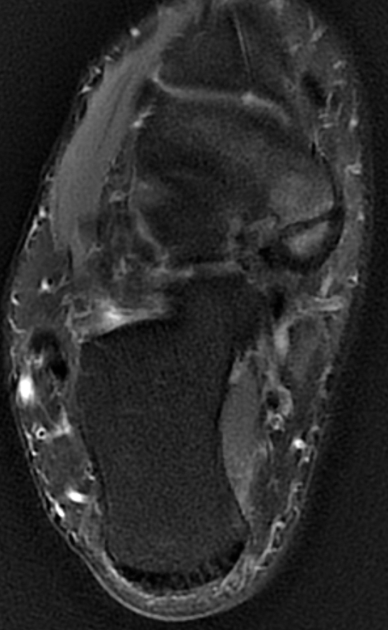
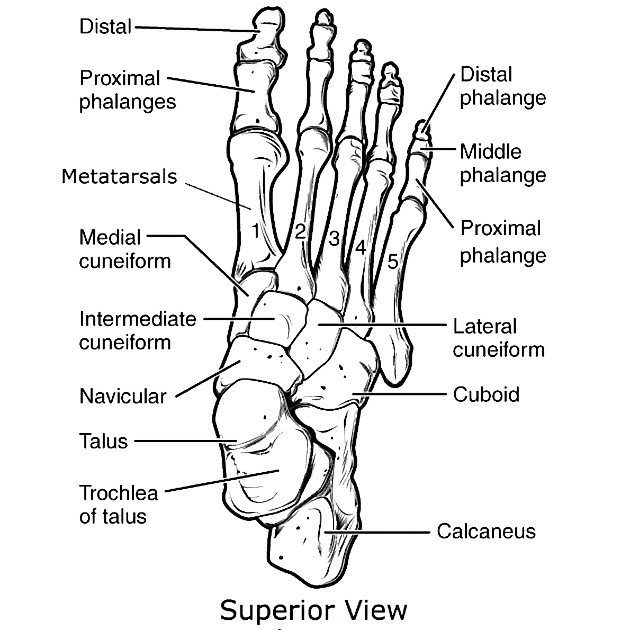
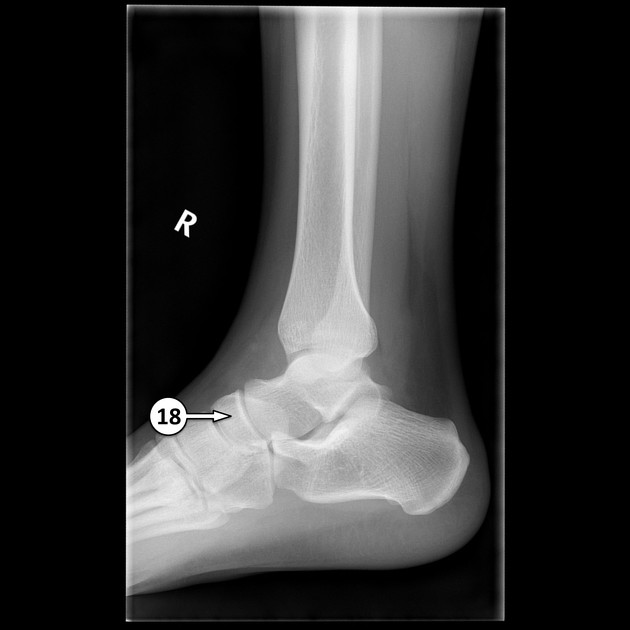
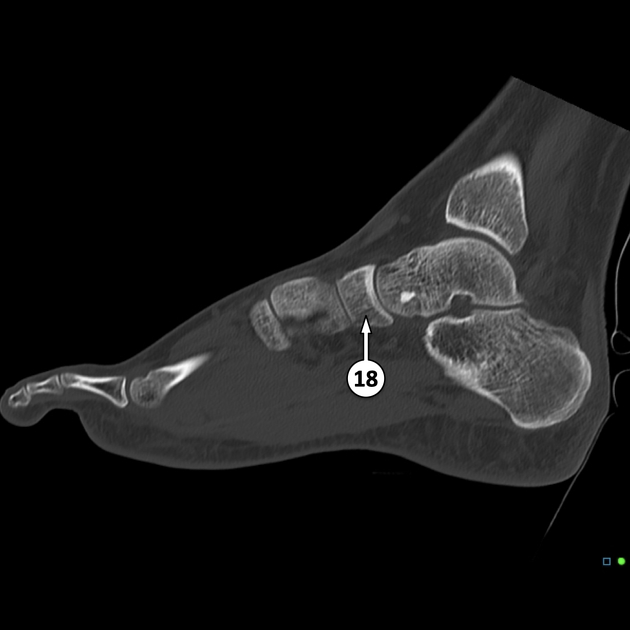
The navicular bone is found in the midfoot and is one of the tarsal bones. Its structure resembles that of a boat. It is the last bone of the foot to ossify fully 1.
