Hypopharynx
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Matt A. Morgan had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Matt A. Morgan's current disclosures- Laryngopharynx
- Hypopharynges
- Hypopharynxes
- Laryngopharynxes
- Laryngopharynges
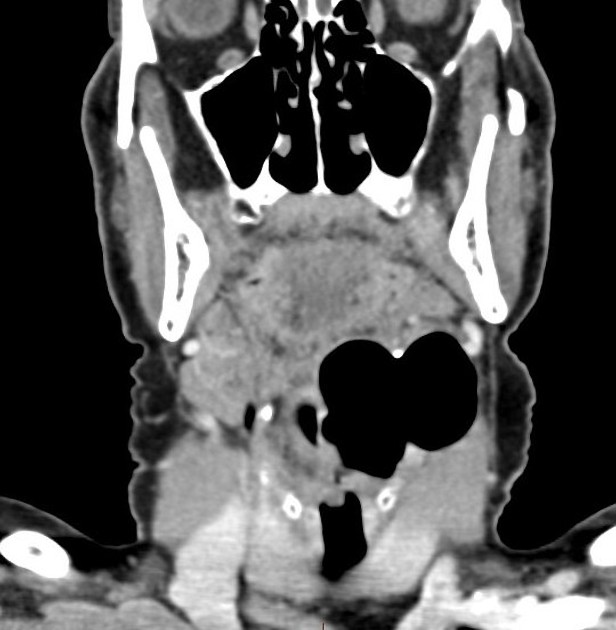
The hypopharynx (rare plural: hypopharynges or hypopharynxes) or laryngopharynx forms the most inferior portion of the pharynx, being the continuation of the oropharynx superiorly and both the larynx and esophagus inferiorly. It also forms part of the upper respiratory tract and the gastrointestinal tract.
Gross anatomy
The hypopharynx begins as the continuation of the oropharynx at the pharyngoepiglottic fold (which is at the level of the hyoid bone) superiorly, and extends inferiorly to the level of the inferior aspect of the cricoid cartilage (at the C6 vertebra level) 4 where it continues as the cervical esophagus 4.
It is a mucosa-lined, muscular tube with its posterolateral walls formed by the inferior constrictor muscle and anterior wall by laryngeal cartilages. It forms part of the pharyngeal mucosal space.
Boundaries
anteriorly: post-cricoid mucosa, posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
posteriorly: mucosal wall, middle and inferior constrictor muscles
superiorly: hyoid bone, glossoepiglottic and pharyngoepiglottic folds
inferiorly: cricoid cartilage, cricopharyngeus muscle
Subsites
Three subsites of the hypopharynx are described, being pertinent to localize where squamous cell carcinoma arises:
-
The upper part of laryngopharynx wraps around the larynx, producing these two recesses 4
posterior wall
Related pathology
References
- 1. Michaels L, Hellquist HB. Ear, Nose and Throat Histopathology. Springer. ISBN:1447111281. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Harnsberger HR, Glastonbury CM, Michel MA et-al. Diagnostic Imaging: Head and Neck. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (2010) ISBN:1931884781. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Tao TY, Menias CO, Herman TE et-al. Easier to swallow: pictorial review of structural findings of the pharynx at barium pharyngography. Radiographics. 2013;33 (7): e189-208. doi:10.1148/rg.337125153 - Pubmed citation
- 4. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2011) Page 37. ISBN: 9780702029714 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Spontaneous retropharyngeal haemorrhage
- Larynx
- Synovial sarcoma
- Oropharynx
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Steeple sign (trachea)
- Visceral space
- Head and neck anatomy
- Respiratory tract
- Zenker diverticulum
- Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Killian dehiscence
- Pyriform sinus
- Epiglottis
- Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis
- Hypopharyngeal carcinoma (staging)
- Croup
- Postcricoid region
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.