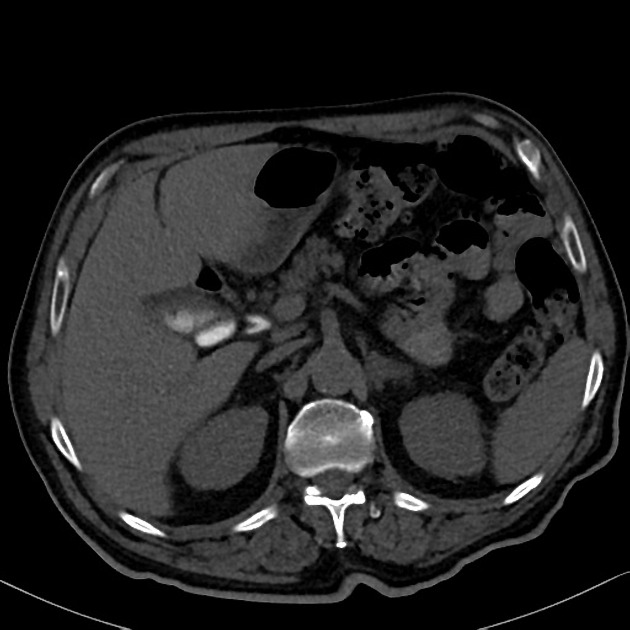
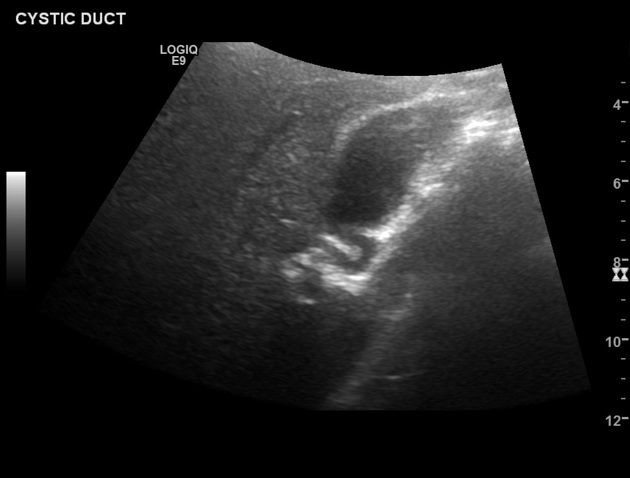
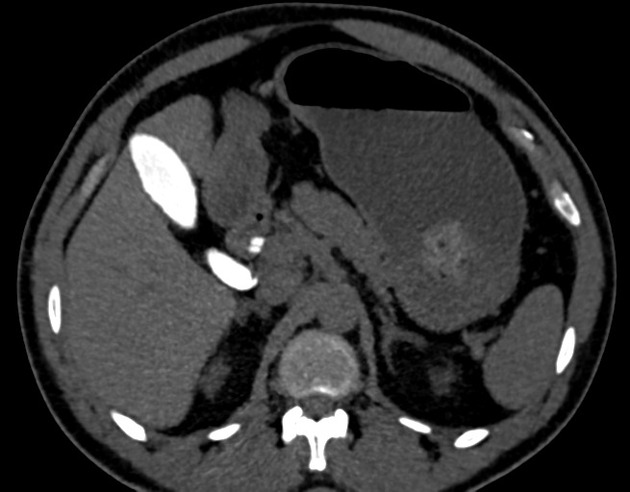
Cystic duct
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Chia Wei Oh had no recorded disclosures.
View Chia Wei Oh's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Cystic ducts
The cystic duct connects the neck of the gallbladder to the common hepatic duct (CHD), draining bile to and from the biliary tree.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The confluence of the cystic duct and the common hepatic duct forms the common bile duct (CBD). The cystic duct is approximately 2-3 cm long and 2-3 mm in diameter. It contains multiple endoluminal mucosal folds known as the spiral mucosal folds (of Heister) 5.
