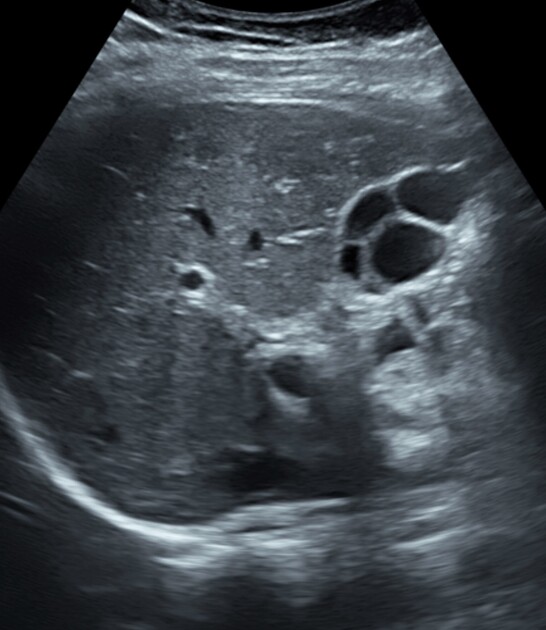
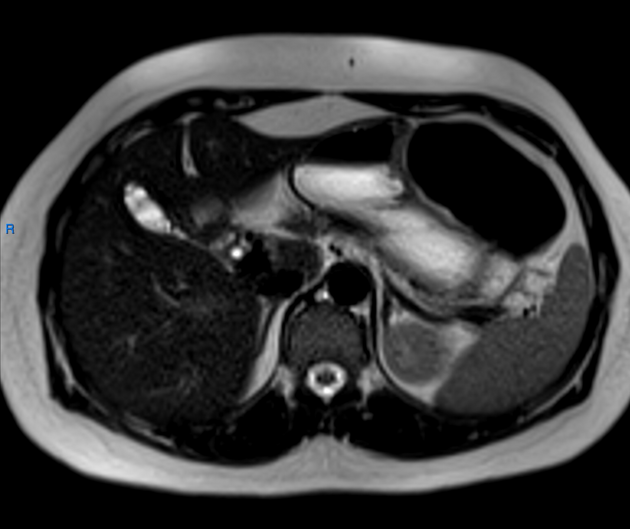
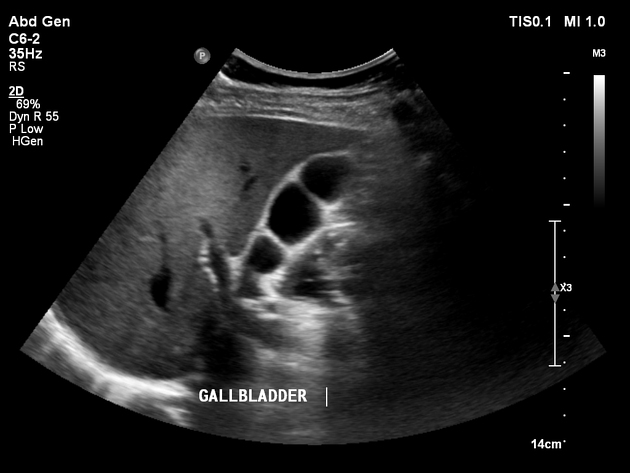
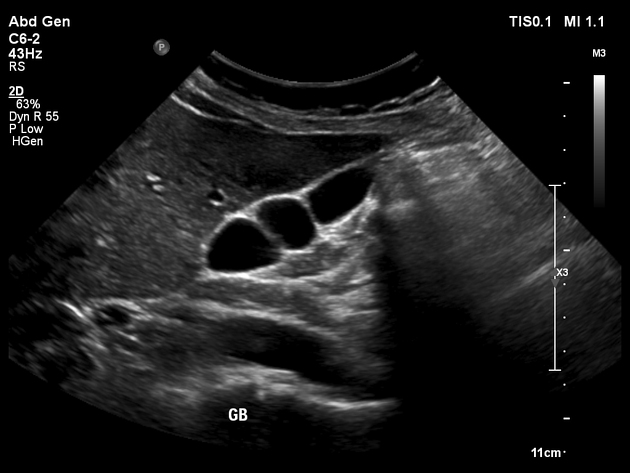
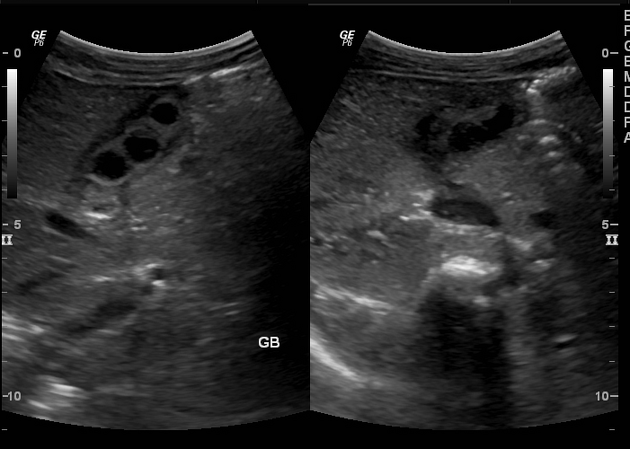
