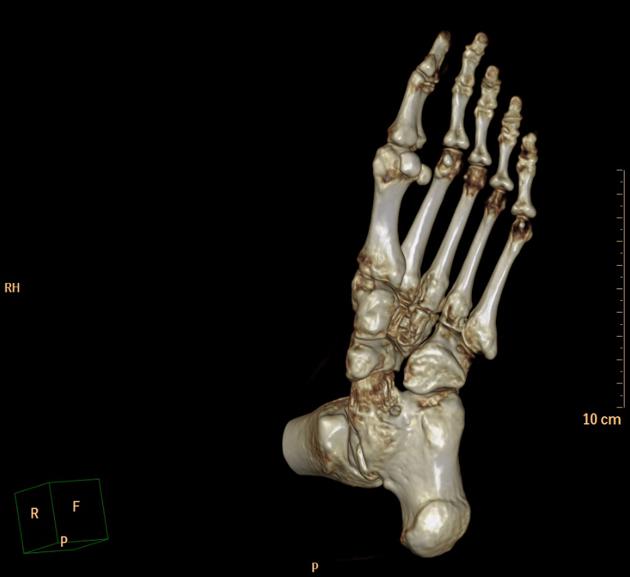
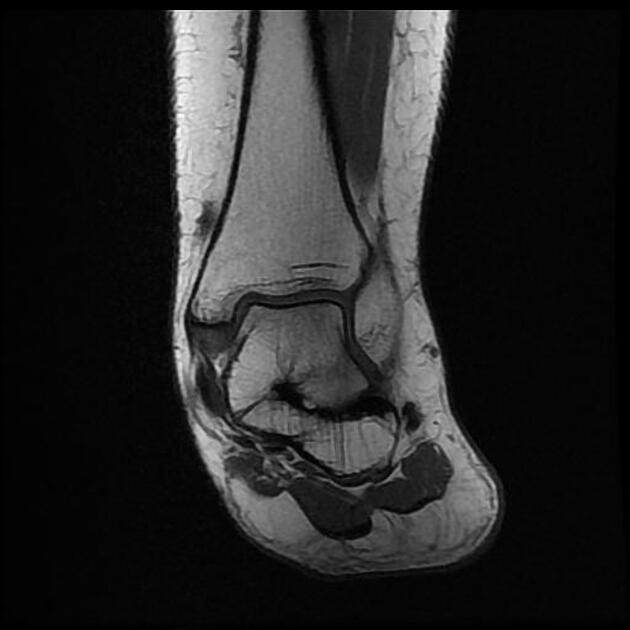
The talocalcaneal coalition is one of the two most common subtypes of the tarsal coalition, the other being the calcaneonavicular coalition. It accounts for 45% of all tarsal coalitions, and although all three facets of the talocalcaneal joint can be involved, the middle facet is most commonly involved.
On this page:
Pathology
Classification
The talocalcaneal coalition is believed to be the result of incomplete or faulty segmentation during development. They may be of three types, depending on the tissue which bridges the two bones. The three types are 1:
bony: synostosis
cartilaginous: synchondrosis
