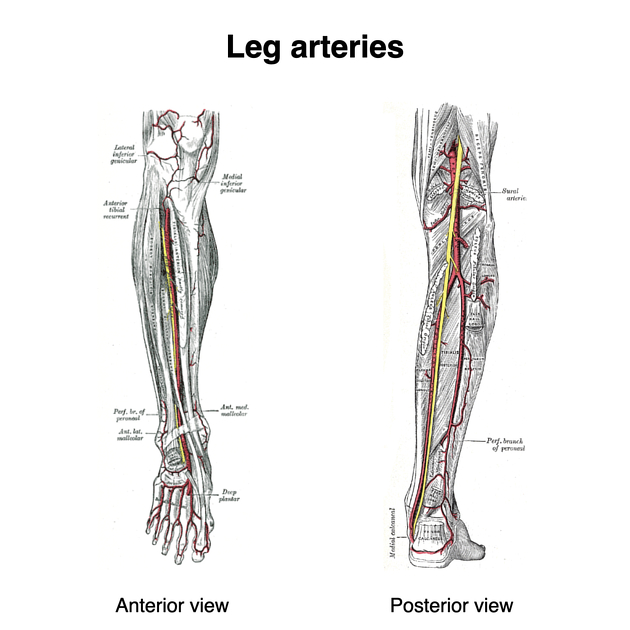
Anterior tibial artery
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Aaron Wong had no recorded disclosures.
View Aaron Wong's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yvette Mellam had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yvette Mellam's current disclosures- Anterior tibial artery (ATA)
- Aberrant anterior tibial artery (AATA)
- High-origin anterior tibial artery
- High-division anterior tibial artery
The anterior tibial artery is the main arterial supply of the anterior compartment of the leg.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The anterior tibial artery arises from the popliteal artery in the popliteal fossa and continues distally as the dorsalis pedis artery.
Course
The anterior tibial artery arises as one of the terminal branches of the the popliteal artery at the distal border of the popliteus muscle, together with the tibioperoneal trunk.
While still in the posterior compartment of the leg, the anterior tibial artery gives off the:
posterior tibial recurrent artery
circumflex fibular artery
It subsequently enters the anterior compartment of the leg via a gap above the interosseous membrane.
The anterior tibial artery courses inferiorly along the interosseous membrane and lateral to the tibialis anterior muscle. It then passes in front of the ankle joint and continues as the dorsalis pedis artery onto the dorsum of the foot.
Branches
Branches include:
anterior tibial recurrent artery: arises immediately, passes upward in the tibialis anterior muscle to anastomose with lateral genicular branches (of the popliteal artery) at the knee
muscular branches
perforating branches: pass behind extensor digitorum longus, piercing the deep fascia and supplying the skin of the anterior leg
anterior medial malleolar artery: anastomoses with the medial malleolar branch of the posterior tibial artery
anterior lateral malleolar artery: anastomoses with the perforating branch of the peroneal artery
Variant anatomy
-
high-origin/high-division anterior tibial artery 4
origin above proximal to the popliteus muscle belly
prevalence ~3%
-
aberrant anterior tibial artery 5
high-origin anterior tibial artery that courses between the posterior tibial cortex and popliteus
prevalence ~2.5%
Clinical importance
Recognition of high-origin and aberrant anterior tibial arteries is important to reduce the risk of inadvertent vascular injury, during knee surgery (e.g. arthroplasty, high tibial osteotomy, lateral meniscal repair, posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction) 4,5.