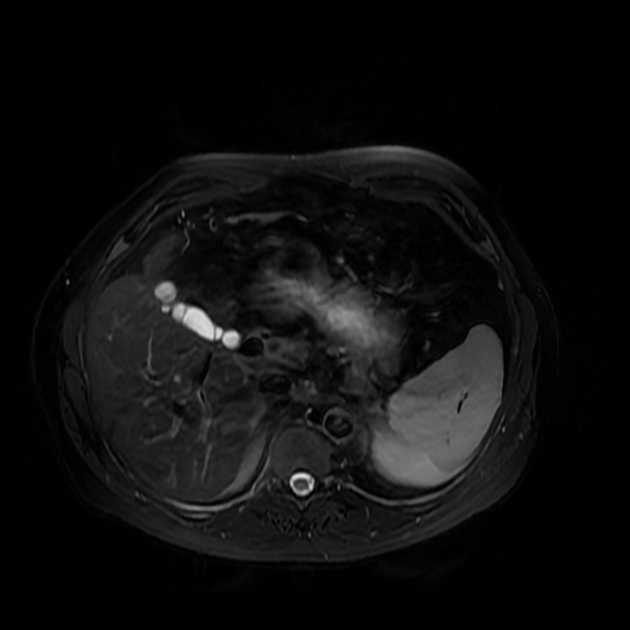
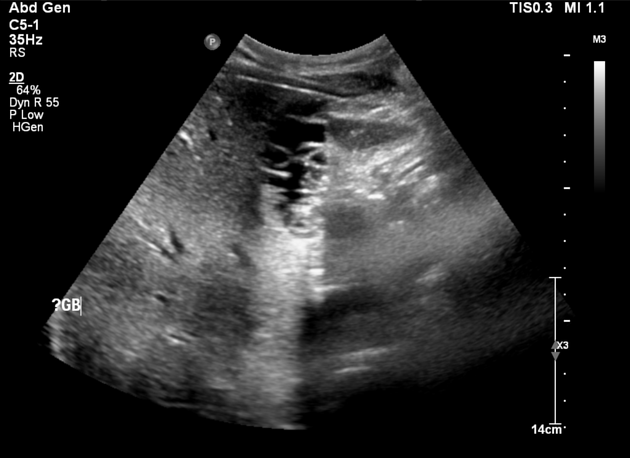
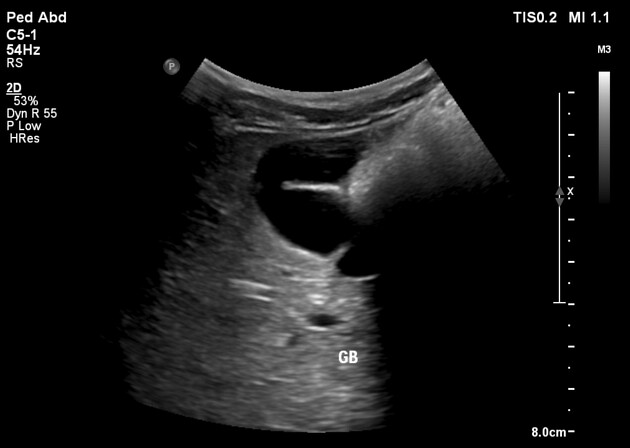
Septate gallbladder
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Hidayatullah Hamidi had no recorded disclosures.