Arterial supply
variable supply, with blood coming from cystic artery, and left and right hepatic arteries 6,7
Venous drainage
Variant anatomy
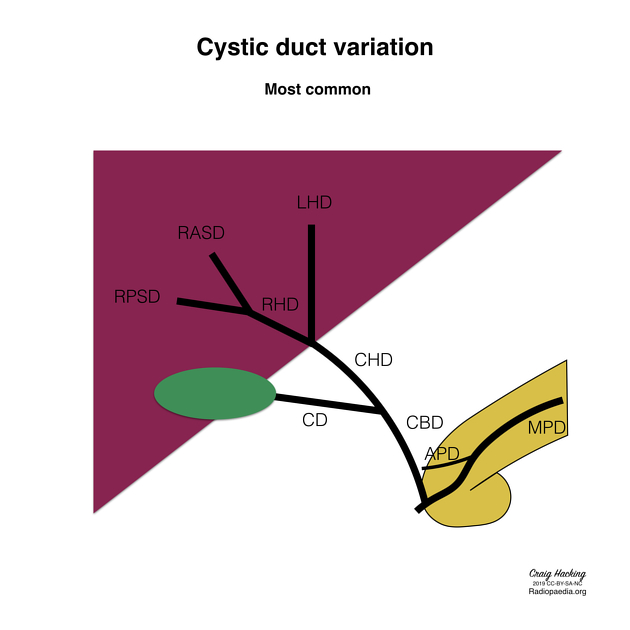
There are three main variations of the cystic duct 3:
low cystic duct insertion: into the distal-third of the CHD (~10%)
medial cystic duct insertion: into the left, not the right, side of the CHD (~15%)
parallel cystic duct course: courses parallel to the CHD for at least 2 cm (~10%)
Related pathology
Conditions that may affect the cystic duct include:
cystic duct obstruction, which can result in cholecystitis
cystic duct-duodenal fistula
malignancy (e.g. cholangiocarcinoma)
References
- 1. Chummy S. Sinnatamby. Last's Anatomy. (1999) ISBN: 9780443056116 - Google Books
- 2. Turner M & Fulcher A. The Cystic Duct: Normal Anatomy and Disease Processes. Radiographics. 2001;21(1):3-22; questionnaire 288-94. doi:10.1148/radiographics.21.1.g01ja093 - Pubmed
- 3. Mortelé K & Ros P. Anatomic Variants of the Biliary Tree: MR Cholangiographic Findings and Clinical Applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177(2):389-94. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.2.1770389 - Pubmed
- 4. Wu Y, Liu Z, Mrikhi R et al. Anatomical Variations of the Cystic Duct: Two Case Reports. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(1):155-7. doi:10.3748/wjg.14.155 - Pubmed
- 5. Pina L, Samoilovich F, Urrutia S, Rodríguez A, Alle L, Ferreres A. Surgical Considerations of the Cystic Duct and Heister Valves. Surg J (N Y). 2015;1(1):e23-7. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1567879 - Pubmed
- 6. Chen W, Ying D, Liu Z, He Z. Analysis of the Arterial Supply of the Extrahepatic Bile Ducts and Its Clinical Significance. Clin Anat. 1999;12(4):245-9. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2353(1999)12:4<245::AID-CA2>3.0.CO;2-W - Pubmed
- 7. Ramesh Babu C & Sharma M. Biliary Tract Anatomy and Its Relationship with Venous Drainage. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2014;4(Suppl 1):S18-26. doi:10.1016/j.jceh.2013.05.002 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Gallbladder perforation
- Perihilar cholangiocarcinoma (staging)
- Common hepatic duct
- Cholangiocarcinoma
- Multiple gallbladders
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Spiral mucosal folds
- Cystic artery
- Mirizzi syndrome
- Hepatocystic triangle
- Acute cholecystitis
- Gallbladder
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (C)
- Cystic vein
- Common bile duct
- Biliary tree anatomy
- Gastrinoma triangle
- Mirizzi syndrome
- Mirizzi syndrome
- Gallbladder
- Cystic duct stump stone
- Cystic duct dilation from obstructed CBD stent
- Gallbladder agenesis
- Bile plug syndrome
- Type II pancreas divisum with low medial insertion of cystic duct
- Normal HIDA scan
- Cystic duct obstruction (HIDA scan)
- Gallbladder remnant cholelithiasis and cholecystitis
- Cystic artery anatomic variation (diagram)
- Cystohepatic (Calot) triangle (diagram)
- Cystic duct (ultrasound)
- Biliary duct anatomic variation (diagram)
- Low medial cystic duct insertion
- Prominent cystic duct - post cholecystectomy
- Choledocholithiasis
- Cystic duct stump stone
- Cystic duct stump stones
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.