Parkinson disease (PD), also known as idiopathic Parkinson disease (iPD), is a neurodegenerative disease and movement disorder characterized by bradykinesia, rigidity and resting tremor due to progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Parkinson disease is by far the most common cause of the parkinsonian syndrome, accounting for approximately 80% of cases (the remainder being due to other neurodegenerative diseases, such as Lewy body dementia) 1.
The most common form is encountered in elderly patients and is common, seen in 2-4% of all individuals older than 65 years of age (with an average prevalence of 1.6% - US population study) 22. A juvenile form of Parkinson disease is also recognized, manifesting between 20-40 years of age 1.
The majority of cases (85-90%) are sporadic. However, 10-15% of patients have a positive family history 1. Some familial forms of Parkinson disease, in fact, are due to genetic mutations (e.g. LRRK2) 21.
Clinical presentation
Parkinson disease is characterized by both motor and non-motor clinical features. The classic motor features of Parkinson disease, which are often asymmetric, include:
-
bradykinesia
this is the cardinal and mandatory feature
typically decrementing in nature and accompanied by hypokinesia
-
many manifestations:
e.g. in the gait, manifests as a festinating and shuffling short-steppage gait, that characteristically has freezing, turning en bloc, and reduced arm swing
e.g. in writing, manifests as progressive micrographia
e.g. in the face, manifests as hypomimia with decreased eye blinking
-
resting tremor
classically 5 Hz 'pill-rolling' resting tremor
most prominent in the distal upper limbs
-
rigidity
often described as 'cog-wheel' in nature in the limbs due to superimposed tremor
also affects the trunk and contributes to the stooped flexed posture (occasionally camptocormia) that is often seen
-
postural instability
sometimes added as a fourth cardinal feature 3
is generally a late feature
Non-motor features include:
constipation: often an early symptom pre-dating the cardinal features
anosmia or hyposmia: often an early symptom predating the cardinal features
-
autonomic dysfunction
postural hypotension: almost 20% at diagnosis, >1/3 patients by 7 years post diagnosis 17
psychosis, especially visual hallucinations (reported to occur in 6-75% of patients (most reports suggest an incidence of 25-50%), more frequently in patients treated with dopaminergic medication 9,10)
-
bradyphrenia and dementia: generally a late feature
in contrast, Lewy body dementia has cognitive impairment either preceding or at most within 12 months of clinical onset of parkinsonian symptoms 2
fatigue and somnolence
Pathology
The pathogenesis of Parkinson disease remains to be fully elucidated. The dopaminergic pathway is predominantly affected in Parkinson disease, and histologically, it is characterized by nigrostriatal dopaminergic degeneration leading to neuronal loss in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc), most conspicuous in the ventrolateral tier of neurons 11. A number of other regions are involved, including parts of the basal ganglia, brainstem, autonomic nervous system and cerebral cortex 3.
At least eleven genes have been implicated in various forms of Parkinson disease 3. Interestingly depending on which genes are involved, various clinical features are more or less prominent (e.g. Kufor-Rakeb syndrome).
Even more interestingly, not all mutations result in Lewy bodies. For example, juvenile Parkinson disease has been linked to mutations in the PARK2 gene, which encodes for the enzyme ubiquitin ligase-L3. In normal individuals, ubiquitin ligase-L3 is involved in ubiquitination of alpha-synuclein (the main component of Lewy bodies) and allows the formation of Lewy bodies. In patients with juvenile Parkinson disease, its function is impaired, and the formation of Lewy bodies is impossible. This finding suggests that Lewy bodies cannot be thought of as synonymous with, and causative of Parkinson disease. Perhaps even Lewy bodies play a protective role in other forms of Parkinson disease, which manifests 20-40 years later 1.
There is also some evidence to support a "dual hit" pathogenesis implicating an infective agent traveling retrogradely from the bowel via the vagus nerve into the brainstem triggering the accumulation of alpha-synuclein 23,24. In support of this theory is that truncal vagotomy seems to have a protective effect 23,24.
Radiographic features
Initial imaging findings are subtle. With advanced disease, non-specific generalized minor cerebral volume loss can be demonstrated.