fibrous: syndesmosis
Talocalcaneal coalitions can be classified according to their location into the following subtypes 2:
anterior facet type
middle facet type
posterior facet type
extra-articular: with or without os sustentaculi
Associations
pes planus with middle facet coalition 7
pes cavus with posterior facet coalition 7
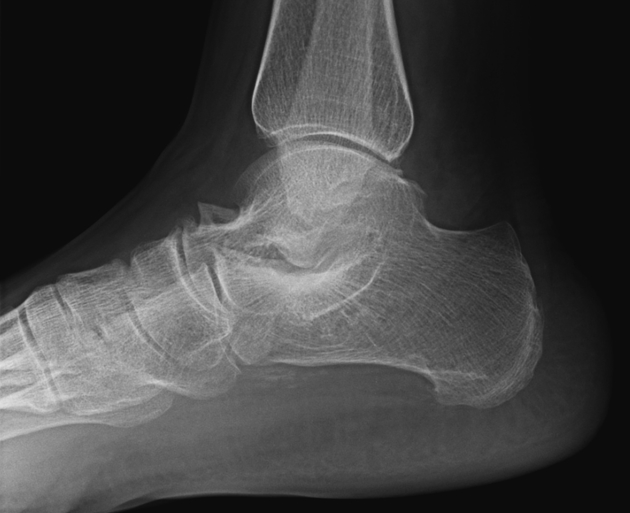
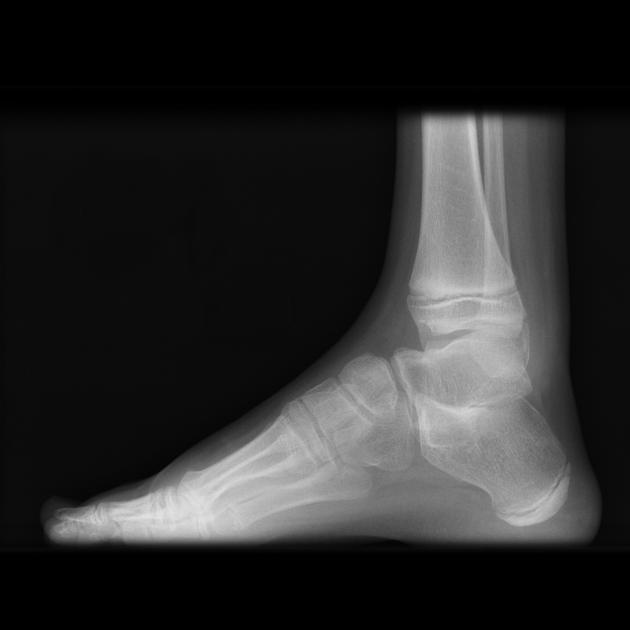
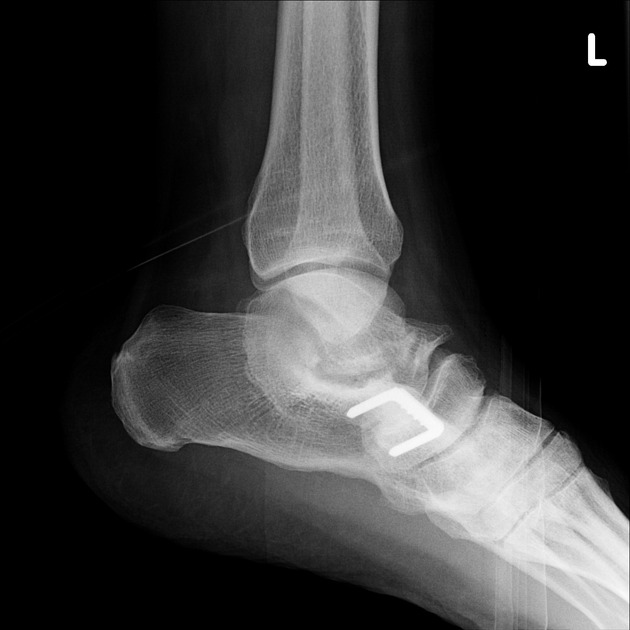
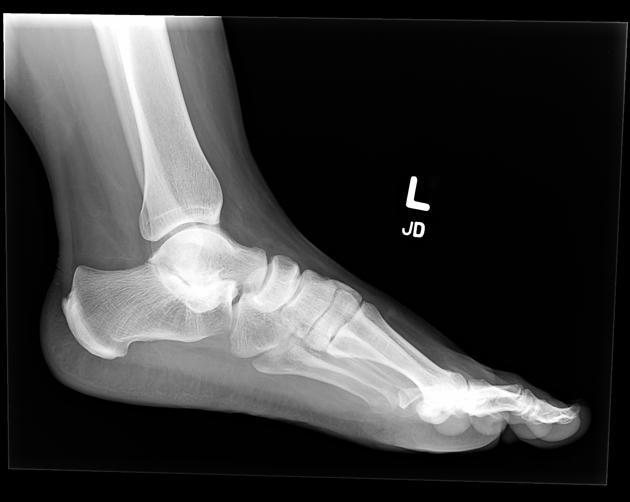
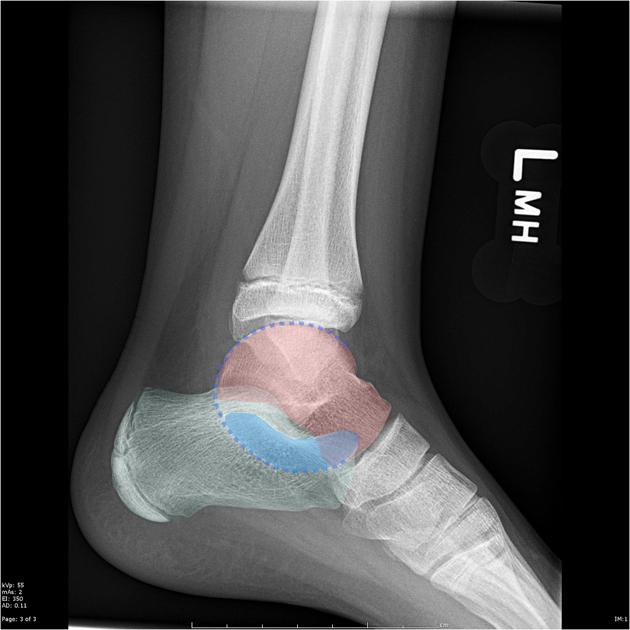
Radiographic features
As with any coalition, it may be bony, cartilaginous or fibrous. Talocalcaneal coalition often requires cross-sectional imaging for accurate diagnosis.
