Hesselbach triangle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Alex Zheng had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Alex Zheng's current disclosures- Inguinal triangle
- Hesselbach's triangle
The Hesselbach triangle or the inguinal triangle is a triangular area on the inferior interior aspect of the anterior abdominal wall within the groin. It is one of the areas of weakness in the anterior abdominal wall
On this page:
Gross anatomy
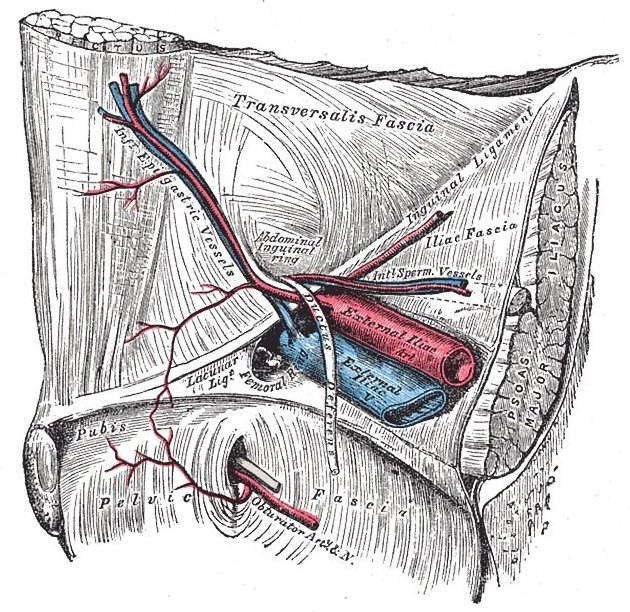
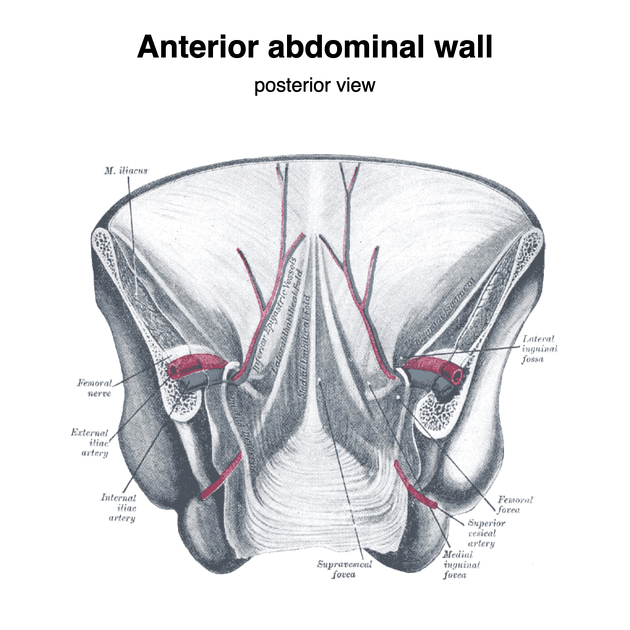
Boundaries
base: inguinal ligament
lateral border: inferior epigastric vessels
medial border: lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle
History and etymology
Named after Franz Kaspar Hesselbach (1759-1816), German anatomist and surgeon 1.
Related pathology
direct inguinal hernias occur medial to the inferior epigastric vessels and through the Hesselbach triangle
indirect inguinal hernias pass lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels into the deep inguinal ring, and are therefore lateral to the Hesselbach triangle
References
- 1. Lassandro F, Iasiello F, Pizza N et al. Abdominal Hernias: Radiological Features. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;3(6):110-7. doi:10.4253/wjge.v3.i6.110 - Pubmed
- 2. Diab. Lexicon Orthopaedic Etymology. (1999) ISBN: 9789057025976 - Google Books
- 3. Prabhakar Rajiah, Biswaranjan Banerjee. Surgical Radiology. (2007) ISBN: 9781905635214 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.