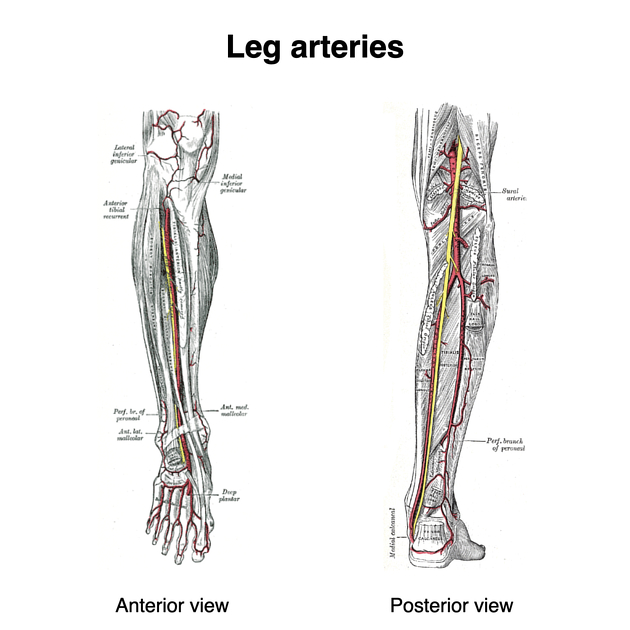
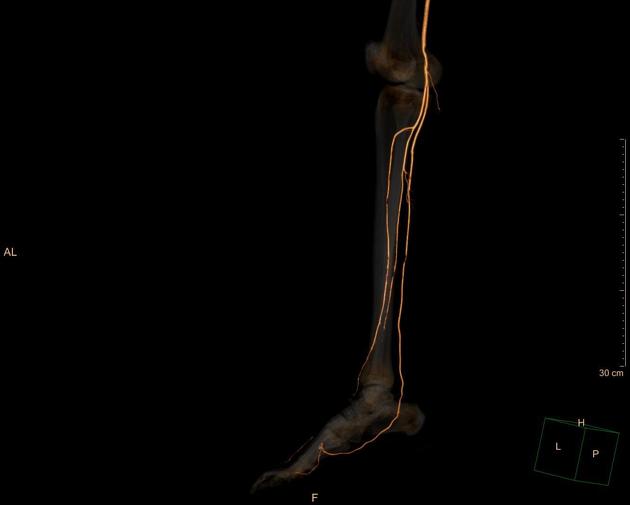
The posterior tibial artery (PTA) is one of the 2 branches of the tibioperoneal trunk in the lower leg and provides oxygenated blood to the posterior compartments of the leg and plantar surface of the foot. It is accompanied by the posterior tibial vein, along its course.
On this page:
Summary
origin: tibioperoneal trunk
-
main branches:
termination: division into medial and lateral plantar arteries within the tarsal tunnel
Origin
The posterior tibial artery originates from the tibioperoneal trunk at the inferior margin of popliteus muscle. It runs inferomedially and runs through the posterior compartment of the leg. It enters the foot by passing posterior to the medial malleolus. Midway from the malleolus to the calcaneal tubercle, it divides into the terminal branches.
Termination
Midway between malleolus and calcaneal tubercle it divides into medial and lateral plantar arteries, within the tarsal tunnel.
Branches and supply
The following branches arise from the posterior tibial artery and supply structures of the posterior leg and sole of the foot:
circumflex fibular artery: supplies proximal fibula
nutrient artery of the tibia: supplies tibia bone
muscular arteries: supply soleus and the deep posterior compartment of the leg
perforating arteries: usually five, supply the skin and fascia of the posterior leg
communicating artery: forms an anastomosis with the fibular artery
medial malleolar artery: anastomoses with the anterior medial malleolar branch of the anterior tibial artery to supply the skin over the medial ankle
calcaneal artery: supplies skin over Achilles tendon, calcaneus, and muscles of medial sole of foot
medial plantar artery (terminal branch): supplies the medial side of the foot, abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis, supplies digital branch to big toe
lateral plantar artery (terminal branch): crosses the sole obliquely and laterally, supplies skin of sole of foot, supplies lateral foot and continues to form the plantar arch, which supplies the metatarsal arteries
Variant anatomy
posterior tibial artery aplasia: the posterior tibial arteries are absent and there is compensatory hyperplasia of the peroneal arteries 3




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.