Ultrasound
B-mode transcranial sonography of the substantia nigra can show increased size of the region of echogenicity 19,20. This is thought to be a sensitive sign, however, the exact sensitivity depends on the exact cut-off value of substantia nigra area used and the type of ultrasound machine employed 19.
MRI
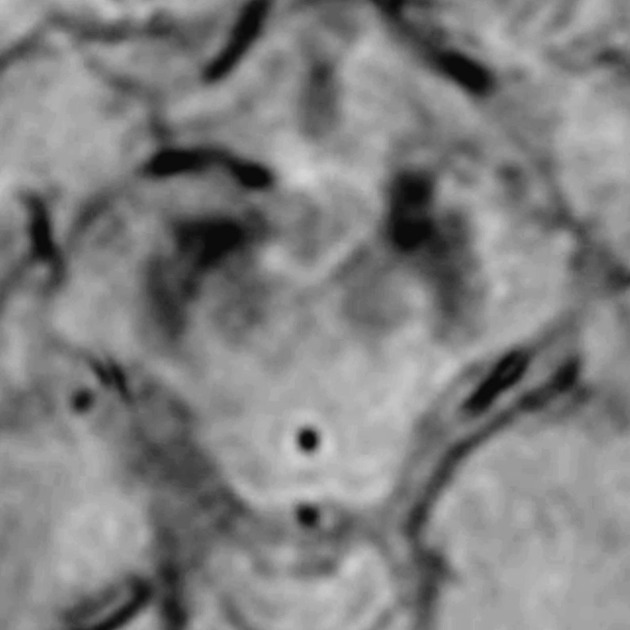
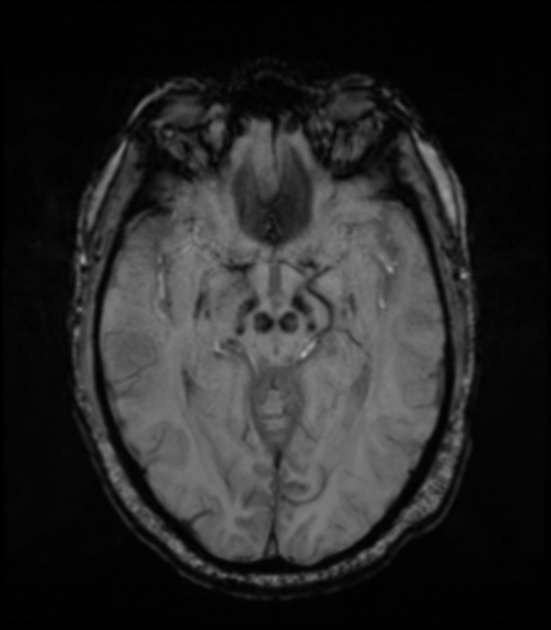
Loss of the normal swallow tail appearance of susceptibility signal pattern in the substantia nigra on axial imaging is perhaps the most promising diagnostic sign 12. Apart from these changes, the signal intensity in substantia nigra depends on loss of neuromelanin and iron accumulation. In addition to aiding diagnosis, MRI is also used to identify features which may indicate secondary parkinsonism rather than primary disease, such as extensive small vessel ischemic change.
Features of Parkinson disease include 1:
-
T1
may show mild hyperintensity of compact and reticular parts of the substantia nigra and red nuclei (due to iron accumulation) 1
may show loss of normal slight hyperintensity in substantia nigra due to loss of neuromelanin 13
-
T2* (GRE/SWI)
-
initially thought to be due to loss of nigrosome-1, but this is likely not accurate 18
reported diagnostic accuracy of over 90%, with a 100% sensitivity and negative predictive value, 95% specificity, and 69% positive predictive value being reported in one study 12
-
may show loss of normal susceptibility signal drop-out of the substantia nigra and red nuclei (due to loss of melanin-containing neurons)
dot-like areas of hyperintensity in the compact part of the substantia nigra 1
may show a confluence of the normal hypointense regions of substantia nigra (due to iron accumulation) 1
-
Although not in routine clinical practice, studies with ultra-high-field MRI (7 T), analyzing the architecture and boundaries of the substantia nigra, have shown promising results regarding both sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of Parkinson disease 4,5.
Nuclear medicine
Both SPECT and PET tracers can be used with high sensitivity for assessment of presynaptic dopaminergic deficits 6,8.