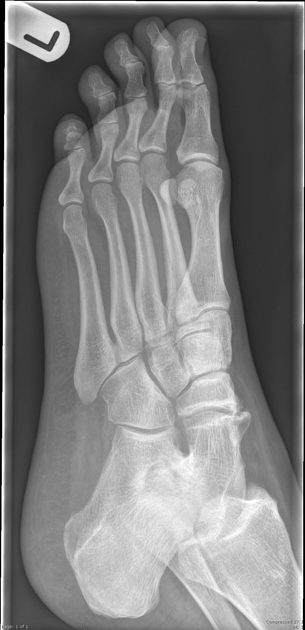
Plain radiograph
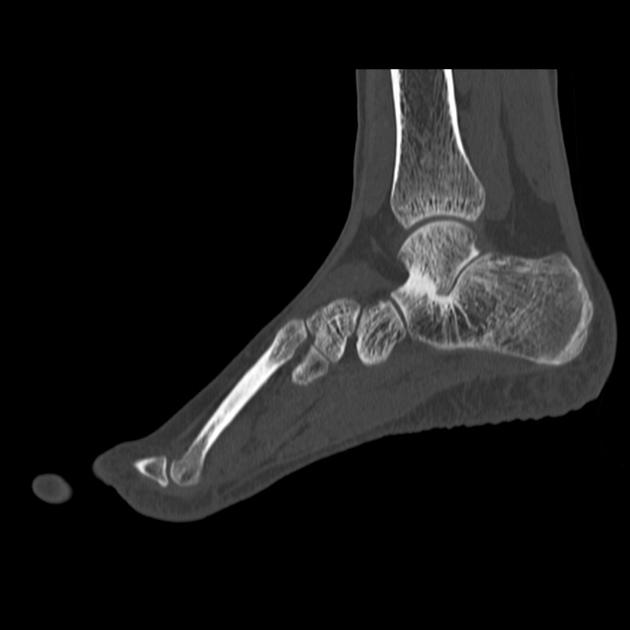
Plain film findings include 3,4:
-
best assessed on a lateral ankle radiograph
posterior continuity of the talus and sustentaculum tali
sensitivity: 50%
specificity: 90%
-
best seen on the lateral ankle radiograph
prominent beak at the anterior aspect of the talus
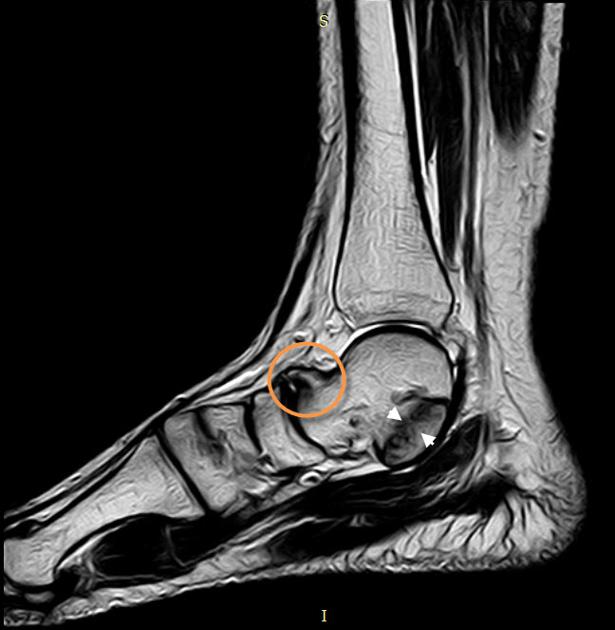
Secondary radiographic features that suggest the diagnosis include close apposition of the middle facet of the talocalcaneal (subtalar) joint or non-visualization of the middle articular facet 1,5. Sclerosis around the articular margins of the talocalcaneal joint may also occur.
