Ileocecal valve
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no recorded disclosures.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures- Ileocaecal junction
- Ileocecal valve
- Valvula Bauhini
- Sphincter coli
- Ileocolonic sphincter
- Ileocaecal sphincter
- Ileocecal sphincter
- Ileocecal junction
- Ileal papilla
- Bauhin’s valve
- Tulpius valve
- Ileocecal eminence
- Ileocaecal eminence
- Colic valve
- Valve of Varolius
- Tulp’s valve
- Ostium ileale
- Tulp valve
- Bauhin valve
- Ileocaecal valve (ICV)
- Bauhin's valves
- Tulp's valves
- Ileocaecal valves
- Ileocecal valves
The ileocecal valve (TA: ostium ileale), also known as Bauhin valve or Tulp valve, separates the terminal ileum from the cecum and functions to regulate flow between these two structures and prevent reflux from the cecum into the small intestine.
On this page:
Terminology
There are a large number of additional synonyms for the ileocecal valve, which include Tulpius valve (variant of Tulp valve), valve of Varolius, ileal papilla, ileocecal eminence and colic valve .
Gross anatomy
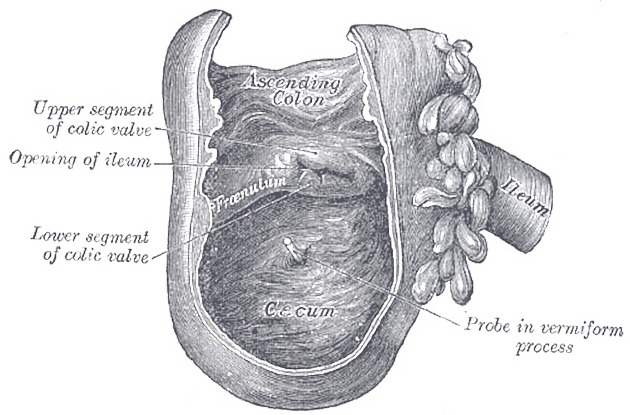
The ileocecal valve consists of two muscular layers of ileum, an upper and lower lip, that are covered by mucosa and protrude into the lumen of the caecaum supported by mucosal folds called frenula. This forms the opening of the terminal ileum into the medial cecum and delineates the upper margin of the cecum from the ascending colon.
The morphology of the ileocecal valve has be described on endoscopy as 1,3,4:
- labial-type: slit-like opening (most common)
- papillary-type: dome-shaped
- lipomatous: significant amount of fat demonstrated in the lips
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Variant anatomy
- lateral (~7.5%) or posterior opening (~5%) of the terminal ileum 2,4
Radiographic appearance
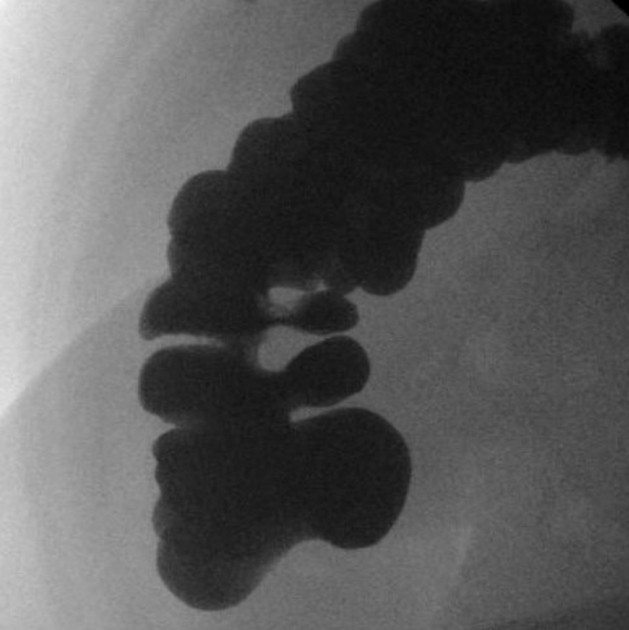
Fluoroscopy
- ileocecal valve is identified on barium enema as an oval or triangular-shaped filling defect with smooth or lobulated surfaces 4
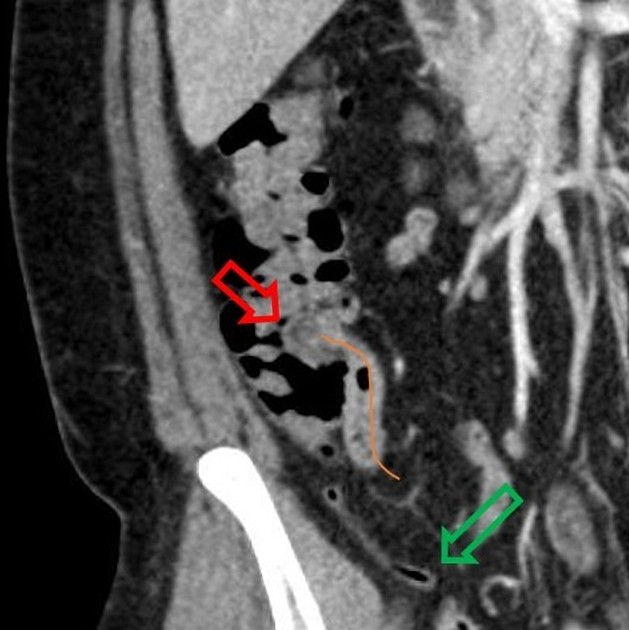
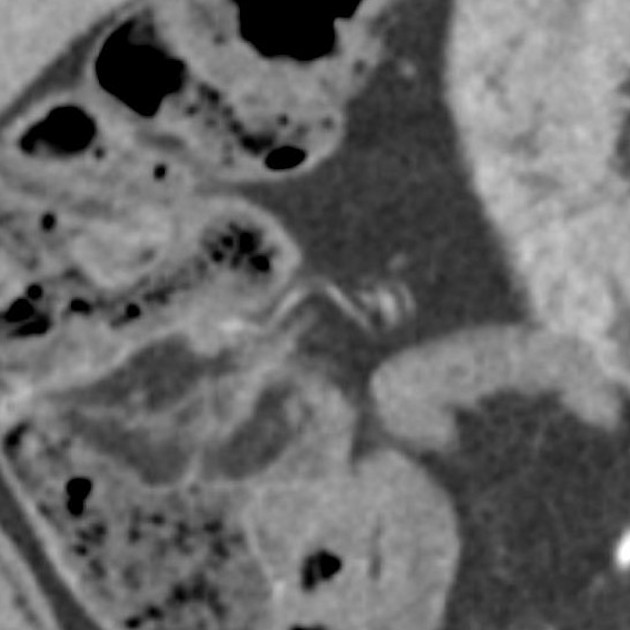
CT
- ileocecal valve is best viewed on supine imaging
- mixed density structure at the junction of the ileum and cecum with an average density of -25 HU (range -60 HU to +18 HU) 4
History and etymology
Costanzo Varolius (1543-1575) was an Italian and papal anatomist who is famously remembered for his contributions to neuroanatomy, including being the first to describe the pons; hence its historical monicker, pons Varolli 6,7.
