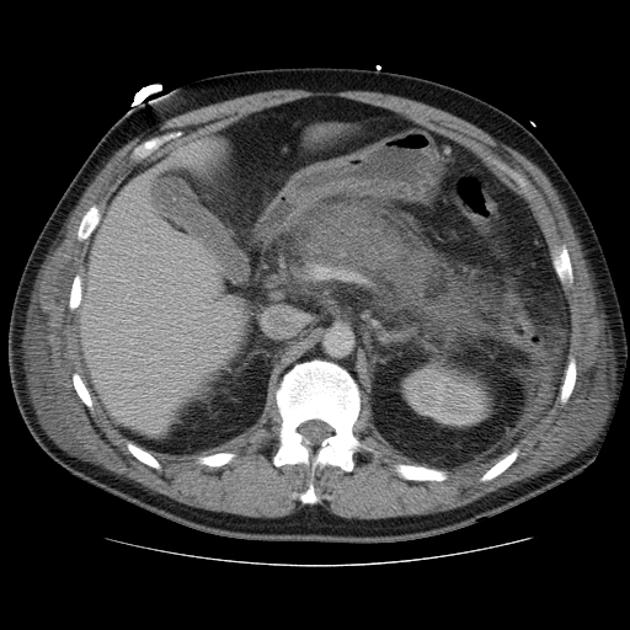
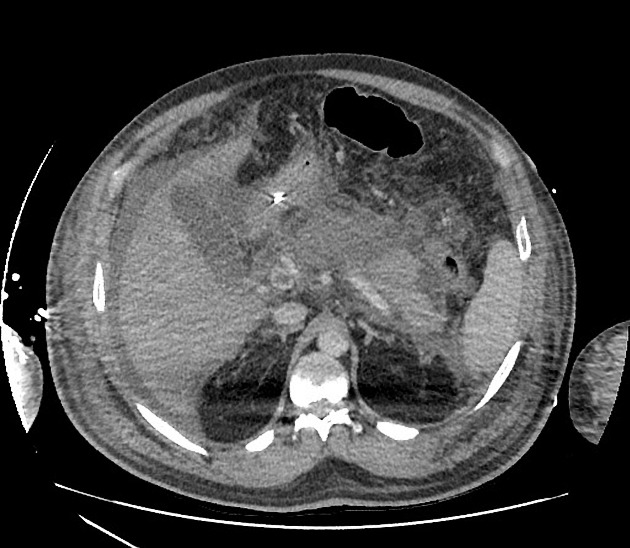
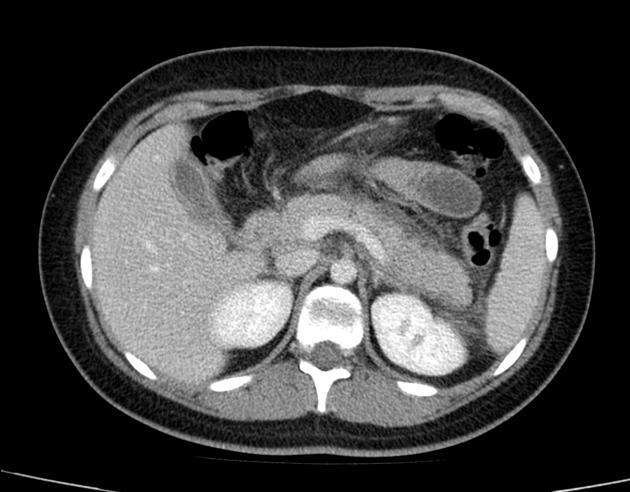
Acute necrotic collection
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Ryan Thibodeau had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Ryan Thibodeau's current disclosures- Acute necrotic collections
- Acute necrotic collections (ANCs)
- Acute necrotic collection (ANC)
- Acute necrotic collection
Acute necrotic collections (ANCs) are an early, local complication of necrotizing pancreatitis.
On this page:
Terminology
The following are the latest terms according to the updated Atlanta classification to describe fluid collections associated with acute pancreatitis 1,2:
-
fluid collections in interstitial edematous pancreatitis
acute peripancreatic fluid collections (APFC): in the first 4 weeks: non-encapsulated peripancreatic fluid collections
pseudocysts: develop after 4 weeks; encapsulated peripancreatic or remote fluid collections
-
fluid collections in necrotizing pancreatitis
acute necrotic collections (ANCs): in the first 4 weeks; non-encapsulated heterogeneous non-liquefied material
walled-off necrosis (WON or WOPN): develop after 4 weeks; encapsulated heterogeneous non-liquefied material
Pathology
Acute necrotic collections develop within the first four weeks and contain a variable amount of fluid/non-liquid necrotic material. They may be pancreatic or peripancreatic in location and can be sterile or infected.
Radiographic features
CT
On contrast-enhanced CT the following features are seen:
-
heterogeneous, non-liquid density collection within the pancreas and/or peripancreatic tissues
fat in the collection allows the diagnosis of an ANC even on nonenhanced CT 4
no defined capsule
no peripheral enhancement
Differential diagnosis
acute peripancreatic fluid collections (APFC): within the first week, differentiation between acute necrotic collections (ANC) and APFC may prove impossible
References
- 1. Thoeni RF. The revised Atlanta classification of acute pancreatitis: its importance for the radiologist and its effect on treatment. Radiology. 2012;262 (3): 751-64. doi:10.1148/radiol.11110947 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C et-al. Classification of acute pancreatitis-2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2012;62 (1): 102-11. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779 - Pubmed citation
- 3. (Ed.) Choi BI. Radiology Illustrated: Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Radiology. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. ISBN:B00HYS9FSE. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Foster B, Jensen K, Bakis G, Shaaban A, Coakley F. Revised Atlanta Classification for Acute Pancreatitis: A Pictorial Essay. Radiographics. 2016;36(3):675-87. doi:10.1148/rg.2016150097 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- benign epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumors
- primary malignant epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumors
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumors
- hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumors
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumors
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic hemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumor
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumor
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumor
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumors
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumors
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.