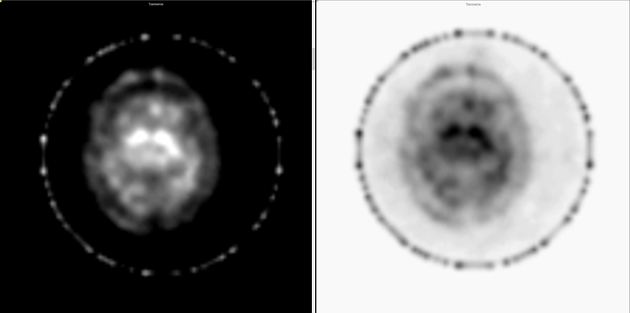
I-123 ioflupane SPECT
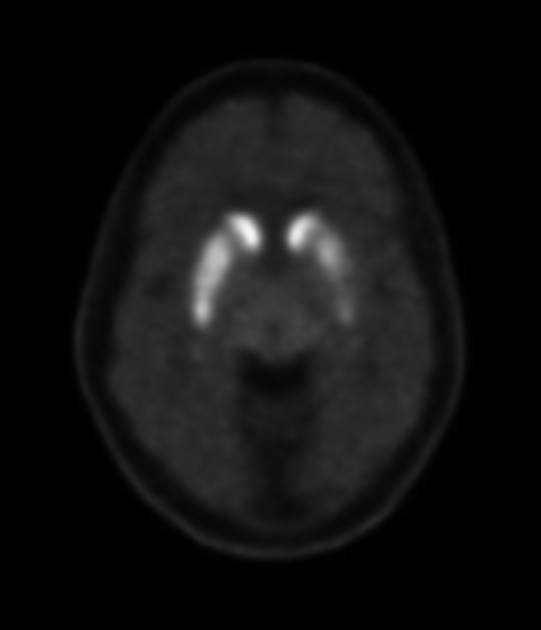
I-123 ioflupane (brand name DaTScan) is taken up by presynaptic dopamine transporters that are abundant in areas rich in axonal synapses form dopaminergic neurons. In the setting of Parkinson disease, the neurons have their cell bodies in the substantia nigra and project axons into the corpus striatum. Imaging with I-123 ioflupane, therefore, demonstrates a lack of normal uptake in the corpus striatum in individuals with Parkinson disease 16.
This appears as a loss of the normal comma-shaped or crescent-shaped tracer uptake in the striatum. Instead, a period-shaped or oval-shaped uptake is seen within the caudate nucleus head without tracer uptake in the putamen. Eventually, even caudate uptake reduces 16. Quantitative assessment reveals reduced uptake in the putamen compared to norms.
Differentiation between Parkinson disease and atypical parkinsonism is also possible, with different tracers 7,8.
Treatment and prognosis
No disease-modifying treatment is available. The mainstay of symptomatic treatment of motor symptoms is pharmacological, with oral levodopa-based regimens, with adjunctive agents including dopamine agonists, MAO-B inhibitors, and COMT inhibitors.
In patients with refractory symptoms, infusional therapies (e.g. apomorphine subcutaneous infusion, levodopa/carbidopa intestinal gel infusion via percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy) or surgical therapies (e.g. deep brain stimulation, conventional lesioning surgeries, MRI-guided focused ultrasound lesioning procedures) may be useful 15.
History and etymology
Parkinson disease was first described by British physician James Parkinson (1755-1824) in his 1817 seminal work "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" 14. In this work he describes a 'shaking palsy' as an "involuntary tremulous motion, with lessened muscular power, in parts not in action and even when supported; with a propensity to bend the trunk forward, and to pass from a walking to a running pace; the senses and intellects being uninjured" 14. Remarkably, other than his comment regarding dementia not being a feature of the disease, his original clinical descriptions are still accurate after more than 200 years.
Differential diagnosis
There is significant overlap between many neurodegenerative diseases, and Parkinson disease is no exception. Clinically the differential includes 1,3:
-
dementia is clinically evident before, concurrently or at most within 12 months of onset of parkinsonian symptoms 2
cerebrovascular disease (vascular parkinsonism)
-
metabolic diseases with parkinsonian signs and symptoms: basal ganglia signal abnormalities are usually more pronounced 1




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.