References
- 1. McMINN. Lasts Anatomy Regional and Applied. CHURCHILL LIVINGSTONE. (2003) ISBN:B0084AQDG8. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Norman Eizenberg. General Anatomy. (2008) ISBN: 9780070134676 - Google Books
- 3. Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley, A. M. R. Agur. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. (2013) ISBN: 9781451119459 - Google Books
- 4. Tindall A, Shetty A, James K, Middleton A, Fernando K. Prevalence and Surgical Significance of a High-Origin Anterior Tibial Artery. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2006;14(1):13-6. doi:10.1177/230949900601400104 - Pubmed
- 5. Marin-Concha J, Rengifo P, Tapia P, Kaiser D, Siepmann T. Prevalence and Characteristics of the Aberrant Anterior Tibial Artery: A Single-Center Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study and Scoping Review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):922. doi:10.1186/s12891-021-04801-9 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Anterior lateral malleolar artery
- Dorsalis pedis artery
- Arterial supply of the lower limb
- Extensor hallucis longus muscle
- Anterior compartment of the leg
- Tibia
- Talus
- Tibialis anterior muscle
- Crural fascia
- Popliteal artery
- Extensor digitorum longus muscle
- Ankle joint
- Lateral compartment of the leg
- Crural arteries
- Deep peroneal nerve entrapment
- Patellar tendon
- Fibular artery
- Tibioperoneal trunk
- Anterior medial malleolar artery
- Peroneal magnus artery
Related articles: Anatomy: Lower limb
- skeleton of the lower limb
- joints of the lower limb
-
hip joint
- ligaments
- muscles
- additional structures
- hip joint capsule
- zona orbicularis
- iliotibial band
-
hip bursae
- anterior
- iliopsoas bursa (iliopectineal bursa)
- lateral
- subgluteal bursae
- greater trochanteric bursa (subgluteus maximus bursa)
- subgluteus medius bursa
- subgluteus minimus bursa
- gluteofemoral bursa
- subgluteal bursae
- postero-inferior
- anterior
- ossification centers
-
knee joint
- ligaments
- anterior cruciate ligament
- posterior cruciate ligament
- medial collateral ligament
- lateral collateral ligament
- meniscofemoral ligament (mnemonic)
-
posterolateral ligamentous complex
- arcuate ligament
- patellar tendon and quadriceps tendon
- anterolateral ligament
- posterior oblique ligament
- oblique popliteal ligament
- medial patellofemoral ligament
- additional structures
- extensor mechanism of the knee
- groove for the popliteus tendon
- knee bursae
- anterior bursae
- medial bursae
- lateral bursae
- posterior bursae
- knee capsule
- lateral patellar retinaculum
- medial patellar retinaculum
- menisci
- pes anserinus (mnemonic)
- ossification centers
- ligaments
- tibiofibular joints
-
ankle joint
- regional anatomy
- medial ankle
- lateral ankle
- anterior ankle
- ligaments
- medial collateral (deltoid) ligament
- lateral collateral ligament
- additional structures
- ankle bursae
- ossification centers of the ankle
- variants
- regional anatomy
- foot joints
- subtalar joint
- mid-tarsal (Chopart) joint
-
tarsometatarsal (Lisfranc) joint
- ligaments
- intermetatarsal joint
- metatarsophalangeal joint
- interphalangeal joint
- ossification centers
-
hip joint
- spaces of the lower limb
-
muscles of the lower limb
- muscles of the pelvic group
- muscles of the thigh
- muscles of the leg
- anterior compartment of the leg
- posterior compartments of the leg
- lateral compartment of the leg
- muscles of the foot
- dorsal muscles
- plantar muscles
- 1st layer
- 2nd layer
- 3rd layer
- 4th layer
- accessory muscles of the lower limb
- accessory gluteal muscles
-
accessory muscles of the ankle
- accessory peroneal muscles
- accessory flexor digitorum longus muscle
- accessory soleus muscle
- peroneocalcaneus internus muscle
- tibiocalcaneus internus muscle
- extensor hallucis capsularis tendon
- anterior fibulocalcaneus muscle
- accessory extensor digiti secundus muscle
- tibioastragalus anticus of Gruber muscle
- vascular supply of the lower limb
- arterial supply of the lower limb
- venous drainage of the lower limb
- innervation of the lower limb
- lymphatic system of the lower limb
- lymphatic pathways
- anteromedial group
- anterolateral group
- posteromedial group
- posterolateral group
- lower limb lymph nodes
- lymphatic pathways




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.