Burkitt lymphoma is an aggressive B-cell lymphoma predominantly affecting children.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Burkitt lymphoma is the most common (40%) type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in childhood. Median age is eight years with a male predominance (M:F = 4:1) 1. It is less common in adults, accounting for 1-2% of lymphomas 4,5.
It is considered endemic in parts of Africa where rates are up to 50 times higher than in the USA. Cases occur sporadically outside of the tropics.
Risk factors
post-transplant immunosuppression
Clinical presentation
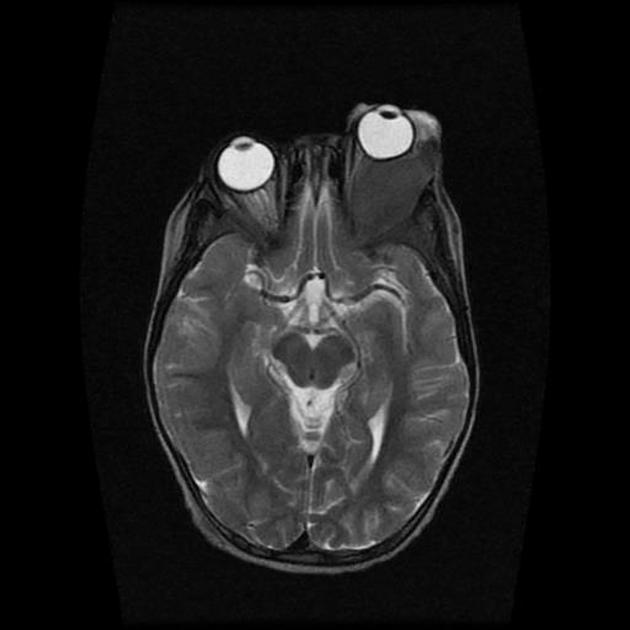
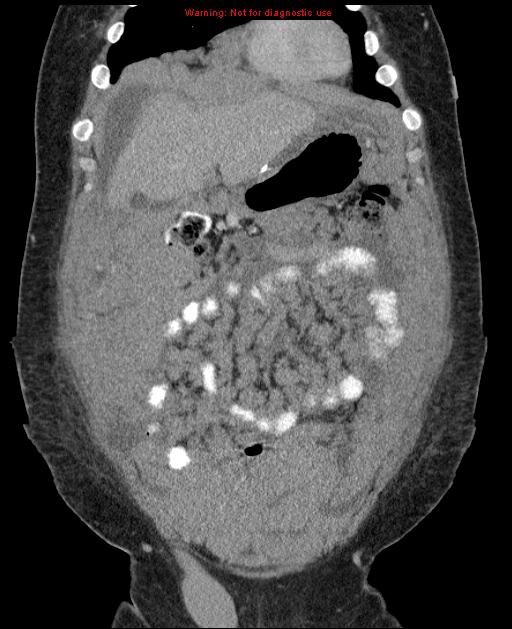
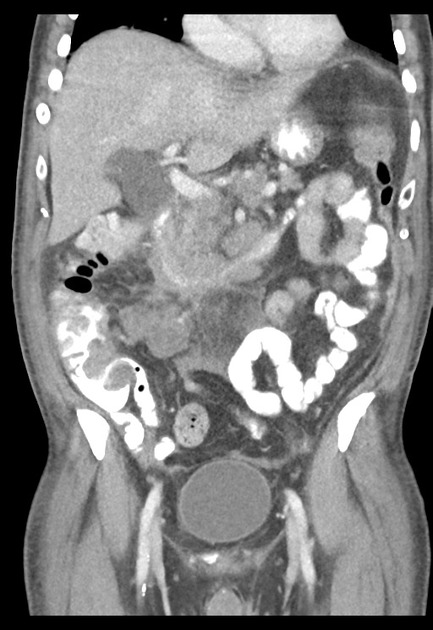
Burkitt lymphoma affects many organs, and this affects presentation. Extranodal involvement is common (~30%) at presentation, often presenting as an abdominal or pelvic mass. Most patients present with widespread disease.
