Orthogonal projection
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Ian Bickle had no recorded disclosures.
View Ian Bickle's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Integral Diagnostics, Shareholder (ongoing)
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures- Orthogonal views
- Orthogonal projections
- Orthogonal view
- Importance of two views
- Importance of two projectionsf
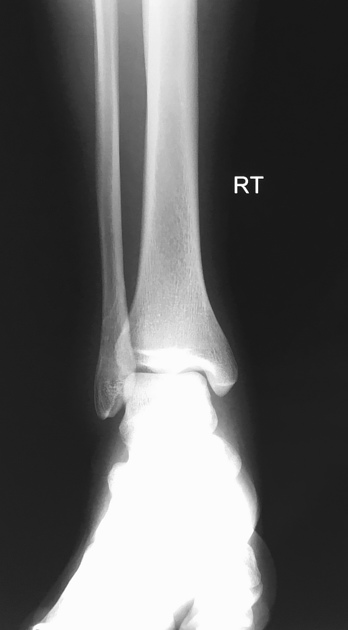
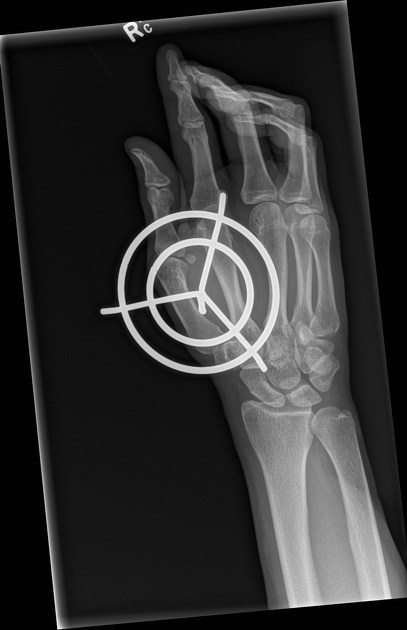
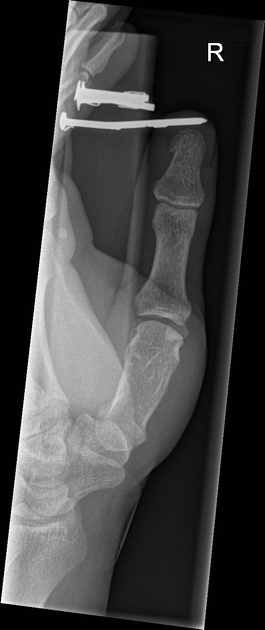
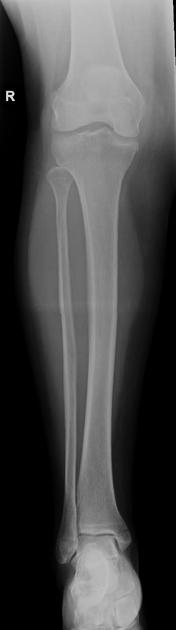
The orthogonal projection or view is, by definition, a radiographic projection obtained 90° from the original view. It forms the basic requirements of a 'radiographic