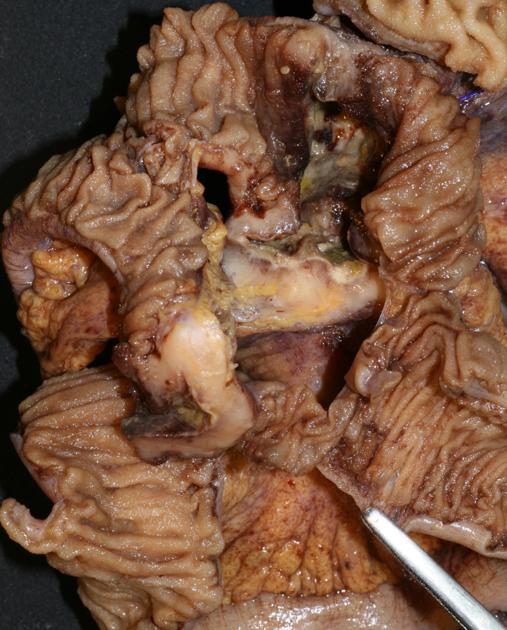
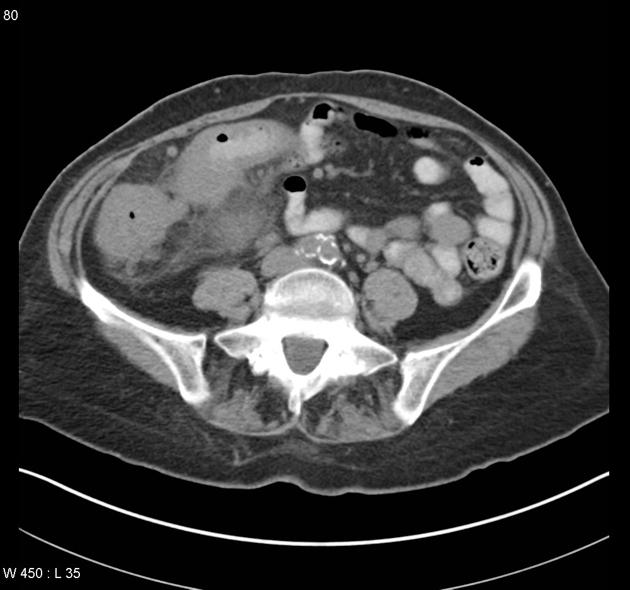
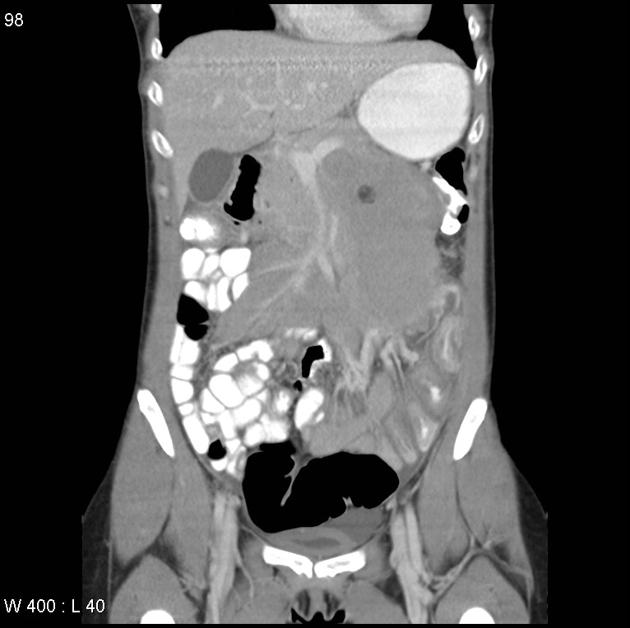
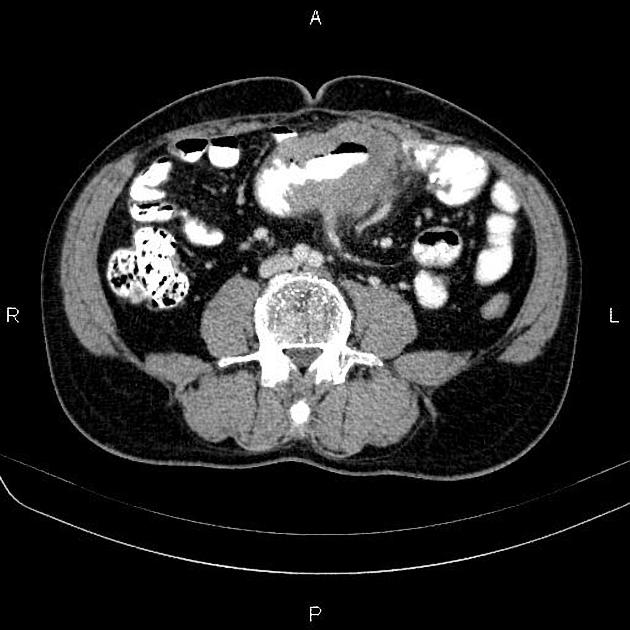
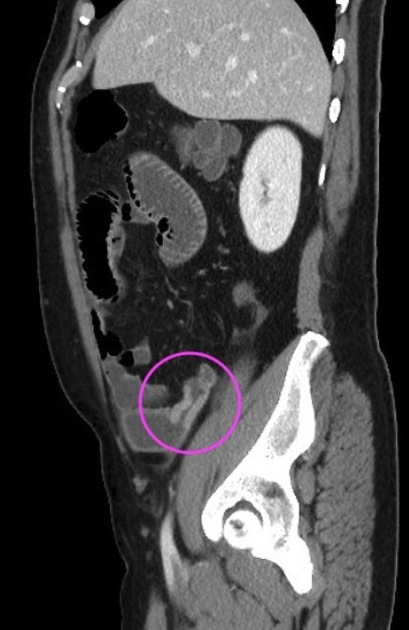
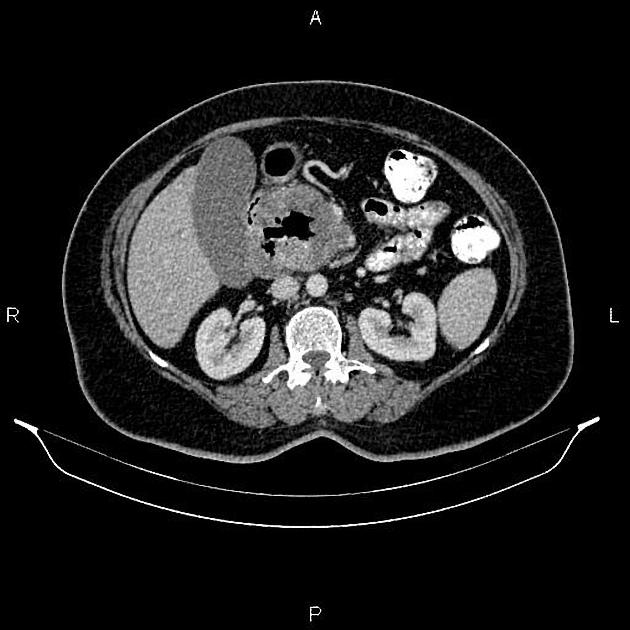
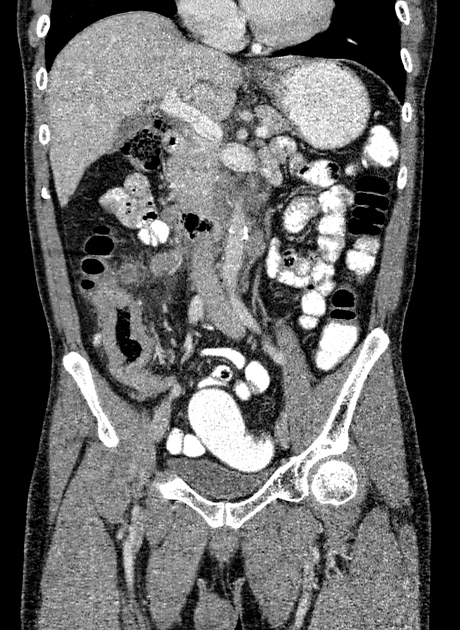
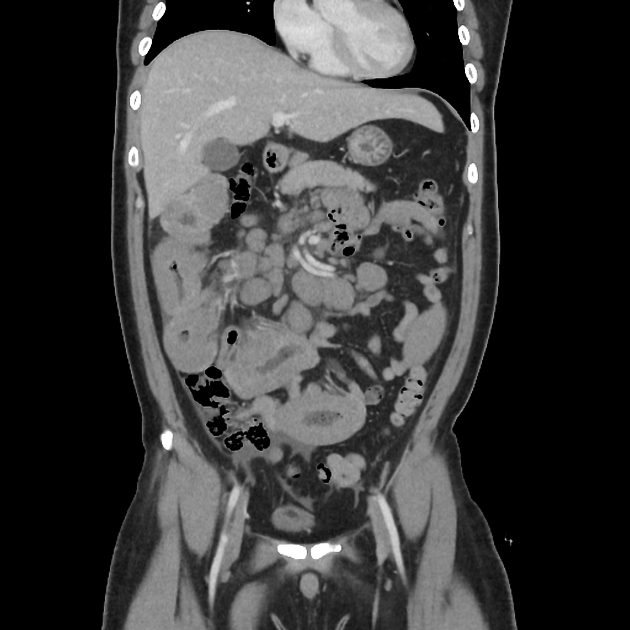
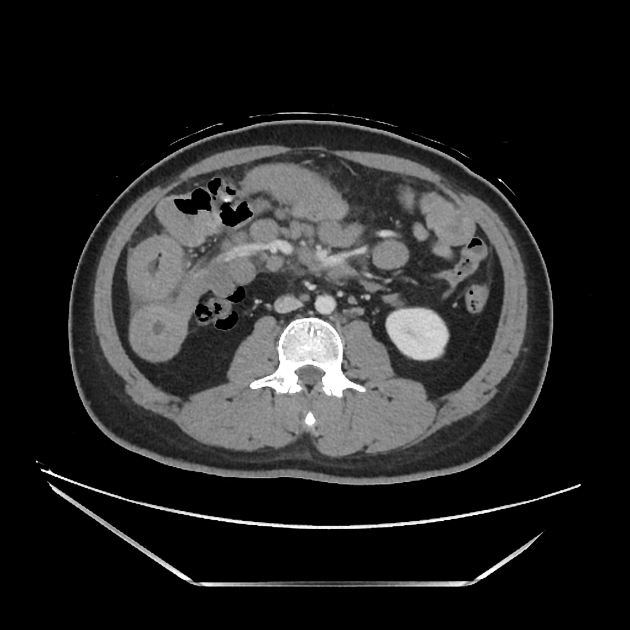
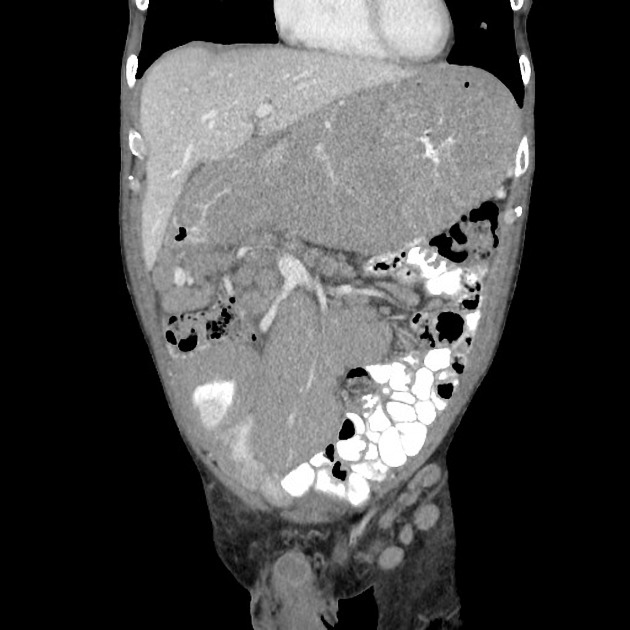
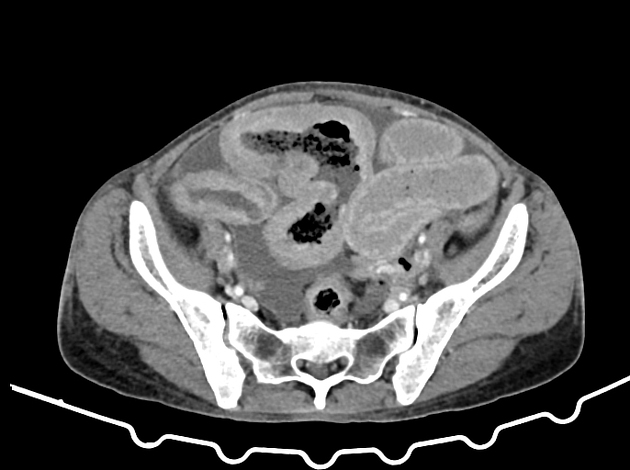