View Hidayatullah Hamidi's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (past)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures- Multiseptated gallbladder
- Honeycomb gallbladder
- Multiseptate gallbladder
Septate gallbladder is a congenital variant where there may be a single septum or multiple septa in the gallbladder splitting its lumen into several parts.
On this page:
Terminology
When there are multiple septa subdividing the gallbladder the condition is also known as multiseptate or honeycomb gallbladder. This is considered to be a separate condition to a single septate gallbladder by some 4.
Septate gallbladder is an independent entity from the junctional fold, where the gallbladder wall folds on itself. Junctional folds are usually thick and incomplete while septa are thin and may be complete.
Epidemiology
Multiseptate gallbladder is rare with only 150 cases in the global literature up to 2021. The condition has presented at all ages from neonate to elderly, most commonly in young adults 4.
Clinical presentation
When there is a single septum the condition is generally asymptomatic and incidentally detected on imaging.
When the gallbladder is multiseptate, which is rarer, the condition is symptomatic in about 75% cases, the commonest being right upper quadrant abdominal pain; other symptoms include nausea, vomiting and jaundice 4.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Pathology
Etiology
In most cases septated gallbladder seems to be congenital due to abnormal embryogenesis of the developing gallbladder ref. However rare acquired cases have been seen due to trauma and inflammation 4.
Macroscopic appearance
There may be communication between the septated parts of gallbladder through small pores ref.
Markers
Liver function tests (LFTs) are normal in the majority of cases 4. A minority of cases show increased alkaline phosphatase, transaminases, bilirubin and/or gamma glutamyl transferase. Inflammatory markers are usually normal.
Radiographic features
Septated gallbladders are usually diagnosed with ultrasound 4.
History and etymology
The first article about multiseptated gallbladder was in German by A Knetsch in 1952 4,5. In 1963 the South African-American radiologist Morris Simon (1926-2005) 6 published a much fuller description which included detailed findings on oral cholecystography which was the gold standard method to evaluate the gallbladder at the time 3,4. Morris Simon was a chest radiologist at Beth Israel Hospital in Boston
References
- 1. Karaca, Turgut, Yoldas, Omer, Bilgin, Bulent Caglar, Bilgin, Selma, Evcik, Ender, Ozen, Saadet. Diagnosis and Treatment of Multiseptate Gallbladder with Recurrent Abdominal Pain. (2011) Case Reports in Medicine. doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/162853
- 2. Al-Salem A, Issa H, Naserullah Z. Septate Gallbladder: A Report of Two Cases. Ann Saudi Med. 2002;22(5-6):351-3. doi:10.5144/0256-4947.2002.351 - Pubmed
- 3. Simon M & Tandon B. Multiseptate Gallbladder. Radiology. 1963;80(1):84-6. doi:10.1148/80.1.84 - Pubmed
- 4. Terkawi R, Qutob D, Hendaus M. Understanding Multiseptated Gallbladder: A Systematic Analysis with a Case Report. JGH Open. 2021;5(9):988-96. doi:10.1002/jgh3.12621 - Pubmed
- 5. Knetsch A. [Subdivided Gallbladders]. Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr. 1952;77(5):587-9. - Pubmed
- 6. Linton O. Morris Simon. Journal of the American College of Radiology. 2011;8(6):451. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2011.02.006 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Multiseptate gallbladder
- Septate gallbladder
- Septate gallbladder
- Boomerang gallbladder
- Gallbladder folds
- Gallbladder hydrops
- Phrygian cap
- Gallbladder folds
- Septate gallbladder
- Septate gallbladder
- Multiseptated gallbladder
- Mucinous adenocarcinoma in gallbladder with fundic duplication
- Septate gallbladder
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- benign epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumors
- primary malignant epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumors
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumors
- hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumors
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumors
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic hemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumor
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumor
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumor
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumors
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumors
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.