Sacrotuberous ligament
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mostafa Elfeky had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mostafa Elfeky's current disclosures- Sacrotuberous ligament (STL)
The sacrotuberous ligament (STL) is a stabilizer of the sacroiliac joint and connects the bony pelvis to the vertebral column.
Gross anatomy
The STL has a broad fan-like origin from the sacrum, coccyx, ilium and sacroiliac joint capsule. Its fibers converge to course caudally to insert into the medial ischial tuberosity and additional fibers (known as the falciform ligament) extend to the ischial ramus 1,3.
It forms a boundary between the greater and lesser sciatic foramen. Many of its fibers blend with other musculotendinous structures 1,3:
provides extensive insertion for the gluteus maximus muscle
distal fibers partially blend with the proximal tendon of the long head of biceps femoris
dorsal sacroiliac ligament
The sacrotuberous ligament is pierced by coccygeal branches of the inferior gluteal artery, the perforating cutaneous nerve, and branches of the coccygeal plexus 3.
Related pathology
-
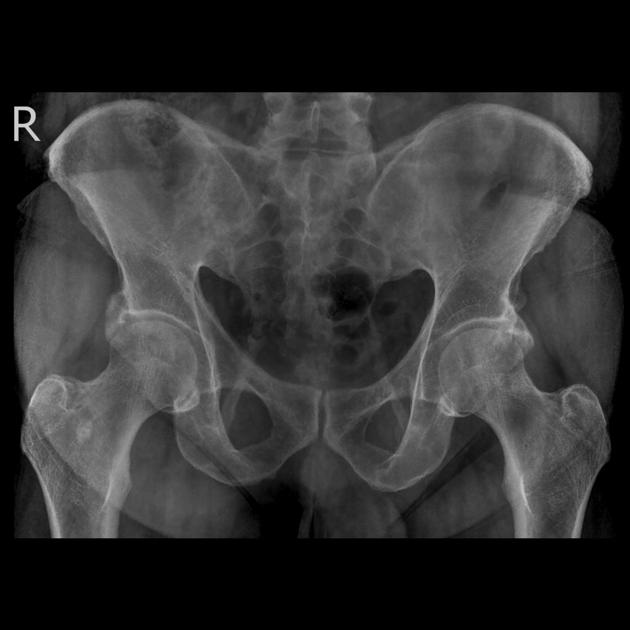
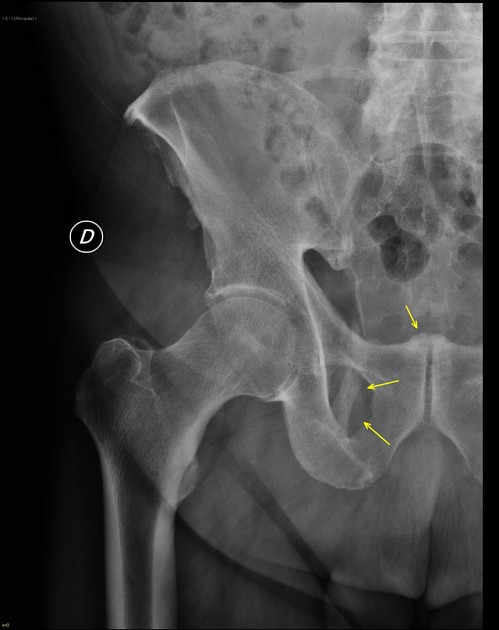
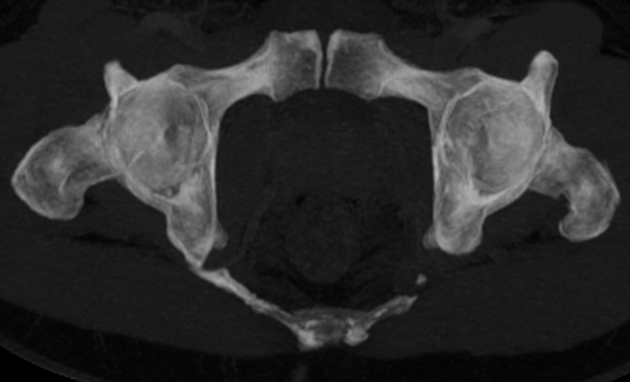
pudendal nerve entrapment syndrome
may be secondary to sacrotuberous ligament calcification (see Case 1)
References
- 1. Bierry G, Simeone FJ, Borg-Stein JP et-al. Sacrotuberous ligament: relationship to normal, torn, and retracted hamstring tendons on MR images. Radiology. 2014;271 (1): 162-71. doi:10.1148/radiol.13130702 - Pubmed citation
- 2. McMINN. Lasts Anatomy Regional and Applied. CHURCHILL LIVINGSTONE. (2003) ISBN:B0084AQDG8. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Mercer, S. R. "Anatomy in practice: the sacrotuberous ligament." NZ Journal of Physiotherapy 33 (2005): 3-92.
- 4. Loukas M, Louis RG, Hallner B et-al. Anatomical and surgical considerations of the sacrotuberous ligament and its relevance in pudendal nerve entrapment syndrome. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006;28 (2): 163-9. doi:10.1007/s00276-006-0082-3 - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Ischioanal fossa
- Bony pelvis
- Coccyx
- Anococcygeal nerve
- Sacrospinous ligament
- Ilium
- Pudendal nerve
- Anal triangle
- Fluorosis
- Posterior sacroiliac ligament
- Sacroiliac joint
- Piriformis muscle
- Ischium
- Lesser sciatic foramen
- Gluteal muscles
- Open book pelvic injury
- Greater sciatic foramen
- Sacrum
- Gluteus maximus muscle
- Lesser sciatic notch
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.