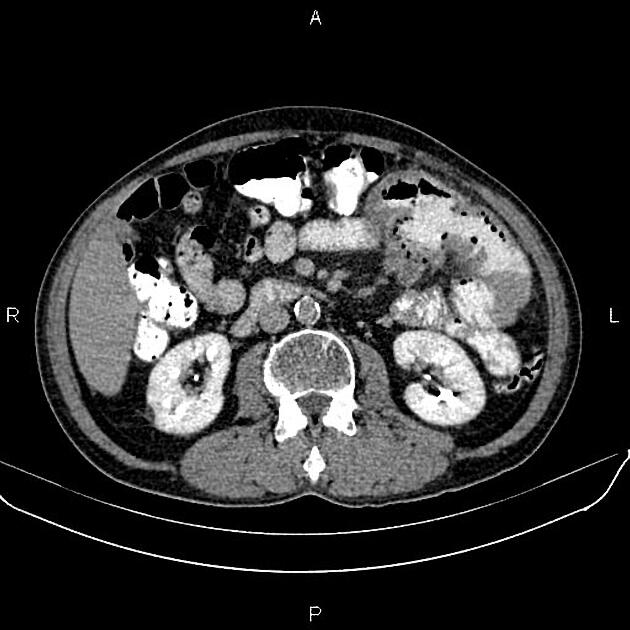
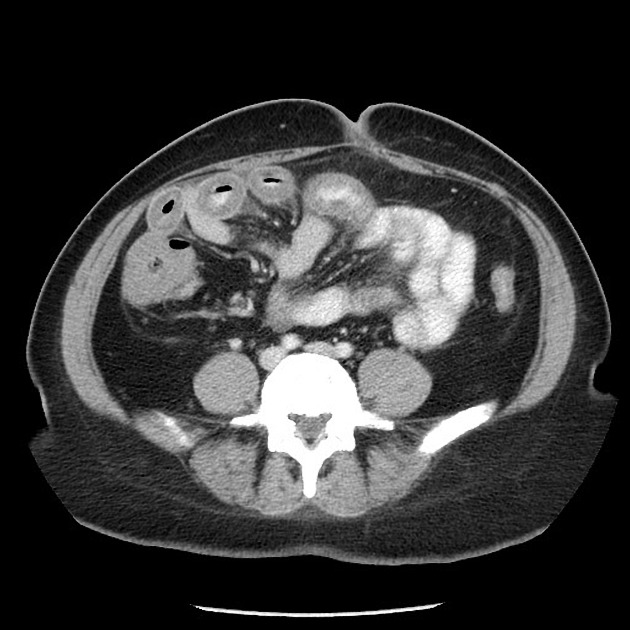
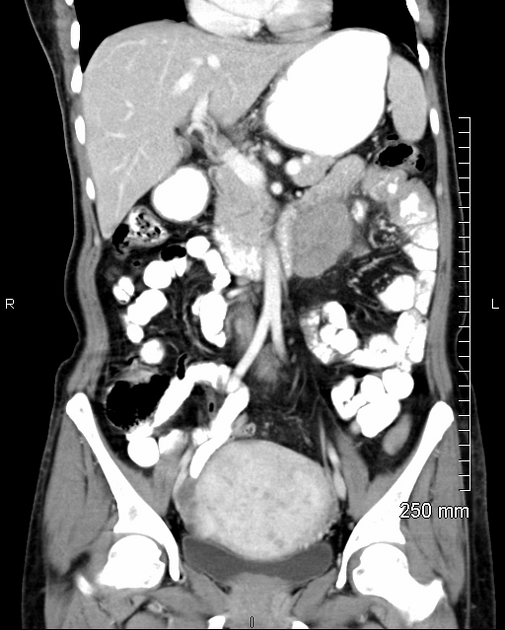
Typically, small-bowel lymphoma involves a single loop of bowel, with 5-20 cm of its length demonstrating 3:
bowel wall thickening: 1-7 cm
aneurysmal (or pseudoaneurysmal) dilatation (30%): occurs due to the replacement of muscularis by tumor or infiltration of myenteric nerve plexus 6
Despite the extensive involvement, small bowel obstruction is uncommon because of lack of desmoplastic reaction, and perforation is rare.
Regional lymph node enlargement in approximately 50% of cases.
Less frequently, the disease may manifest as a solid mass lesion (polypoidal/excentric). Differentiation from adenocarcinoma may be difficult. However, the presence of extensive retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly favors lymphoma, whereas adjacent fat infiltration supports adenocarcinoma.
Treatment and prognosis
Most frequently, the involved segment is resected, with subsequent chemoradiotherapy 2. A rare, but important, complication is perforation of the small bowel. This can occur prior or during treatment and is more common in cases due to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 8,9.







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.