Alzheimer disease is a common neurodegenerative disease, responsible for 60-80% of all dementias, and imposing a significant burden on developed nations. It is associated with an accumulation and deposition of cerebral amyloid-β (Aβ) and is the most common cerebral amyloid deposition disease.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Alzheimer disease is the most common cause of dementia, responsible for 60-80% of all dementias 2,7. The prevalence is strongly linked to age, with >1% of 60-64-year-old patients being diagnosed with the condition, compared to 20-40% of those over 85-90 years of age 2.
Risk factors
Risk factors include 2,7:
advanced age
female gender
-
apolipoprotein E (ApoE) ε4 (epsilon 4) allele carrier status 21
inheriting a single allele increases risk ~3x
both alleles: ~8x
physical inactivity
head trauma
current smoking
family history of dementia
mutations of amyloid precursor protein
chronic inflammation e.g. psoriatic arthritis 12
risk factors for iatrogenic acquisition (e.g. cadaveric pituitary-derived growth hormone) 22
In addition to the genetic and environmental factors above, the age of presentation is also influenced by socioeconomic factors 2,4:
formal education
income
occupational status
social network and family support
Individuals with premorbid higher function/supports are able to compensate for early disease changes to a greater degree and thus present later. Consequently, when well-supported patients eventually present, they tend to have more marked morphological changes on imaging 4.
Clinical presentation
Traditionally, Alzheimer disease has been clinically characterized predominantly by memory deficits, already in initial stages. It has become increasingly evident that in addition to the typical presentation, a number of atypical clinical patterns exist, which are nonetheless pathologically Alzheimer disease.
Classical/typical Alzheimer disease
The typical patient with Alzheimer disease will present initially with antegrade episodic memory deficits 1,5. Over time (often years), the disease progresses, with eventual involvement of attentional and executive processes, semantic memory, praxis, and visuoperceptual abilities 1. Neuropsychiatric symptoms are also common and eventually affect almost all patients. These include apathy, depression, anxiety, aggression/agitation, and psychosis (delusions and hallucinations) 2.
Atypical/variant Alzheimer disease
These entities, often recognized clinically well before they were identified to be pathologically identical to Alzheimer disease, are characterized by slowly progressive focal cortical atrophy, with symptoms and signs matched to the affected area 1.
Examples include:
frontal variant of Alzheimer disease
Diagnosis
Clinical diagnosis is made by identifying a progressive decline in memory both with clinical examinations and neuropsychologic tests and has been historically based on the NINCDS-ADRA criteria, which divides patients according to the certainty of the diagnosis into 5:
definite: clinical diagnosis and histologic confirmation
-
probable: typical clinical syndrome without histologic confirmation
81% sensitive, 73% specific 5
possible: atypical clinical features without histologic confirmation but no alternative diagnosis
Although using longitudinal clinical criteria is highly sensitive in diagnosing a dementia of any type (>90%), they are relatively inaccurate (<70%) in diagnosing Alzheimer disease specifically 3.
Importantly, the NINCDS-ADRA criteria only include imaging and laboratory examination or blood and CSF in excluding other causes.
The only definitive diagnostic test is brain biopsy which in practice is rarely obtained. As such, the combination of clinical features and neuroimaging are usually considered sufficient, although, especially with the recognition of variants, this approach undoubtedly misdiagnoses a significant number of cases.
A number of CSF biomarkers are being used which may further aid in diagnosis. These include beta-amyloid, total tau, and hyperphosphorylated tau 2.
Pathology
Alzheimer disease is characterized by the accumulation within the brain of cerebral amyloid-β (Aβ or Abeta) forming neuritic plaques, neurofibrillary tangles and eventually progressive loss of neurons 2,7. Cerebral amyloid-β particularly deposits in association areas of the neocortex, the posterior cingulate and precuneus, as well as the limbic cortex, although the reason for this distribution has not been elucidated 7.
The underlying reason for the accumulation of senile (neuritic) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles remains poorly understood, as does the reason for non-uniform distribution in the cortex. There is, however, increasing evidence to suggest that chronic inflammation is at least partially responsible. Such inflammation can lead to prolonged parenchymal activation of microglial cells which in turn results in the release of inflammatory mediators with subsequent neuronal damage and amyloid-induced neurodegeneration 12.