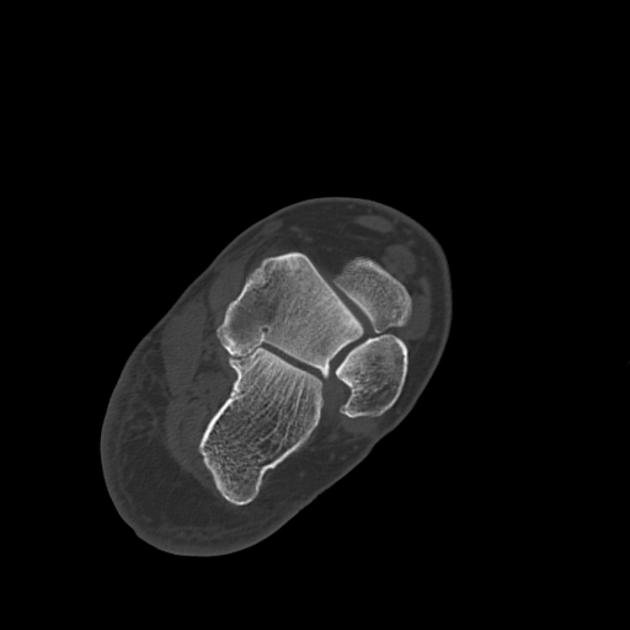
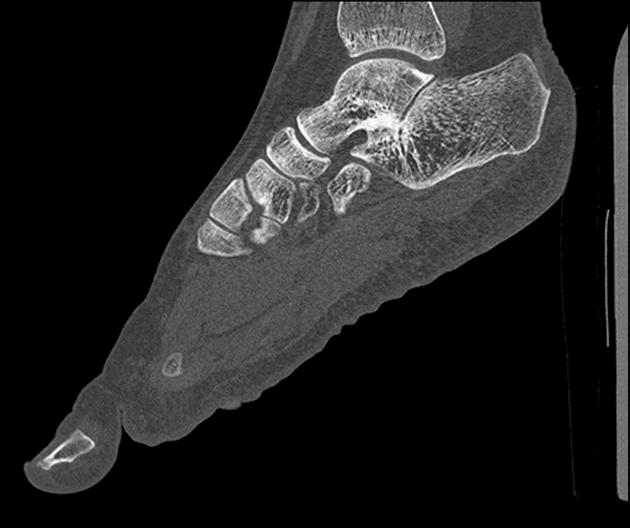
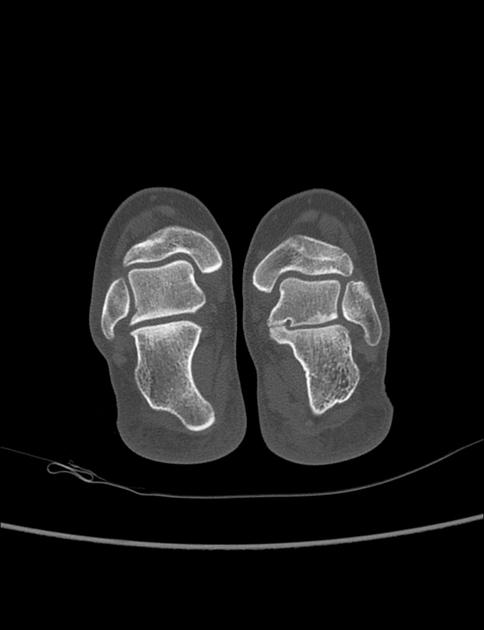
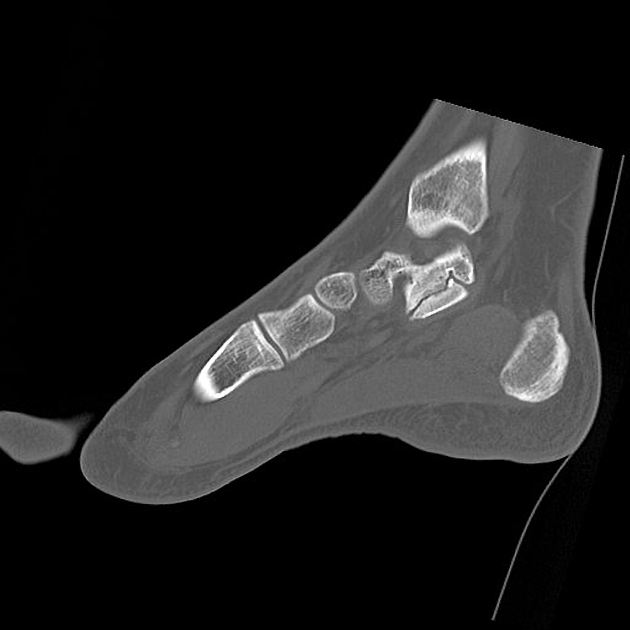
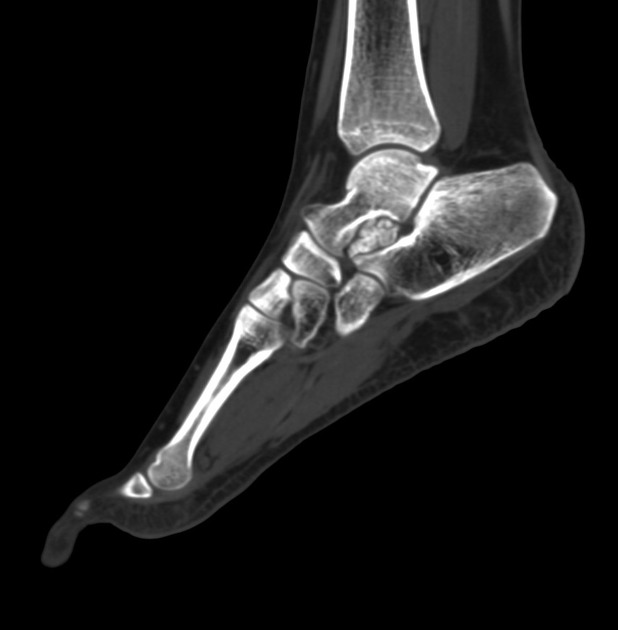
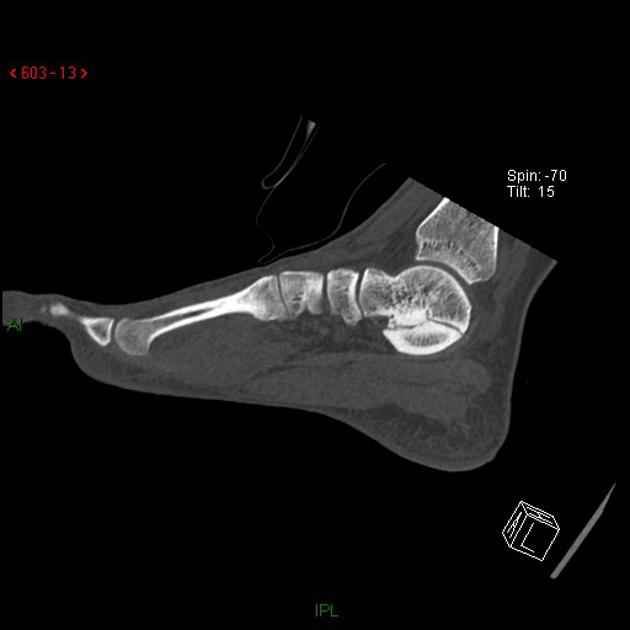