Pathology
Three forms of Burkitt lymphoma have been described 1,2:
endemic Burkitt lymphoma: linked to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Plasmodium falciparum malaria infections
sporadic Burkitt lymphoma: etiology unknown
immunodeficiency-associated Burkitt lymphoma: occurs in patients with HIV, post-transplant or congenital immunosuppression
Burkitt lymphoma is an aggressive tumor with a doubling time of 24 hours. It can present in a wide variety of locations:
head and neck, e.g. facial bones, Waldeyer ring
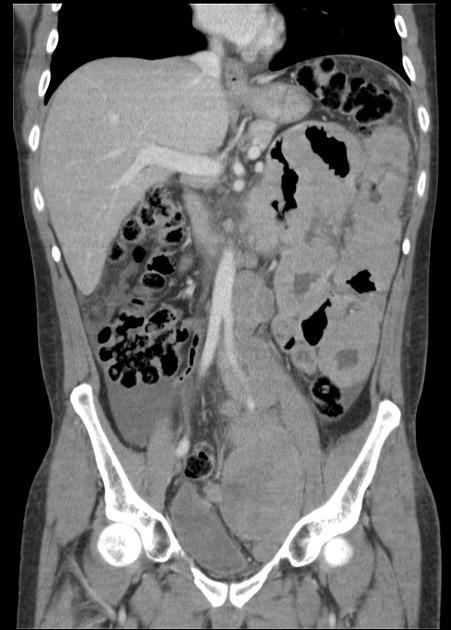
pleural space (~70%)
gastrointestinal tract, especially the ileocecal region
mesentery, peritoneum, retroperitoneum
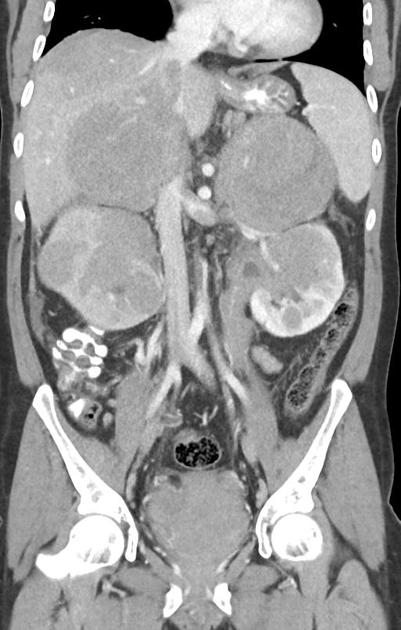
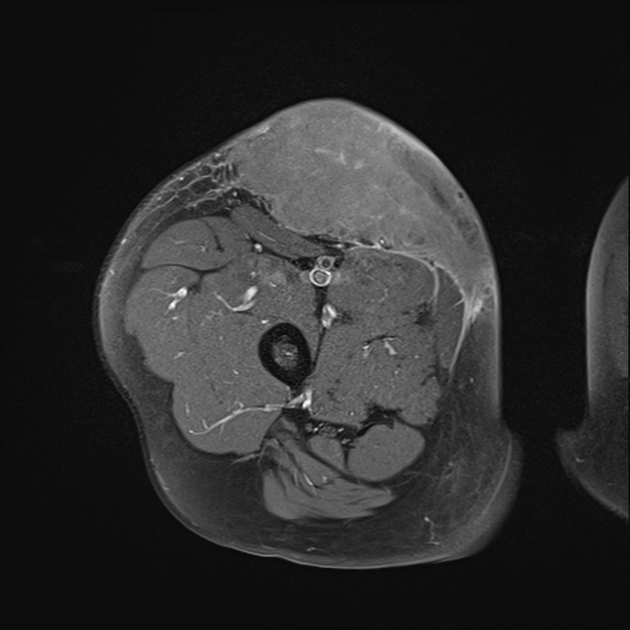
kidneys
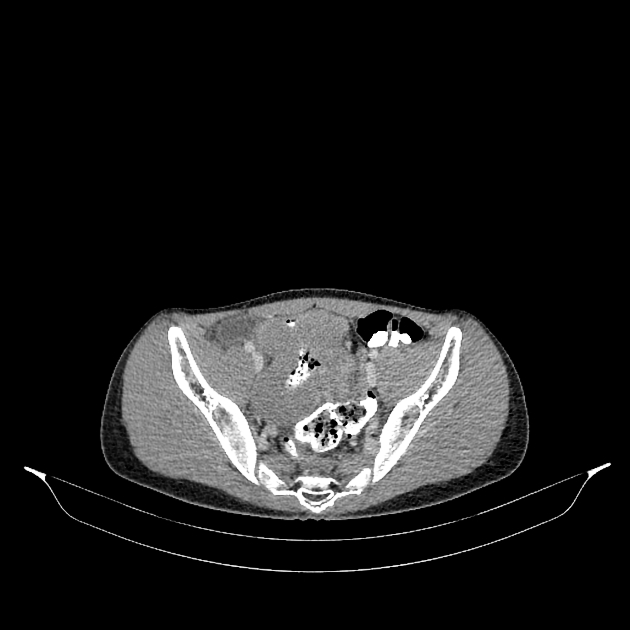
gonads (~75%)
Nodal involvement is more common in adults than in children 5.
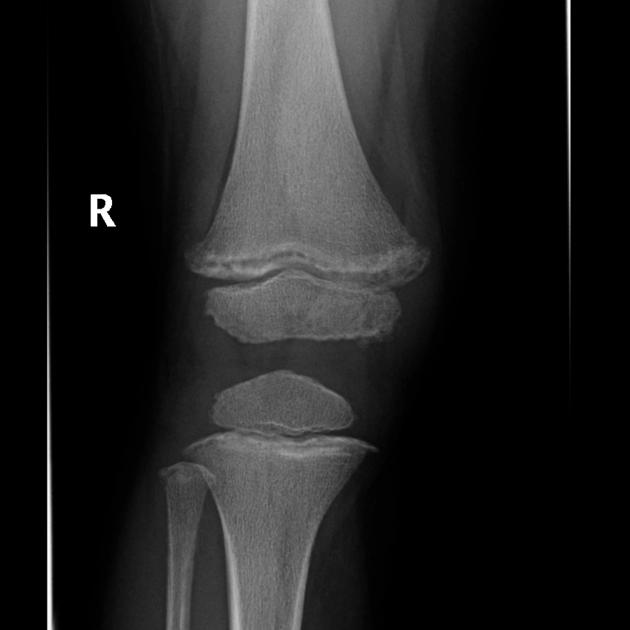
Radiographic features
Radiographic features vary widely depending on organ involvement:
Treatment and prognosis
Burkitt lymphoma can be treated with chemotherapy. In children, the prognosis is good with survival rates >90%. In adults, the prognosis is poorer, with a 5-year survival rate of ~50% and is even worse with bone marrow or CNS involvement (>30% 5-year survival rate) 4.
History and etymology
First described by Denis Parsons Burkitt (1911-1993), an Irish surgeon, in 1958 in Uganda, Africa 6,7.
Differential diagnosis
other forms of high-grade B-cell lymphoma
Crohn disease may mimic Burkitt lymphoma on ultrasound, barium studies, and CT 3




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.