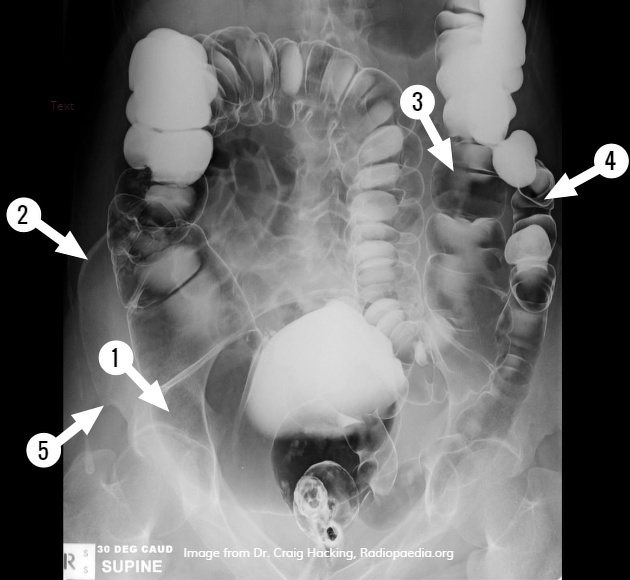
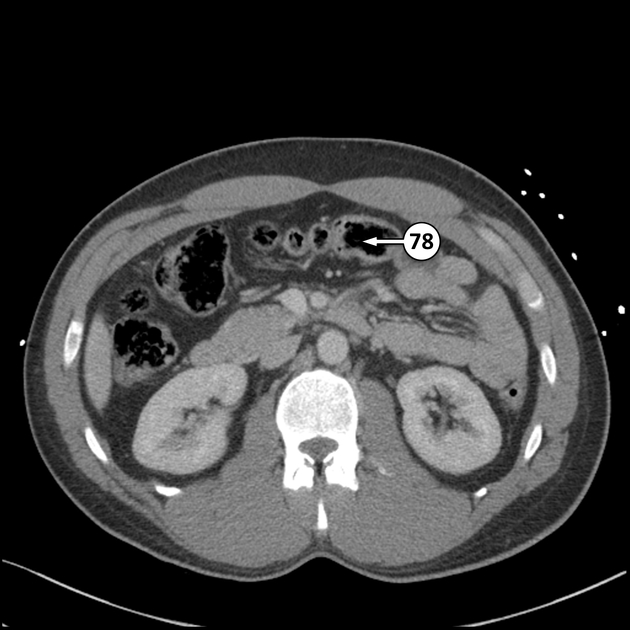
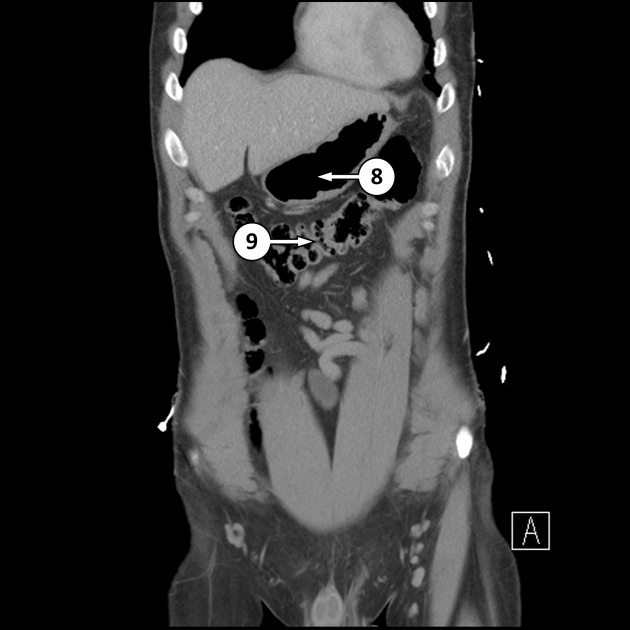
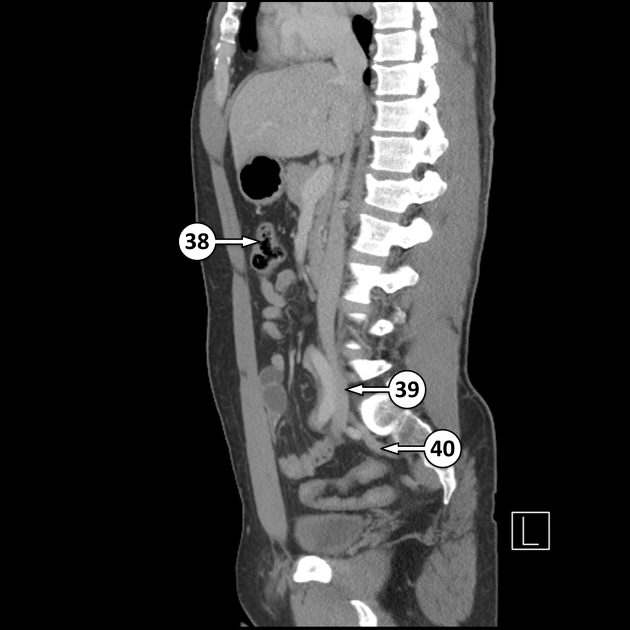
Transverse colon
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Calum Worsley had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Calum Worsley's current disclosures- Transverse colons
The transverse colon is the longest and most mobile part of the large intestine. It measures up to 45 cm in length.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The transverse colon is the continuation of the ascending colon from the right colic flexure. It passes from the right to left hypochondrium in a downward convex path crossing both the epigastric and umbilical zones. In the left hypochondrium, it curves sharply on itself beneath the lower end of the spleen, forming the left colic flexure where it continues as the descending colon.
It is almost completely invested by peritoneum, and is connected to the inferior border of the pancreas by a large and wide duplicature of that membrane, the transverse mesocolon. The gastrocolic ligament also attaches the transverse colon to the stomach. The phrenicocolic ligament attaches to the left colic flexure and connects it to the diaphragm, with variable connection to the inferior aspect of the spleen.
Relations
superiorly (right to left): liver, gallbladder, greater curvature of the stomach, spleen
inferiorly: small bowel
anteriorly: greater omentum and anterior abdominal wall
posteriorly (right to left): 2nd part duodenum, head and body of pancreas, small bowel
Arterial supply
middle colic artery (branch of superior mesenteric artery) supplies proximal two-thirds