In extremely rare instances, Alzheimer disease may be iatrogenic 22. This has been demonstrated in cadaveric pituitary-derived growth hormone recipients, similar to what has been observed in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease 22.
Genetics
Inheriting a single copy of the ApoE gene, encoding for apolipoprotein E, elevates the probability of developing Alzheimer disease three times, whilst inheriting both copies increases one's risk eightfold. It seems that ApoE is important for the way in which oligodendrocytes process cholesterol and leads to decreased myelination of the neurons in the brain 21.
Radiographic features
Although CT is able to demonstrate the characteristic patterns of cortical atrophy, MRI is more sensitive to these changes and better able to exclude other causes of dementia (e.g. multi-infarct dementia) and as such is the favored modality. In addition to structural imaging, molecular imaging with PET is increasingly of value in the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease.
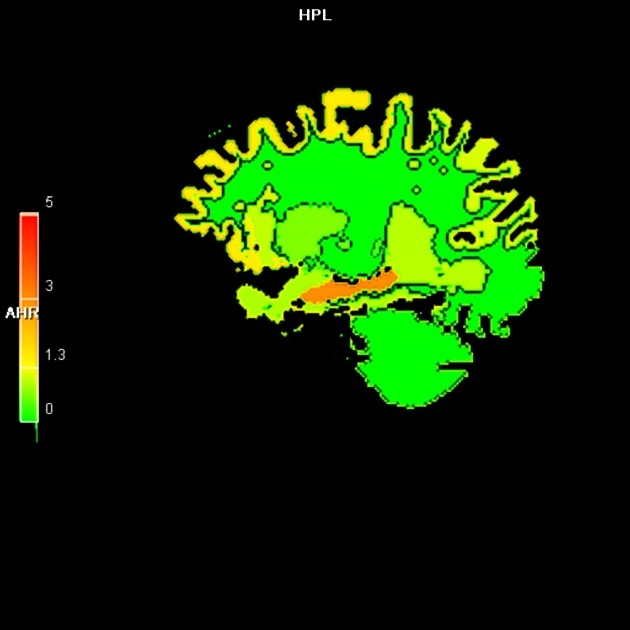
Braak staging on imaging shows the sequential involvement of various structures as follows 10:
stage I and II: earliest involvement of entorhinal cortex
stage III and IV: involves limbic system and hippocampus
stage V and VI: involves cortex (precuneus in particular) with temporal lobes
MRI
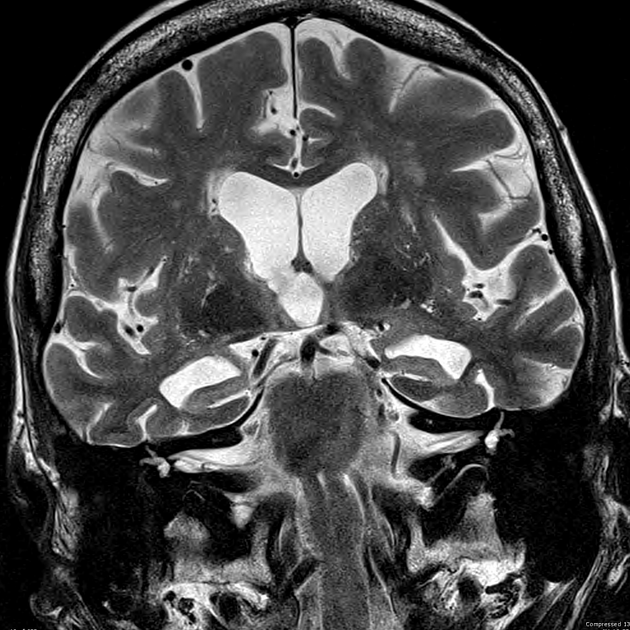
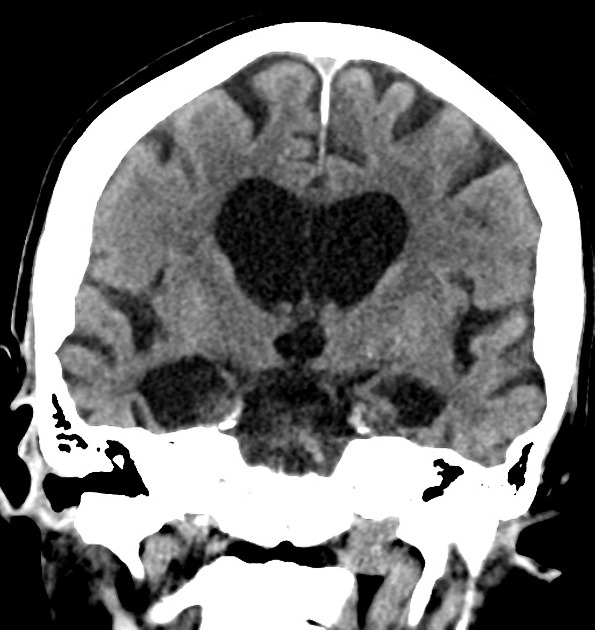
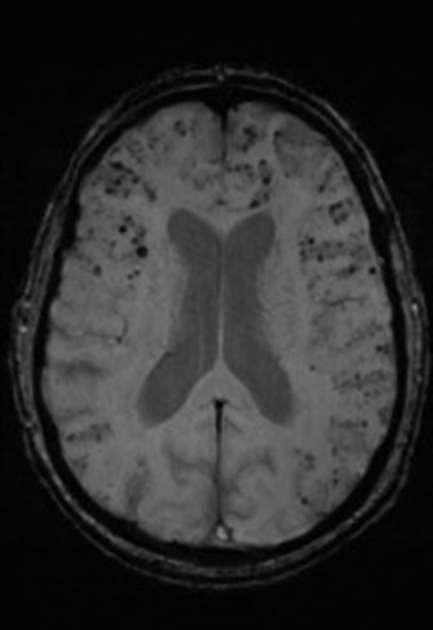
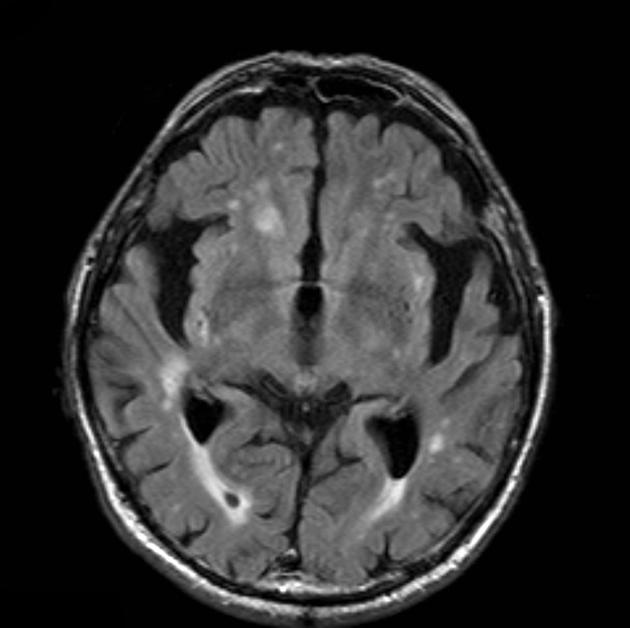
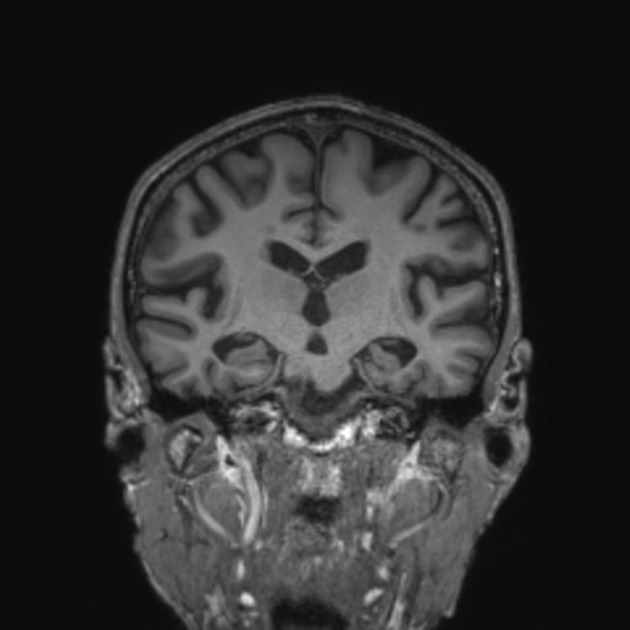
The primary role of MRI (and CT for that matter) in the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease is the assessment of volume change in characteristic locations which can yield a diagnostic accuracy of up to 87% 3. Unfortunately, such volume loss is not apparent early in the course of the disease 7.
