Femoral triangle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yoshi Yu's current disclosures- Radiologic femoral triangle
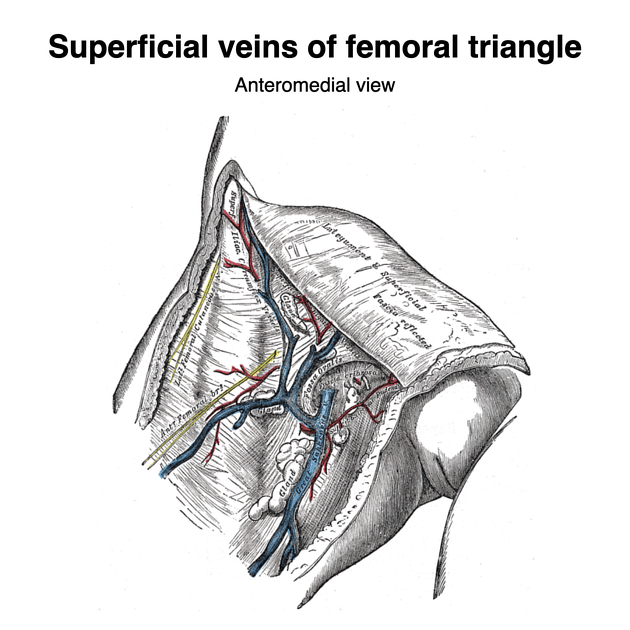
The femoral triangle is an anatomical space in the anterior upper thigh that contains several palpable structures.
Gross anatomy
Boundaries
The major boundaries can be recalled with the mnemonic SAIL 1,2:
lateral border: medial border of sartorius
medial border: medial border of adductor longus
superior border: inguinal ligament
roof: skin, subcutaneous tissue, a continuation of Scarpa's fascia, great saphenous vein (joins the femoral vein), superficial lymph nodes, fascia lata
Contents
From lateral to medial 1:
-
femoral sheath (thickening of the deep fascia of the thigh) which has three compartments (from lateral to medial):
femoral artery and its branches (within the lateral compartment of the femoral sheath) and the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve
femoral vein (within the intermediate compartment of the femoral sheath) and deep lymph nodes
femoral canal (the medial compartment of the femoral sheath) which contains fat and lymph nodes (of Cloquet)
The basic order can be recalled with the mnemonics seen here.
Radiographic features
CT
The femoral triangle is best seen on coronal reformats but because of its curved nature around the anterior thigh it cannot always be fully seen. Cherian and Parnell 2 have proposed a radiologic femoral triangle (as opposed to the above described anatomic femoral triangle) with the following boundaries:
laterally: femoral vein
medially: pectineus muscle
superiorly: inguinal ligament
Cherian and Parnell state that the importance of the radiologic femoral triangle is that it is a site for femoral hernias identifiable on MDCT and acts as a surrogate site for the femoral canal 2.
References
- 1. Shadbolt CL, Heinze SB, Dietrich RB. Imaging of groin masses: inguinal anatomy and pathologic conditions revisited. Radiographics. 2001;21 Spec No: S261-71. Pubmed citation
- 2. Cherian PT, Parnell AP. Radiologic anatomy of the inguinofemoral region: insights from MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189 (4): W177-83. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.2489 - Pubmed citation
- 3. McMINN. Lasts Anatomy Regional and Applied. CHURCHILL LIVINGSTONE. (2003) ISBN:B0084AQDG8. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Eizenberg, Ahern G. General anatomy. McGraw-Hill Medical. ISBN:0070134677. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Fascia lata
- Femoral canal
- Sartorius muscle
- Genitofemoral nerve
- Femoral vein
- Femoral sheath
- Iliopsoas muscle
- Psoas major muscle
- Great saphenous vein
- Femoral triangle contents (mnemonic)
- Adductor canal
- Femoral triangle boundaries (mnemonic)
- Ectopic testis
- Saphenous nerve
- Adductor longus muscle
- Femoral nerve
- Profunda femoris artery
Related articles: Anatomy: Lower limb
- skeleton of the lower limb
- joints of the lower limb
-
hip joint
- ligaments
- muscles
- additional structures
- hip joint capsule
- zona orbicularis
- iliotibial band
-
hip bursae
- anterior
- iliopsoas bursa (iliopectineal bursa)
- lateral
- subgluteal bursae
- greater trochanteric bursa (subgluteus maximus bursa)
- subgluteus medius bursa
- subgluteus minimus bursa
- gluteofemoral bursa
- subgluteal bursae
- postero-inferior
- anterior
- ossification centers
-
knee joint
- ligaments
- anterior cruciate ligament
- posterior cruciate ligament
- medial collateral ligament
- lateral collateral ligament
- meniscofemoral ligament (mnemonic)
-
posterolateral ligamentous complex
- arcuate ligament
- patellar tendon and quadriceps tendon
- anterolateral ligament
- posterior oblique ligament
- oblique popliteal ligament
- medial patellofemoral ligament
- additional structures
- extensor mechanism of the knee
- groove for the popliteus tendon
- knee bursae
- anterior bursae
- medial bursae
- lateral bursae
- posterior bursae
- knee capsule
- lateral patellar retinaculum
- medial patellar retinaculum
- menisci
- pes anserinus (mnemonic)
- ossification centers
- ligaments
- tibiofibular joints
-
ankle joint
- regional anatomy
- medial ankle
- lateral ankle
- anterior ankle
- ligaments
- medial collateral (deltoid) ligament
- lateral collateral ligament
- additional structures
- ankle bursae
- ossification centers of the ankle
- variants
- regional anatomy
- foot joints
- subtalar joint
- mid-tarsal (Chopart) joint
-
tarsometatarsal (Lisfranc) joint
- ligaments
- intermetatarsal joint
- metatarsophalangeal joint
- interphalangeal joint
- ossification centers
-
hip joint
- spaces of the lower limb
-
muscles of the lower limb
- muscles of the pelvic group
- muscles of the thigh
- muscles of the leg
- anterior compartment of the leg
- posterior compartments of the leg
- lateral compartment of the leg
- muscles of the foot
- dorsal muscles
- plantar muscles
- 1st layer
- 2nd layer
- 3rd layer
- 4th layer
- accessory muscles of the lower limb
- accessory gluteal muscles
-
accessory muscles of the ankle
- accessory peroneal muscles
- accessory flexor digitorum longus muscle
- accessory soleus muscle
- peroneocalcaneus internus muscle
- tibiocalcaneus internus muscle
- extensor hallucis capsularis tendon
- anterior fibulocalcaneus muscle
- accessory extensor digiti secundus muscle
- tibioastragalus anticus of Gruber muscle
- vascular supply of the lower limb
- arterial supply of the lower limb
- venous drainage of the lower limb
- innervation of the lower limb
- lymphatic system of the lower limb
- lymphatic pathways
- anteromedial group
- anterolateral group
- posteromedial group
- posterolateral group
- lower limb lymph nodes
- lymphatic pathways







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.