Anterior commissure
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Azza Elgendy had no recorded disclosures.
View Azza Elgendy's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosuresThe anterior commissure (AC) is a transversely oriented commissural white matter tract that connects the two cerebral hemispheres along the midline. It is a very important anatomical landmark that connects different parts of the limbic system on both sides and plays a role in the interhemispheric transfer of visual, auditory, and olfactory information between temporal lobes 1. However, the role of the anterior commissure is not yet well understood.
Gross anatomy
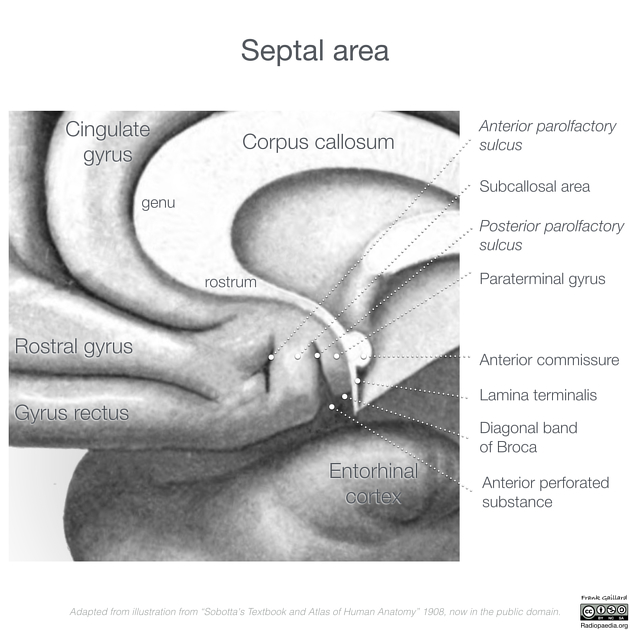
The anterior commissure corresponds to a white matter tract almost completely surrounded by grey matter (the canal of Gratiolet) that crosses the midline just ventral to the supraoptic recess of the third ventricle and the columns of the fornix.
The anterior commissure is composed of two fascicles (or limbs or crura): an anterior fascicle and posterior fascicle 3. The anterior fascicle is smaller and passes from midline anteriorly to the orbitofrontal cortex 3. The posterior fascicle passes from midline posterolaterally between the putamen and globus pallidus, before then dividing into temporal and parieto-occipital divisions 3. The temporal division of the posterior fascicle ends in the amygdaloid nucleus of the temporal pole bilaterally 2.
See also
References
- 1. Wilde E, Bigler E, Haider J et al. Vulnerability of the Anterior Commissure in Moderate to Severe Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury. J Child Neurol. 2006;21(9):769-76. doi:10.1177/08830738060210090201 - Pubmed
- 2. Peltier J, Verclytte S, Delmaire C, Pruvo J, Godefroy O, Le Gars D. Microsurgical Anatomy of the Temporal Stem: Clinical Relevance and Correlations with Diffusion Tensor Imaging Fiber Tracking. J Neurosurg. 2010;112(5):1033-8. doi:10.3171/2009.6.JNS08132 - Pubmed
- 3. Baudo M, Colombo E, Pérez M et al. Three-Dimensional Anatomy of the Anterior Commissure: A Tractography and Anatomical Study. World Neurosurg. 2022;159:e365-74. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2021.12.059 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Commissural fibres of the brain
- Basal nucleus of Meynert
- Dysgenesis of the corpus callosum
- Sagittal stratum
- Optic chiasm
- Canal of Gratiolet
- Third ventricle
- Telencephalon
- Commissure (disambiguation)
- Cerebrum
- Hypothalamus
- Supplementary motor area
- Anterior commissure of the larynx
- Cavum septum pellucidum
- Fornix (brain)
- Rhombencephalosynapsis
- Axial plane for imaging of the brain
- Anterior commissure - posterior commissure line
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (A)
- Lamina terminalis
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.