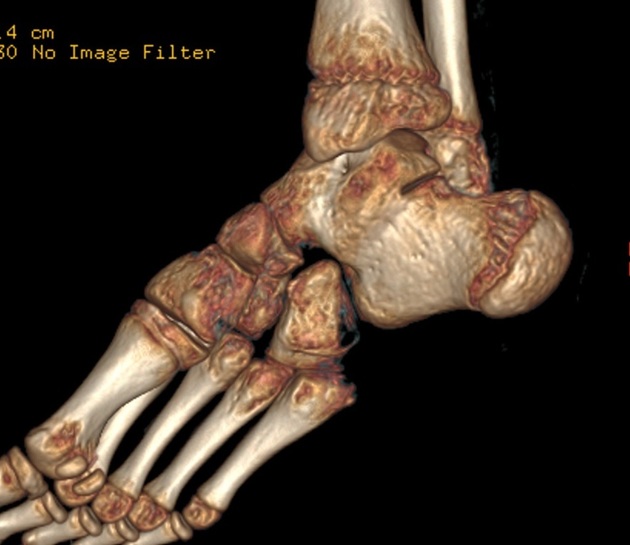
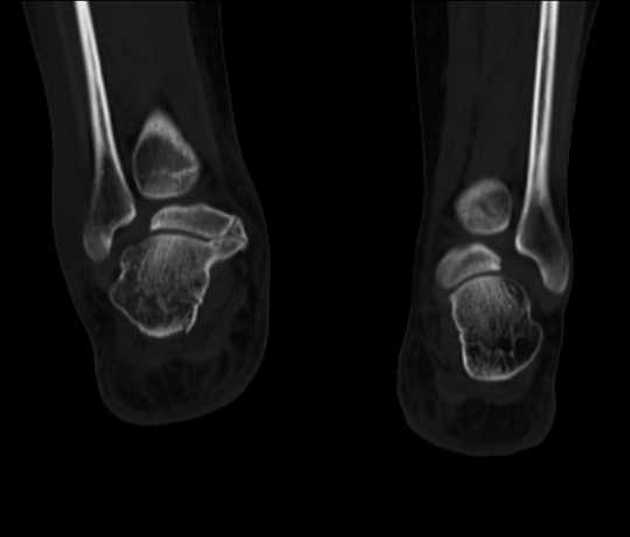
CT
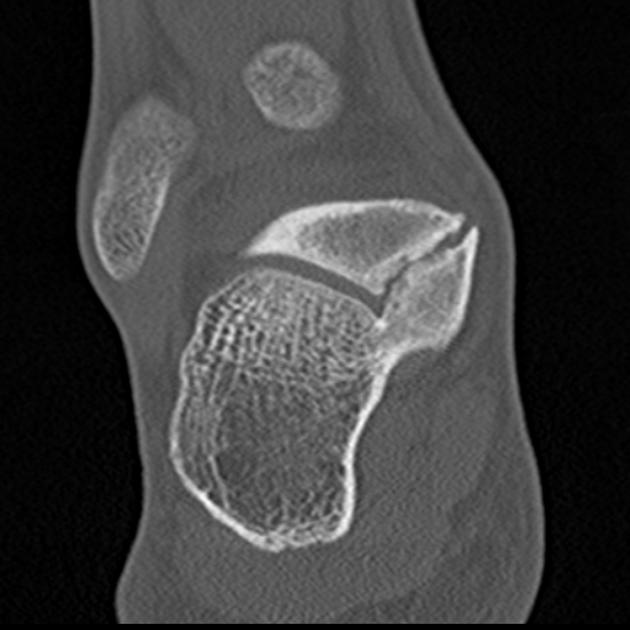
At CT, coronal reformats are usually the best to appreciate the coalition. The bony coalition is seen as a complete bar of bone between the talus and calcaneus. In a non-osseous coalition, there is usually irregularity of the articular surface, narrowing of the joint space and subchondral sclerosis. CT can also nicely demonstrate the presence of an os sustentaculi.
