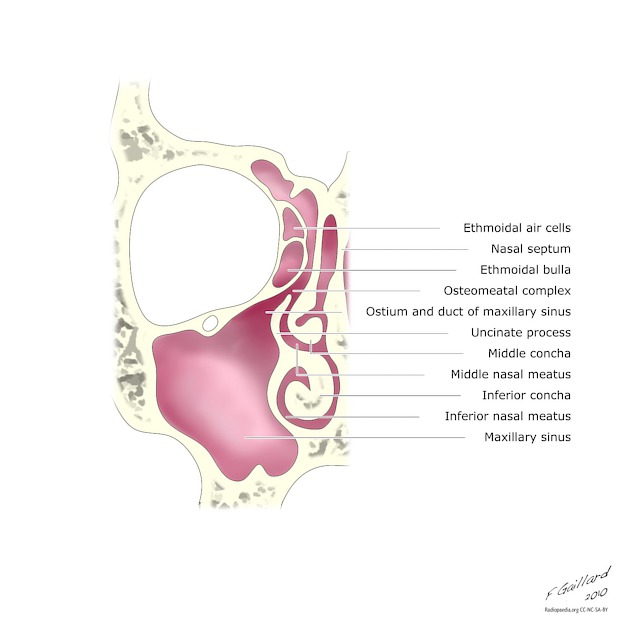
Uncinate process
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Maxime St-Amant had no recorded disclosures.
View Maxime St-Amant's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Uncinate apophysis
- Uncinate process of ethmoid bone
The uncinate process of the ethmoid bone is a thin hook-like osseous structure of the wall of the lateral nasal cavity. It is a component of the ostiomeatal complex.
Gross anatomy
Together with the ethmoid bulla, it forms the boundaries of the hiatus semilunaris and ethmoid infundibulum.
The course of the free edge of the uncinate process is variable. Its tip is usually attached to the lateral nasal wall (most common) or to the lateral surface of the middle turbinate. It can also attach more laterally to the lamina papyracea, agger nasi cell or ethmoid roof. Attachment of its tip is important as it dictates the drainage pathway of the frontal recess:
when attached to the nasal wall or middle turbinate, it makes up the medial wall of the frontal recess, redirecting drainage to the ethmoid infundibulum prior to the passage into the middle meatus
when attached more laterally, the uncinate process makes up the lateral wall of the frontal recess, redirecting drainage directly to the middle meatus, bypassing the ethmoid infundibulum which then forms a blind-ending recess known as the recessus terminalis
Practical points
the uncinate process is usually removed during functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) – uncinectomy
a retained uncinate process is a common cause of failed frontal FESS
it is important to report attachment of its tip as forceful traction during surgery may damage the ethmoid roof
References
- 1. Ballenger's Otorhinolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery, 17th Edition. (2008) ISBN: 9781550093377 - Google Books
- 2. Aldo C. Stamm, Wolfgang Draf. Micro-Endoscopic Surgery of the Paranasal Sinuses and the Skull Base. (2012) ISBN: 9783642571534 - Google Books
- 3. Matti Anniko, Manuel Bernal-Sprekelsen, Victor Bonkowsky et al. Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery. (2010) ISBN: 9783540689409 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Ostiomeatal complex
- Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)
- Chronic sinusitis
- Pancreaticoduodenal veins
- Superior mesenteric vein
- Point-of-care ultrasound (curriculum)
- Horseshoe pancreas
- Ethmoid infundibulum
- Silent sinus syndrome
- Recessus terminalis
- Frontal recess
- Ostiomeatal complex parts (mnemonic)
- Hiatus semilunaris
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.