ascending branch of left colic artery (branch of inferior mesenteric artery) supplies distal one-third
Venous drainage
via similarly named veins to splenic vein to the portal venous system
Innervation
sympathetic: superior mesenteric plexus and inferior mesenteric plexus
parasympathetic: derived from pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-S4)
Lymphatic drainage
Lymphatics accompany vessels and drain to paracolic nodes, and to the superior mesenteric group (proximal two-thirds) and inferior mesenteric group (distal two-thirds).
Radiographic features
Fluoroscopy
Double contrast barium enemas provided good anatomical detail from the rectum to the cecum. The patient may need to be rolled into various positions to get the barium sulfate contrast medium to coat the lumen of the colon.
see also
References
- 1. Susan Standring. Gray's Anatomy. (2008) ISBN: 9780443066849 - Google Books
- 2. Paul Butler, Adam Mitchell, Jeremiah C. Healy et al. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (2012) ISBN: 9780521766661 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Inferior mesenteric plexus
- Hirschsprung disease
- Omentum
- Superior hypogastric plexus
- Superior mesenteric artery
- Lesser sac hernia
- Right hemicolectomy
- Left supramesocolic space
- Left colic artery
- Stomach
- Anterior right subhepatic space
- Ascending colon
- Arc of Barkow
- Toxic megacolon
- Descending colon
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (T)
- Right colic flexure
- Transverse mesocolon
- Duodenojejunal flexure
- CT colonography reporting and data system
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.