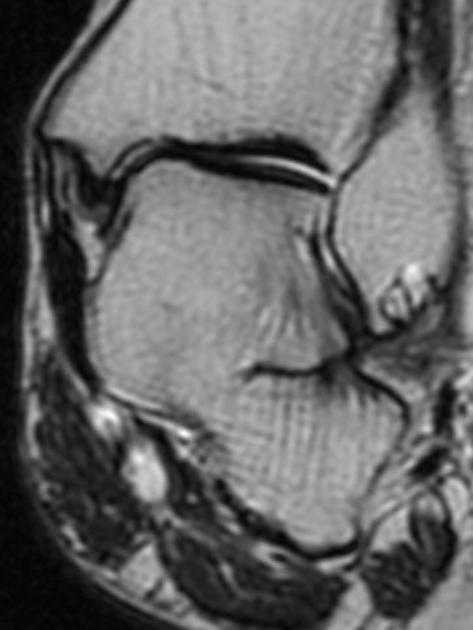
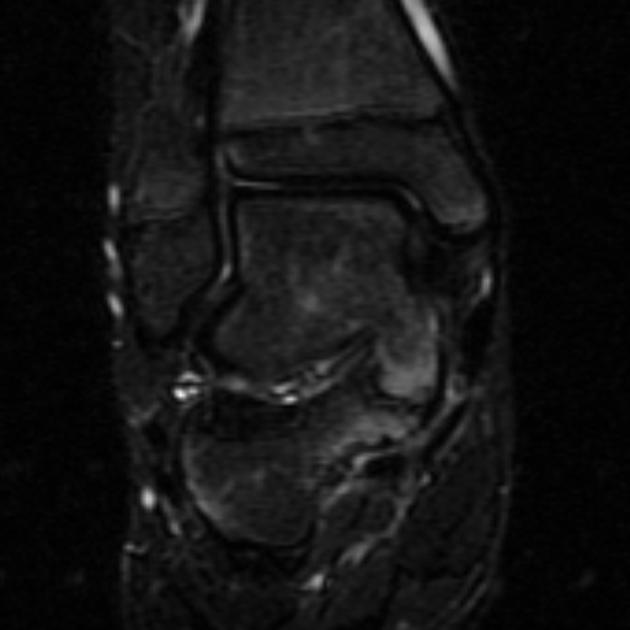
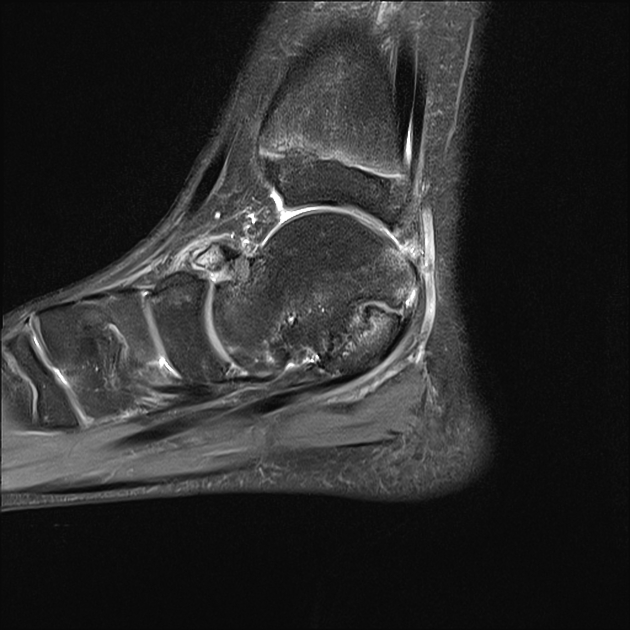
MRI
MRI is more helpful for the assessment of cartilaginous or fibrous coalitions and also demonstrates bone marrow and soft-tissue edema.
Nuclear medicine
On bone scan, increased radionuclide uptake at the site of the coalition may occur due to altered biomechanics at the joint, although this is a non-specific finding.
History and etymology
The talocalcaneal coalition was first described by the Hungarian anatomist Emil Zuckerkandl in 1877 2.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.