Levator ani muscle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Elnasif Ahmad had no recorded disclosures.
View Elnasif Ahmad's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Pelvic floor
- Muscular pelvic diaphragm
- Levator ani muscle complex
- Levator ani muscles
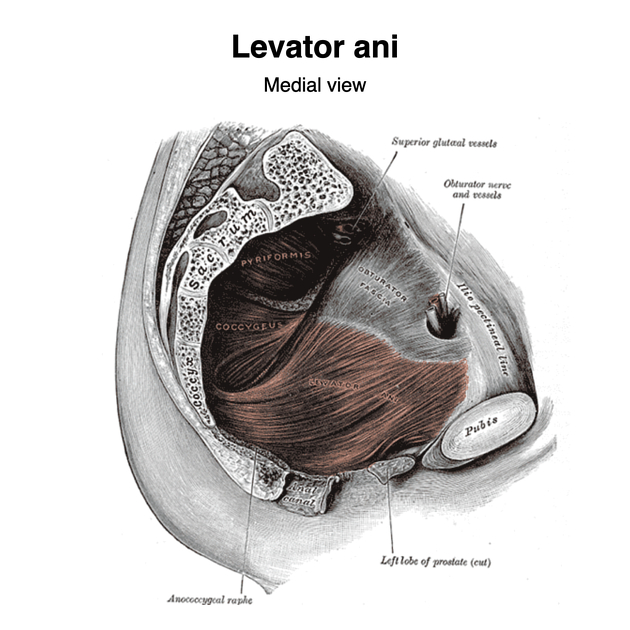
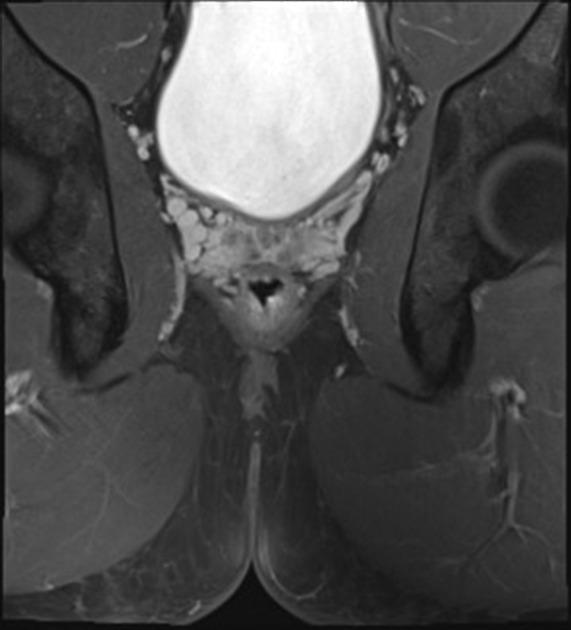
The levator ani muscle, also known as the muscular pelvic diaphragm, is the musculotendinous sheet that forms the majority of the pelvic floor, supports the pelvic viscera, and aids in urinary and fecal evacuation as well as maintaining continence.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The levator ani has three main components, each of which is paired 1,2,5:
-
pubococcygeus (pubovisceral) muscle
subparts: puboperineal, pubovaginal, puboanal muscles
iliococcygeus muscle
puborectalis muscle
The pubococcygeus muscle runs posteriorly from the body of the pubis and anterior part of the tendinous arch (part of the obturator fascia) to fuse in the midline at the perineal body and musculature of the prostate/vagina 7.
The iliococcygeus muscle runs from the posterior part of the tendinous arch to join itself in the midline, forming the anococcygeal raphe which extends from the anal verge to the tip of the coccyx. Anteriorly and medially, it also fuses with the pubococcygeus 7.
Puborectalis takes attachment from the pelvic surfaces of both ischiopubic rami, anterolaterally. It passes posterior to the rectum to form a muscular sling.
The coccygeus muscle (also known as ischiococcygeus) although a muscle of the pelvic floor, is not formally considered part of the levator ani muscle 3. It is a triangular muscle with its base attaching to the lateral aspect of the inferior sacrum and coccyx and apex attached to the ischial spine. It flexes the coccyx anteriorly and partially fuses with the sacrospinous ligament.