The diagnosis should be made on the basis of two features:
mesial temporal lobe atrophy (particularly the hippocampus, entorhinal cortex and perirhinal cortex) 10
temporoparietal cortical atrophy
Mesial temporal lobe atrophy can be assessed directly or indirectly. Direct assessment is of hippocampal or parahippocampal volume loss while indirect assessment relies on an enlargement of the parahippocampal fissures. The former is more sensitive and specific but ideally, requires actual volumetric calculations rather than 'eyeballing' the scan 3.
These measures have been combined in the medial temporal atrophy score which has been shown to be predictive of progression from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to dementia 5,6. Another described alternative is the entorhinal cortical atrophy score (ERICA score).
Additionally, and particularly relevant to posterior cortical atrophy or early-onset Alzheimer disease, is the presence of parietal/precuneus atrophy. This is often best seen on the interhemispheric surface of the parietal lobe (see neurodegenerative MRI brain: an approach) by examining the posterior cingulate sulcal and parieto-occipital sulcal size and degree of atrophy of the precuneus and cortical surface of the parietal lobe. This has also been combined into a scoring system (see posterior atrophy score of parietal atrophy (Koedam score)).
Brain volume measurements, assessed with segmentation, demonstrate that patients with Alzheimer disease have accelerated rates of brain volume loss, typically around twice normal (1% vs ~0.5% per year) 7. This is even more marked in the hippocampi, with affected individuals exhibiting three times the volume loss per year (~4.5% vs ~1.5% per year) 7.
In addition to the above features, white matter high T2 signal, commonly described as chronic small vessel ischemic change, correlates with and precedes cognitive impairment 19.
Nuclear medicine
A variety of nuclear medicine investigations are useful in assessing patients with mild cognitive impairment and suspected Alzheimer's disease. They can be helpful in supporting the diagnosis or prognosticating the likelihood of progressive decline 19.
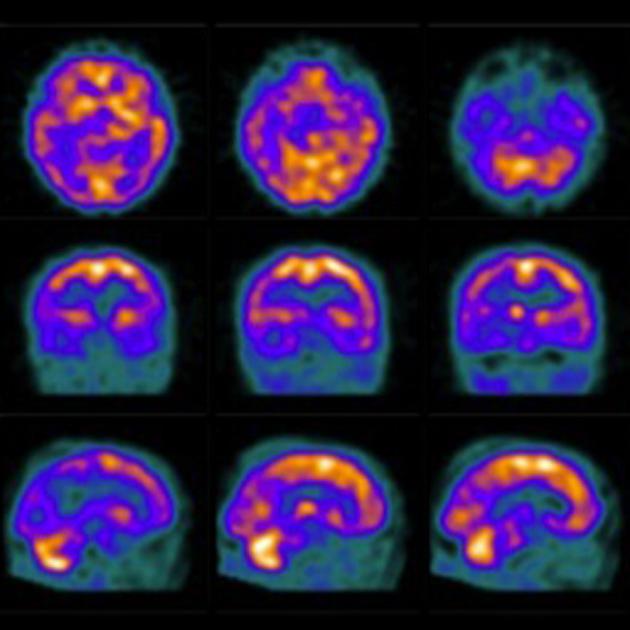
SPECT and PET are able to detect regional hypoperfusion/hypometabolism in a biparietal and bitemporal distribution, while amyloid and tau agents accumulated in the grey matter and medial temporal lobes respectively 19.
One of the primary advantages of nuclear medicine evaluation is that it is able to detect abnormalities prior to symptom onset. Amyloid deposition occurs earliest, followed by accumulation of tau, followed by a decrease in glucose metabolism 19.
FDG PET
F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET typically shows bilateral temporoparietal, precuneus and posterior cingulate hypometabolism which is usually symmetric. Uptake may be asymmetric in the early stages. The anterior cingulate, visual cortex (provided the eyes were kept open during uptake time), basal ganglia, thalami, occipital lobes and cerebellum are usually spared. Classically, even late in the disease, the sensorimotor cortices are relatively spared 10. Frontal lobes may be involved in late stage 7.