series', having 'two orthogonal projections of the region of interest'. The importance of two views has been known for many years 1 as a single view can potentially miss pathology obvious on a second view.
On this page:
Images:
Acute imaging
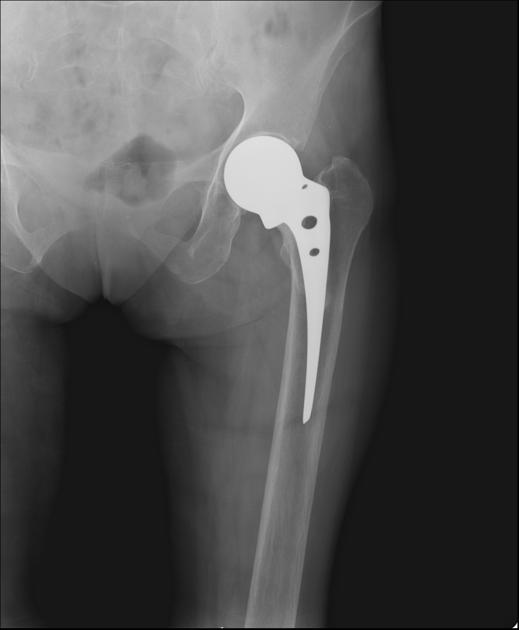
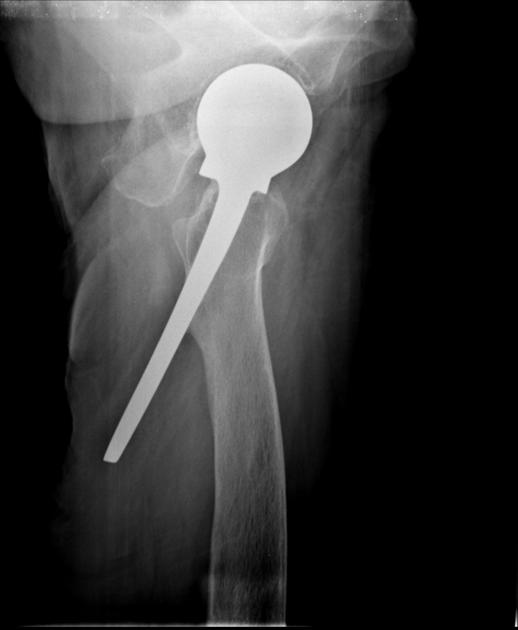
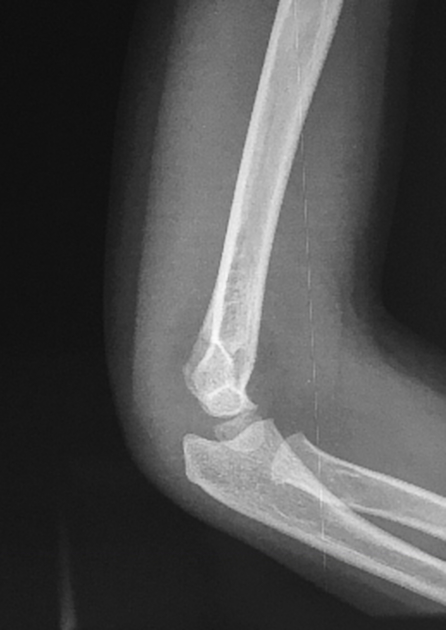
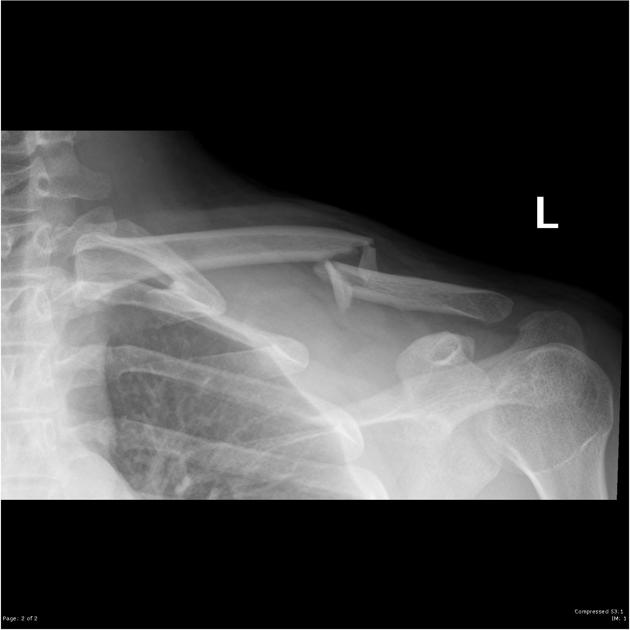
Cases can appear normal in one projection and abnormal in the next. Consequently, plain radiographic imaging in the acute setting is seldom a single projection, often comprising of two or more angles of the same region. Orthogonal projections in the acute setting are necessary to convey the three-dimensional nature of the anatomy in question.