Caspar Bauhin (1560-1624) was a Swiss anatomist, although best remembered for his botanical works. Both his father and brother, John, were also physicians 5. Bauhin glands, a synonym of the anterior lingual salivary glands were also named for him 6.
Nicolas Tulp (1593-1674), a.k.a. Nicolas Tulpius, was a Dutch physician 6.
Related pathology
References
- 1. Silva A, Beaty S, Hara A et al. Spectrum of Normal and Abnormal CT Appearances of the Ileocecal Valve and Cecum with Endoscopic and Surgical Correlation. Radiographics. 2007;27(4):1039-54. doi:10.1148/rg.274065164 - Pubmed
- 2. Iafrate F, Rengo M, Ferrari R, Paolantonio P, Celestre M, Laghi A. Spectrum of Normal Findings, Anatomic Variants and Pathology of Ileocecal Valve: CT Colonography Appearances and Endoscopic Correlation. Abdom Imaging. 2007;32(5):589-95. doi:10.1007/s00261-007-9198-0 - Pubmed
- 3. Regge D, Gallo T, Nieddu G et al. Ileocecal Valve Imaging on Computed Tomographic Colonography. Abdom Imaging. 2005;30(1):20-5. doi:10.1007/s00261-004-0225-0 - Pubmed
- 4. Jelbert A, Swinson S, Atkin K, Bhalerao S, Babu S. Imaging of the Ileocaecal Valve. Tech Coloproctol. 2008;12(2):87-92. doi:10.1007/s10151-008-0404-z - Pubmed
- 5. Anton Sebastian. A Dictionary of the History of Medicine. (1999) ISBN: 9781850700210 - Google Books
- 6. William Alexander Newman Dorland. Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. (2007) ISBN: 9781416023647 - Google Books
- 7. Tubbs R, Loukas M, Shoja M et al. Costanzo Varolio (Constantius Varolius 1543-1575) and the Pons Varolli. Neurosurgery. 2008;62(3):734-7; discussion 734. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000317323.63859.2a - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Barium studies of the small bowel
- Terminal ileum
- Small bowel mesentery internal hernia
- Inframesocolic space
- Large bowel obstruction
- Jejunoileal bypass
- Ileum
- Right hemicolectomy
- Incompetent ileocaecal valve
- Billroth II gastrojejunostomy
- Ascending colon
- Duplex appendix
- Cecum
- Intestinal transplant
- Acute appendicitis
- Bucket handle mesenteric injury
- Lipomatosis of the ileocaecal valve
- Appendix
- Gallstone ileus
- Intussusception reduction
- Ileocecal valve (Gray's illustrations)
- Ileocecal fossae (Gray's illustrations)
- Cecal volvulus
- Terminal ileal diverticulitis
- Appendicitis
- Peritonitis following traumatic small bowel perforation
- Acute appendicitis
- Ileocecal adenocarcinoma
- Intestinal malrotation
- Ileocaecal valve
- Ileocecal adenocarcinoma with intussusception
- Appendicitis with localised perforation and abscess formation
- Caecal volvulus
- Small bowel obstruction by Meckel diverticulum and omphalomesenteric ligament
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.