Amyloid PET
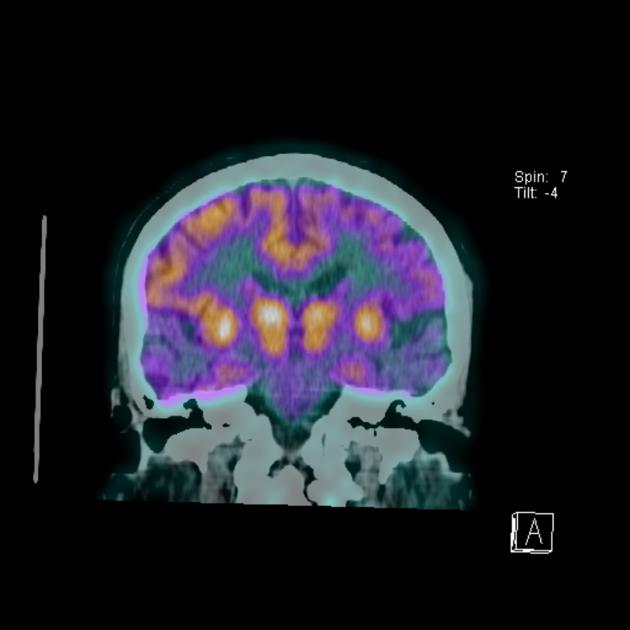
C-11 Pittsburgh compound B (half-life 20 minutes), as well as newer longer half-life compounds such as F-18 florbetapir (trade name Amyvid), F-18 flutemetamol (trade name Vizamyl), and F-18 florbetaben (trade name NeuraCeq), are PET tracers that bind preferentially to beta-amyloid fibrils and thus may be able to improve the specificity of antemortem diagnosis 8,9, although there is considerable overlap with normal controls 2,7. Additionally, it should be noted, that the degree of amyloid deposition does not correlate with the degree of cognitive impairment 19.
With increased cerebral amyloid-β (Aβ) deposition, increased activity is demonstrated in the cortex with loss of the normal grey matter-white matter differentiation seen in controls 7,19. It is particularly useful in excluding Alzheimer disease as the cause of dementia, as a negative amyloid PET scan renders the diagnosis unlikely 7. In contrast, 20-25% of cognitively healthy individuals demonstrate amyloid deposition 19.
Tau PET
PET agents that bind tau proteins in neurofibrillary tangles are being investigated (e.g. 18F-flortaucipir, trade name Tavid) which result in increased activity in the expected locations of deposition in Alzheimer disease (hippocampus, entorhinal cortex and temporal and parietal cortex) 7,10. They correlate to the severity of dementia/cognitive impairment but are, however, not specific to Alzheimer disease and will also deposit in other tauopathies (e.g. chronic traumatic encephalopathy and progressive supranuclear palsy) 10,19.
Treatment and prognosis
There is no cure for this disease; some drugs have been developed trying to improve symptoms or, at least, temporarily slow down their progression.
cholinesterase inhibitors e.g. donepezil
partial NMDA receptor antagonists, e.g. memantine
-
medications for behavioral symptoms
antidepressants
anxiolytics
antiparkinsonian (movement symptoms)
antiseizure medications/sedatives (behavioral)
-
monoclonal antibodies
aducanumab: has been claimed to reduce amyloid-beta plaque in human subjects although its efficacy and long-term benefits remain controversial 18
numerous other amyloid-lowering agents are being investigated and these have resulted in a complication closely related to cerebral amyloid angiopathy related inflammation, known as amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) 20
Differential diagnosis
In cases where bilateral mesial temporal lobe volume loss is present on imaging in an elderly amnestic patient, the main differential is limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE) 11. Not only is this entity increasingly recognized as a significant cause of dementia of Alzheimer's type despite being pathologically distinct, but it can also co-exist with Alzheimer's disease 11. At present, there is no definitive way of establishing the diagnosis other than retrospectively at autopsy. A number of features may suggest the diagnosis 11:
rostrocaudal involvement of the amygdala and hippocampus (amygdala involved first followed by hippocampal head and anterior body)
profound and asymmetric amygdala and hippocampal volume loss with relatively little involvement of other parts of the brain.
negative amyloid-PET
History and etymology
It was Emil Kraepelin, a German psychiatrist in 1910, who included the disease in his treatise on psychiatry with the only name of "Alzheimer's dementia" excluding the Italian physician Gaetano Perusini, who - like Alois Alzheimer - had contributed with his studies to understand the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms 13-17.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.