Taeniae coli
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yoshi Yu's current disclosures- Taena coli
- Taenia coli
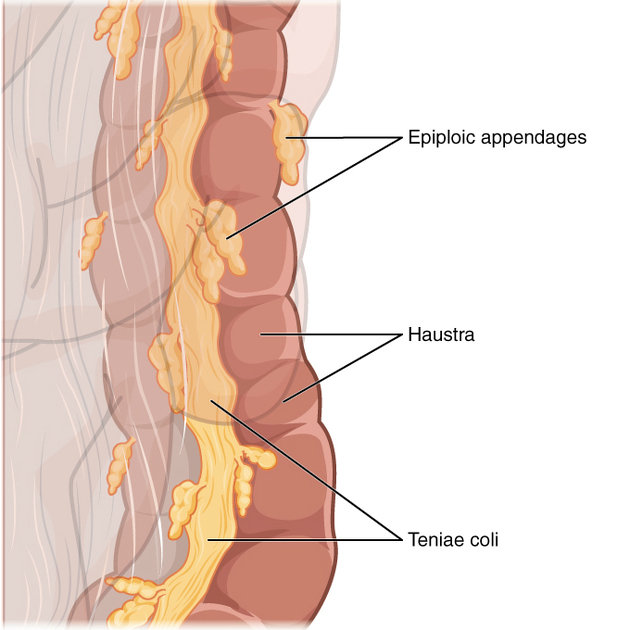
The taeniae coli are three longitudinal bands of smooth muscle on the outer colonic wall that extend from the cecum to the distal sigmoid colon.
Gross anatomy
The taeniae coli lie superficial to the inner circumferential layer of the colonic smooth muscle and result in the classic interrupted haustral markings appearance of the colon (unlike the continuous valvulae conniventes within the small bowel).
Proximally, the taeniae coli converge at the base of the appendix in the cecum where they form a complete longitudinal layer.
In the ascending and descending colon, the bands are located anteriorly (free taenia), posteromedially (mesocolic taenia), and posterolaterally (omental taenia). In the transverse colon, due to dependent rotation of the bowel, the positions of the taeniae coli shift to be respectively located inferiorly, posteriorly, and superiorly.
In the sigmoid colon, the taeniae coli gradually broaden to form anterior and posterior layers that fuse laterally to form a complete longitudinal muscle layer surrounding the rectum.
Clinical importance
In an appendectomy, if the appendix is not immediately obvious, the taeniae coli can be used as a guide to identify the appendix where they merge at its base.
References
- 1. Chummy S. Sinnatamby. Last's Anatomy. (2011) ISBN: 9780702033940 - Google Books
- 2. Susan Standring. Gray's Anatomy. (2020) ISBN: 9780702077050 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.