The levator ani forms a U-shape and is deficient medially and anteriorly, an area referred to as the urogenital hiatus 6. This region is instead supported by the deep perineal pouch and perineal membrane below 6.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Arterial supply
the three muscles are supplied by the inferior rectal and internal pudendal arteries
Innervation
pelvic surface: branches of S3, S4
perineal surface: branches of the pudendal nerve
Variant anatomy
thinning or aplasia of one or both sides is common (~50%) 4
References
- 1. Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinically oriented anatomy. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. ISBN:0781775256. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Gray's Anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0443066841. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Anal Fistula. Springer New York. ISBN:B00GXY468Y. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Loubeyre P, Copercini M, Petignat P et-al. Levator ani muscle complex: anatomic findings in nulliparous patients at thin-section MR imaging with double opacification. Radiology. 2012;262 (2): 538-43. doi:10.1148/radiol.11111014 - Pubmed citation
- 5. Kearney R, Sawhney R, DeLancey JO. Levator ani muscle anatomy evaluated by origin-insertion pairs. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;104 (1): 168-73. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000128906.61529.6b - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 6. Richard Drake, A. Wayne Vogl, Adam W. M. Mitchell. Gray's Anatomy for Students E-Book. (2019) ISBN: 9780323611053 - Google Books
- 7. William Henry Hollinshead, Cornelius Rosse. Textbook of Anatomy. (1985) ISBN: 9780061412639 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Nerve to piriformis
- Bladder neuroanatomy
- Coccyx
- Perineal branch of S4
- Pubococcygeal line
- Rectal cancer
- Perineal hernia
- Pararectal space
- Inferior pubic ramus
- Pubis
- Presacral space
- Sacrum
- Supravesical hernia
- Rectal prolapse
- Inferior rectal nerve
- Female urethra
- Cystocele
- Levator ani muscle
- Urinary bladder
- Inferior hypogastric plexus
- High extrasphincteric peri-anal fistula with supralevator abscess
- MRI defecography with multi-compartment prolapse
- Pelvic floor prolapse - cystocele
- Focused assessment with sonography for trauma (negative eFAST)
- Pelvic floor encysted collection
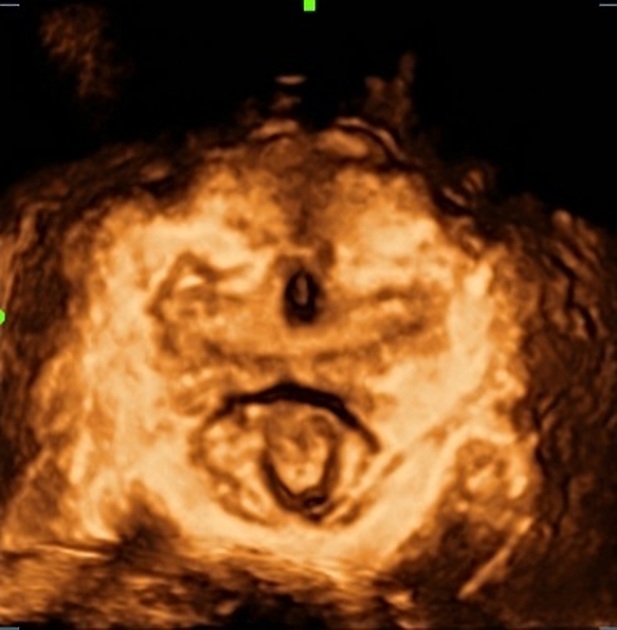
- Levator ani imaging (3D transperineal ultrasound)
- Urethral diverticulum (transperineal ultrasound)
- Female perineal muscles (Gray's illustration)
- Male perineal muscles (Gray's illustration)
- Levator ani (Gray's illustration)
- Angiomyxoma
- Primary vaginal carcinoma
- Peritoneocele, enterocele and anismus
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.