Large intestine
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no recorded disclosures.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures- Colon
- Large bowel
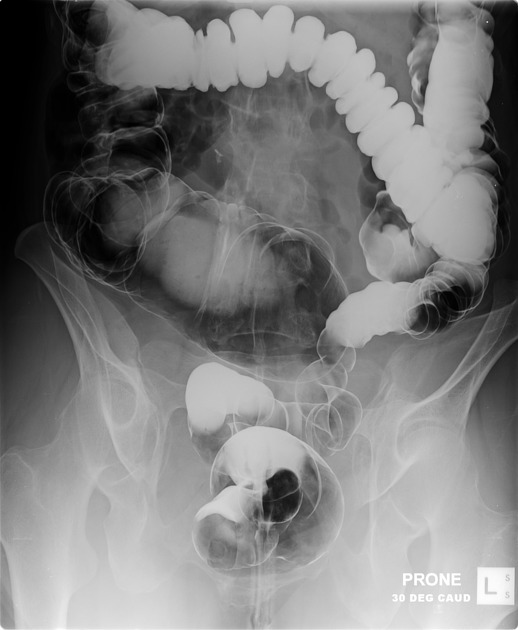
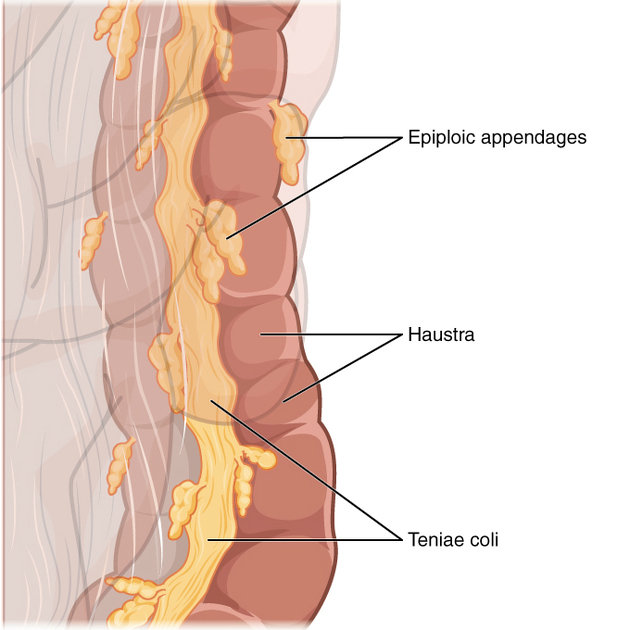
The large intestine (also known as the large bowel) is a 1.5 meter muscular tube that extends from the cecum to the rectum. It has three outer longitudinal muscular layers called taenia coli, which are about 30 cm shorter than the length of the large bowel causing characteristic sacculations interrupted by incomplete rings called haustra 1. The large bowel is divided into the following parts:
- cecum
- ascending colon
- right colic flexure
- transverse colon
- left colic flexure
- descending colon
- sigmoid colon
- rectum
NB: some people use the term colon as a synonym for the large intestine/bowel, however anatomically, the colon does not include the rectum, and therefore colon and large intestine are not synonymous.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (2012) ISBN:0521766664. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Backwash ileitis
- Rectal cancer
- Water-soluble contrast challenge
- Typhlitis
- Toxic megacolon
- Cecum
- Faeces
- Lower gastrointestinal bleeding
- Colonic pseudo-obstruction
- Congenital pouch colon
- Epiploic appendage
- Traditional serrated adenoma
- Gallstone ileus
- 3-6-9 rule (bowel)
- Abdominal x-ray review: bowel
- Urinary diversion
- Left colic flexure
- Gastrointestinal amyloidosis
- Adynamic ileus
- Transverse colon
- Meckel’s diverticulum causing acute small intestinal obstruction
- Colon diverticulosis
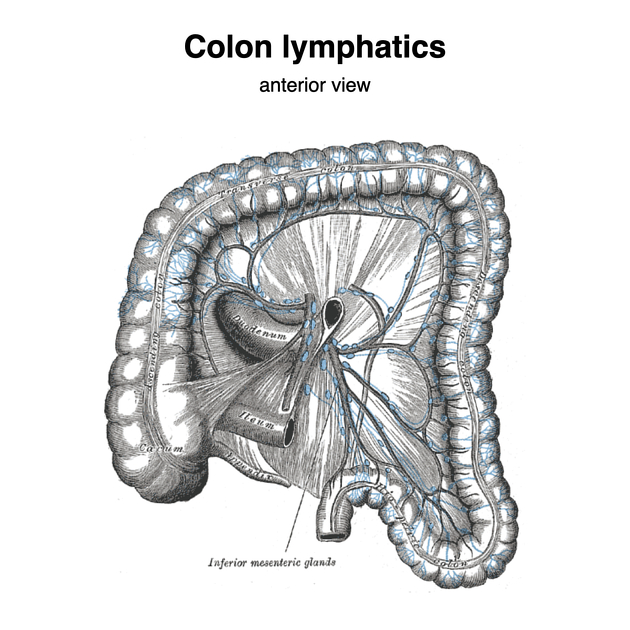
- Lymphatics of the colon (Gray's illustration)
- Intestinal obstruction due to adhesions
- Colonic adenocarcinoma
- Conjoined twins - cephalo-thoraco-omphalopagus
- Chilaiditi syndrome
- Normal abdominal x-ray - large bowel gas pattern
- Epiploic appendagitis
- Colon adenocarcinoma
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.