Palatine tonsil
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Kang O, Hacking C, MacManus D, et al. Palatine tonsil. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 15 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-49879
rID:
49879
Article created:
8 Dec 2016,
Owen Kang
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Owen Kang had no recorded disclosures.
View Owen Kang's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures
Revisions:
14 times, by
9 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Synonyms:
- Palatine tonsil
- Tonsils
- Faucial tonsil
- Faucial tonsils
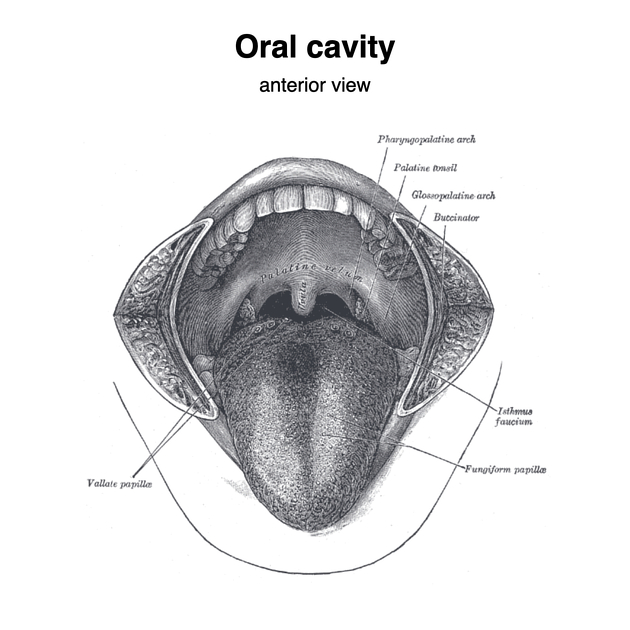
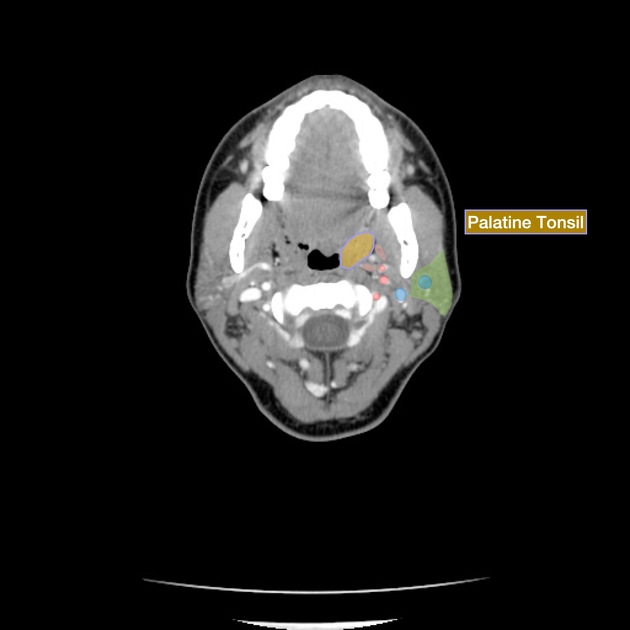
The palatine tonsils, also known as the faucial tonsils or simply the tonsils, are a bilateral collection of lymphoid tissue in the oropharyngeal mucosa. They form part of Waldeyer's ring.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The palatine tonsils are located in the oropharyngeal isthmus (isthmus of fauces). Each is often described to have two borders, two poles, and two surfaces:
- anterior and posterior borders (described in relations below)
- upper and lower poles: extending to the soft palate and dorsum of the tongue respectively
- medial and lateral surfaces (described in relations below)
Relations
- anteriorly: palatoglossal arch
- posteriorly: palatopharyngeal arch
- medially: covered by pharyngeal mucosa
- laterally: tonsillar capsule (thickened pharyngeal submucosa), superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
Arterial supply
- arterial supply is primarily from the tonsillar branch of facial artery, with contributions from the ascending pharyngeal, lingual and ascending palatine arteries
Venous drainage
- venous drainage is via a venous plexus which drains into the pharyngeal plexus and external palatine vein
Lymphatic drainage
- lymph nodes: deep cervical group
- jugulodigastric nodes: inferior to the angle of the mandible
Innervation
- tonsillar branches
Histology
Consists of:
- non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
- incompletely encapsulated
- long-branched tonsillar crypts: e.g. intratonsillar cleft
Related pathology
References
- 1. Sinnatamby CS. Last's Anatomy, Regional and Applied. Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0702033952. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Articles:
- Ascending palatine artery
- Tonsillolith
- Lesser palatine artery
- Organomegaly
- Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
- Greater palatine artery
- Descending palatine artery
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Lesser palatine nerves
- Oropharynx
- Positron emission tomography
- Branchial apparatus
- Pharyngeal mucosal space
- Oral cavity
- Oropharyngeal isthmus
- Waldeyer's ring
- Peritonsillar space
Cases:
- Retropharyngeal lymph nodes
- Croup
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Adenoidal and palatine tonsil enlargement
- Normal palatine tonsils
- Pharyngeal diphtheria
- Pleomorphic adenoma
- Adenotonsillar enlargement
- Sprengel shoulder with omovertebra
- Adenoidal hypertrophy and palatine tonsil enlargement
- Adenoidal and tonsillar hypertrophy
- Adenoidal and palatine tonsil enlargement
- Adenoidal and palatine tonsillar hypertrophy
- Adenoid and palatine tonsil (lateral neck radiograph)
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.