On this page:
Summary
location: lies within the medial aspect of the midfoot
relations: the talus bone, cuboid bone and the three cuneiform bones
arterial supply: branches of the dorsalis pedis, posterior tibial and medial plantar arteries 4
Gross anatomy
Articulations
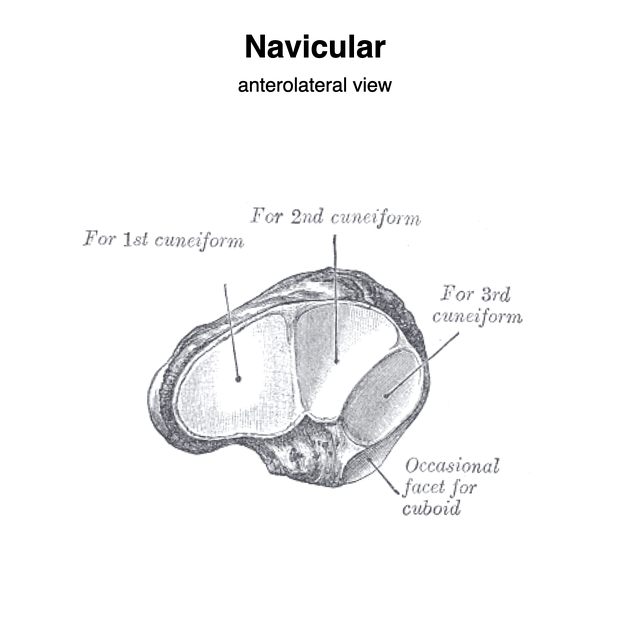
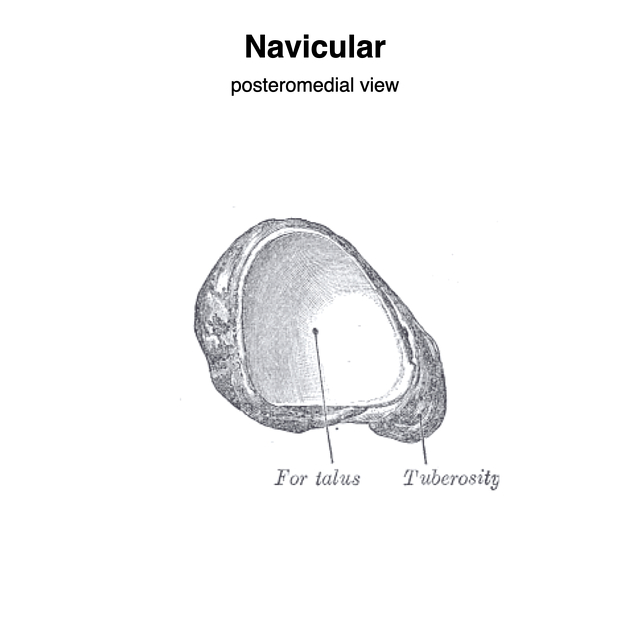
The navicular bone articulates proximally with the head of the talus bone, laterally with the cuboid bone and distally to the lateral, intermediate and medial cuneiform bones 2.
Attachments
Musculotendinous
The tibialis posterior tendon inserts into the medial side of the navicular bone at the navicular tuberosity 2.
Ligamentous
Dorsal cuneonavicular ligament and plantar cuneonavicular ligament are two ligaments that join each cuneiform bone to the navicular.
Plantar calcaneonavicular (part of the spring ligament) attaches to the lateral aspect of the groove of the navicular tuberosity.
Talonavicular ligament connects the neck of talus to the dorsal aspect of the navicular
Cuboidonavicular ligament extends to the cuboid and navicular along the dorsal aspect
Arterial supply
A branch of dorsalis pedis artery gives off three to five smaller branches which supply the navicular from the medial side.
On the lateral aspect of the bone, small branches arise from the posterior tibial artery. Branches of the medial plantar artery also supply the plantar surface of the bone 4. In the central navicular there is a region of watershed blood supply which predisposes the bone to stress fractures.
Variant anatomy
Accessory ossicle: Present on the medial aspect of the navicular, known as an accessory navicular as result of a separate ossification center.
Bipartite (rare)
Development
Ossification
The navicular derives from a single ossification center (in the absence of anatomical variation) and appears approximately at 3 years of age. It is thought to be one of the later bones in the midfoot to ossify. In girls, this may be between between 18-24 months, and in boys between 30-36 months 4.
History and etymology
Historically, the term navicular was also confusingly used to refer to the scaphoid bone in the hand. This is not that surprising as navicular and scaphoid both mean boat-shaped, the former derived from Latin and the latter from Greek. Hence the classical anatomist would talk of the 'os naviculare pedis' or 'os naviculare manus' for the navicular bones of the foot and hand respectively.
To avoid confusion going forwards, it was decided by anatomists in 1955 to use navicular solely for the foot and scaphoid for the hand, as detailed in the Parisiensia Nomina Anatomica, one of the forerunners of the Terminologia Anatomica. Therefore 'os naviculare pedis' was shortened to simply 'os naviculare' 5.
More rarely, has been the use of the word scaphoid to refer to the navicular, usually as part of the term "tarsal scaphoid", more commonly in non-English articles 6.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.