Transverse mesocolon
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Roland Zac White had no recorded disclosures.
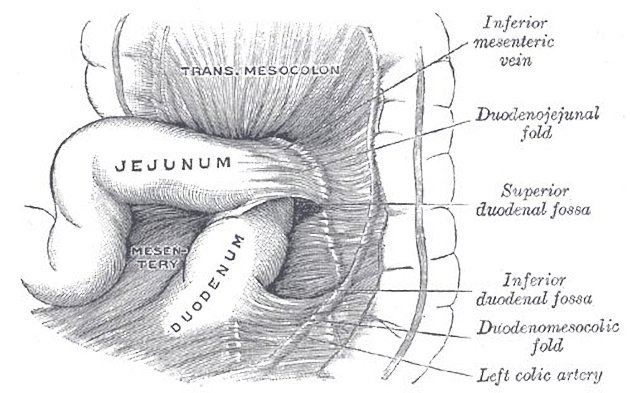
View Roland Zac White's current disclosuresThe transverse mesocolon is a broad, meso-fold of peritoneum, which connects the transverse colon to the posterior wall of the abdomen.
It is continuous with the two posterior layers of the greater omentum, which, after separating to surround the transverse colon, join behind it, and are continued backward to the vertebral column, where they diverge in front of the anterior border of the pancreas. This fold contains between its layers the vessels which supply the transverse colon.
The root of the transverse mesocolon extends across the anterior infra-ampullary segment of the descending duodenum (2nd part), the head of the pancreas and continues along the lower edge of the body and tail of the pancreas, and divides the peritoneal cavity into the supracolic and infracolic spaces.
Transverse mesocolon is a derivative of dorsal mesentery in the embryo and contains:
- transverse colon (in the free margin)
- middle colic vessels and their branches
- lymphatics and lymph nodes
- autonomic nerve fibers
- extraperitoneal fatty tissue
References
- 1. Standring S (editor). Gray's Anatomy (39th edition). Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0443066841. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Duodenojejunal flexure
- Inframesocolic space
- Internal hernia due to gastric bypass surgery
- Middle colic artery
- Left inframesocolic space
- Left colic artery
- Anterior right subhepatic space
- Posterior right subhepatic space
- Mesentery
- Anterior pararenal space
- Colon cut-off sign
- Right subhepatic space
- Root of the mesentery
- Abdominal hernia
- Supramesocolic space
- Transverse colon
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.