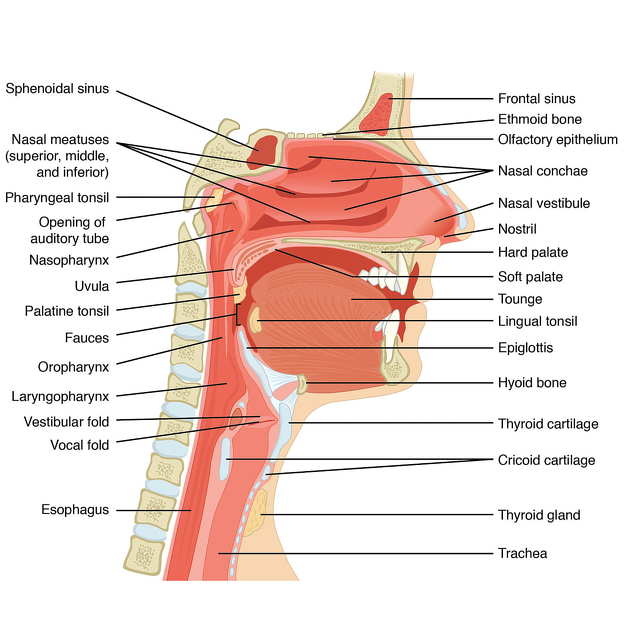
Nasopharynx
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Nasopharynges
- Nasopharynxes
The nasopharynx (plural: nasopharynges or nasopharynxes) forms the superior-most part of the pharynx, in continuity with the inferior oropharynx, and the posterior continuation of the anterior nasal cavity. It also forms part of the upper respiratory tract.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Boundaries
anteriorly: posterior nares and posterior margin of nasal septum 1,2
inferiorly: soft palate 2. Levator veli palatini accompanies the Eustachian tube and inserts into posterior part of soft palate. Tensor veli palatini runs around the nasopharynx and hooks around the pterygoid hamulus before inserts into membranous part of nasopharynx 5.
-
superiorly: basisphenoid and basiocciput 1,2
roof of the nasopharynx is called the vault (or fornix) of the pharynx, where the mucosa firmly attaches to the sphenoid and pharyngobasilar fascia
adenoid lymphoid tissue is also located at the roof 5
posteriorly: C1 and C2 1
-
laterally
the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube is located in the center of the lateral wall 1,2 It pierces the pharyngobasilar fascia. Posterior to the cartilaginous end of the tube is ridge named torus tubarius. Behind the torus tubarius is fossa of Rosenmuller 5
lymphoid tissue aggregates, also known as the tubal tonsil occur around the opening of the Eustachian tube 1,3
the fossa of Rosenmüller lies between the posterior margin of the Eustachian tube and the posterior wall of the nasopharynx 1,2
separated posterolaterally from the carotid sheath by styloid process and styloid muscle 5
Arterial supply
ascending palatine branch of facial artery 2
Venous drainage
-
the veins form plexuses which drain into the internal jugular vein
Lymphatic drainage
Lymphatic drainage in the nasopharynx occurs laterally and medially:
lateral drainage pathway: lymph vessels traverse the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and drain into the lateral retropharyngeal, deep cervical and posterior triangle lymph nodes 4
medial drainage pathway: lymph vessels from the roof and posterior wall drain into the median retropharyngeal lymph nodes 4
Innervation
-
sensory
pharyngeal nerve of the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN Vb) 2
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) 2
-
motor
pharyngeal plexus: contains branches of cranial nerves IX and X together with sympathetic fibers 2
References
- 1. DSc SSP. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, Expert Consult - Online and Print, 40e. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN: 9780443066849
- 2. Joiner M C, van der Koegel A. Basic Clinical Radiobiology, Fifth Edition. CRC Press. (2016) ISBN: 9781444179637
- 3. Grossman RI, Yousem DM. Neuroradiology. Mosby. (2003) ISBN: 9780323005081
- 4. Mukherji SK, Armao D, Joshi VM. Cervical nodal metastases in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: what to expect. (2001) Head & neck. 23 (11): 995-1005. doi:10.1002/hed.1144 - Pubmed
- 5. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2011) Page 33. ISBN: 9780702029714 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Sinonasal mucosal melanoma
- Persistent hypophyseal canal
- Botryoid rhabdomyosarcoma
- Chordoma
- Eustachian tube
- Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
- Adenoid tonsil
- Spontaneous retropharyngeal haemorrhage
- Intra-adenoidal retention cysts
- Oncocytic papillary cystadenoma of the upper respiratory tract
- Oropharynx
- Panda sign (sarcoidosis)
- Pharynx
- Hypotympanum
- Oropharyngeal (p16-negative) cancer (staging)
- Visceral space
- Pituitary adenoma/PitNET
- Antrochoanal polyp
- Paediatric nasal cavity masses
- Head and neck anatomy
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Antrochoanal polyp
- Hypoglycaemic encephalopathy
- Adenoid hypertrophy
- Adenoid hypertrophy
- Adenoid hypertrophy
- Adenoidal hypertrophy
- Subperiosteal abscess of the orbit
- Dermoid cyst of the eyelid
- Ocular globe rupture
- Antrochoanal polyp
- Adenoidal hypertrophy
- Sinonasal polyposis
- Adenoid hypertrophy
- Elongated uvula - paediatric
- Tornwaldt cyst
- Arachnoid cyst: extremely large
- Schneiderian papilloma
- Spheno-choanal polyp
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma with perineural spread
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.