One should always strive to perform (as radiographers) or request (as referrers) orthogonal views. When orthogonal views are not possible, views taken at an alternative angle to the first are still more beneficial than no second view at all.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
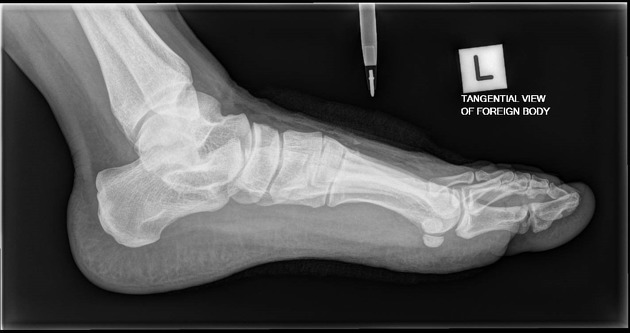
Foreign body imaging
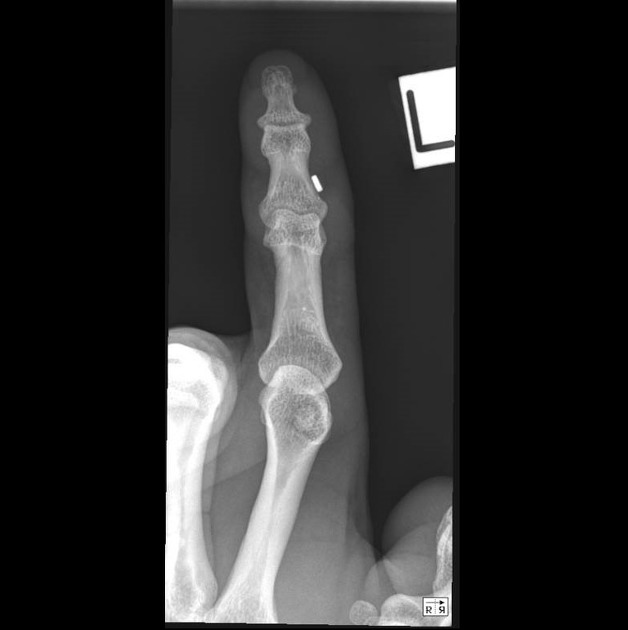
Plain radiographic investigations of foreign bodies often require orthogonal projections to better understand the position in relation to anatomical structures. The orthogonal projections of foreign bodies can include the 'en face' or 'tangential' projection, whereby the radiographer performs imaging orthogonal to the foreign body rather than anatomical structures.
See also
References
- 1. Bull J. A Review of Cerebral Angiography. Proc R Soc Med. 1949;42(11):880-90. doi:10.1177/003591574904201111
Incoming Links
Related articles: Radiographs (adult)
- general radiography (adult)
-
radiographic positioning terminology
- orthogonal projection
-
systematic radiographic technical evaluation (mnemonic)[+][+]
- portable radiography
- chest radiography
- abdominal radiography
-
upper limb radiography
-
shoulder girdle radiography
- scapula series
-
shoulder series
- shoulder (AP view)
- shoulder (internal rotation view)
- shoulder (external rotation view)
- shoulder (superior-inferior axial view)
- shoulder (inferior-superior axial)
- shoulder (West Point view)
- shoulder (Velpeau view)
- shoulder (modified trauma axial view)
- shoulder (supine lateral view)
- shoulder (modified transthoracic supine lateral)
- shoulder (lateral scapula view)
- shoulder (AP glenoid view)
- shoulder (Garth view)
- shoulder (outlet view)
- shoulder (Stryker notch view)
- acromioclavicular joint series
-
clavicle series
- clavicle (AP view)
- clavicle (AP cephalic view)
- clavicle (oblique view)
- sternoclavicular joint series
- arm and forearm radiography
- wrist and hand radiography
- wrist series
- scaphoid series
- hand series
- thumb series
- fingers series
- rheumatology hands series
- bone age (radiograph)
-
shoulder girdle radiography
-
lower limb radiography
- pelvic girdle radiography
- thigh and leg radiography
- ankle and foot radiography
- skull radiography
-
paranasal sinus and facial bone radiography
- facial bones
- mandible
- nasal bone
- zygomatic arches
- paranasal sinuses
- temporal bones
- dental radiography
- orthopantomography
- temporomandibular joints
- temporomandibular joint (AP axial view)
- temporomandibular joint (axiolateral oblique view)
-
spinal radiography
- cervical spine series
-
thoracic spine series
- thoracic spine (AP view)
- thoracic spine (lateral view)
- thoracic spine (oblique view)
- lumbar spine series
- sacrococcygeal radiography
Related articles: Radiographs (paediatric)
-
pediatric radiography
- radiographic positioning terminology
- systematic radiographic technical evaluation (mnemonic)
- pediatric immobilization
- foreign body ingestion series (pediatric)
- foreign body inhalation series (pediatric)
- shunt series
- chest radiograph (pediatric)
- abdomen radiograph (pediatric)
- upper limb radiography (pediatric)
- lower limb radiography (pediatric)
- skull radiography (pediatric)
- spine radiography (pediatric)
-
skeletal survey
-
skeletal survey (non-accidental injury)
- torso
- pediatric chest (AP erect view)
- pediatric chest (oblique ribs view)
- pediatric abdomen (AP supine view)
- pediatric spine (whole lateral view)
- upper limb (both sides)
- lower limb (both sides)
- pediatric femur (AP view)
- pediatric knee (lateral view)
- pediatric tibia fibula (AP view)
- pediatric ankle (lateral view)
- pediatric foot (DP view)
- torso
-
skeletal survey (non-accidental injury)





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.