Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mohammad Taghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mohammad Taghi Niknejad's current disclosures- Pancreatic mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinomas of pancreas
- Pancreatic mucinous cystadenocarcinomas
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma (pancreas)
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of pancreas
Mucinous cystadenocarcinomas of the pancreas are a type of pancreatic mucinous tumor. It is considered the more malignant counterpart of a mucinous cystadenoma of the pancreas.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Like the more benign mucinous cystadenomas, these are found almost exclusively in females 4.
Radiographic features
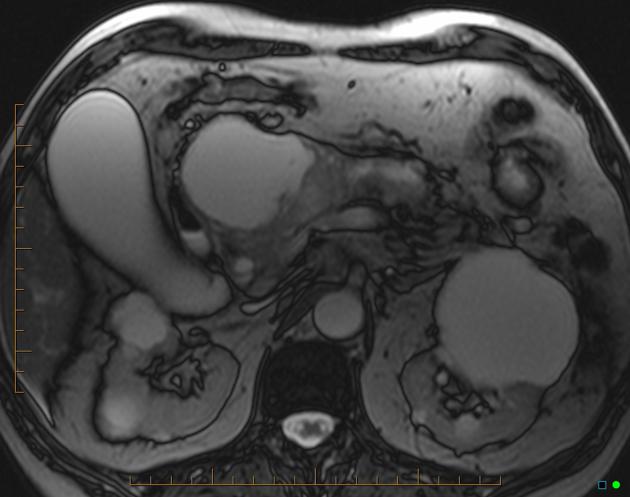
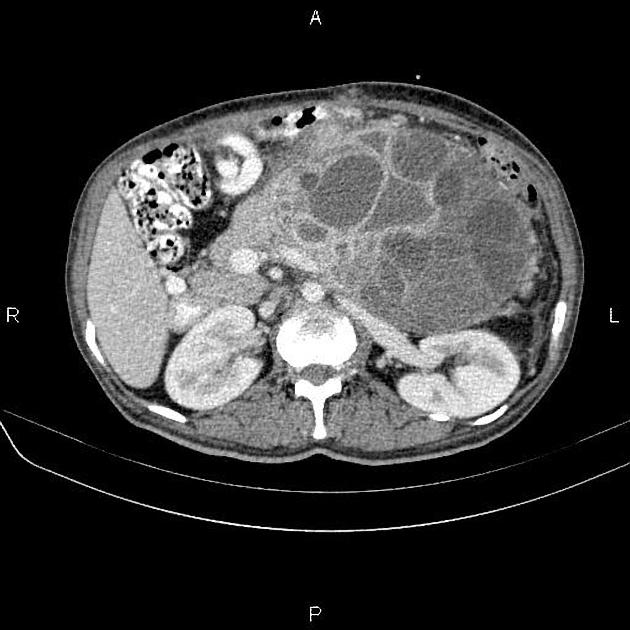
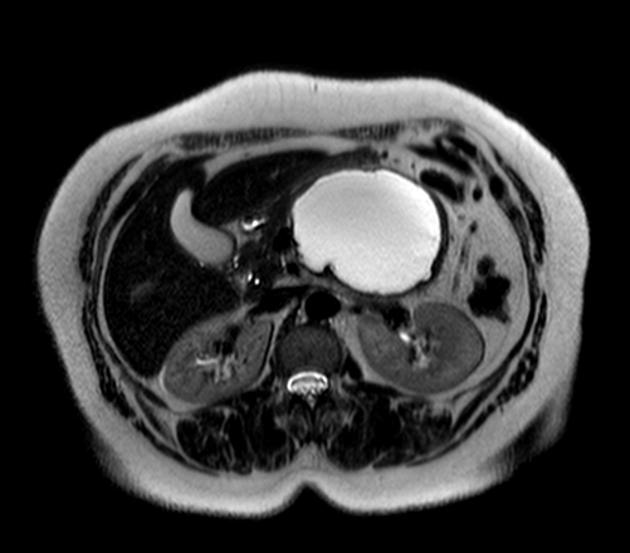
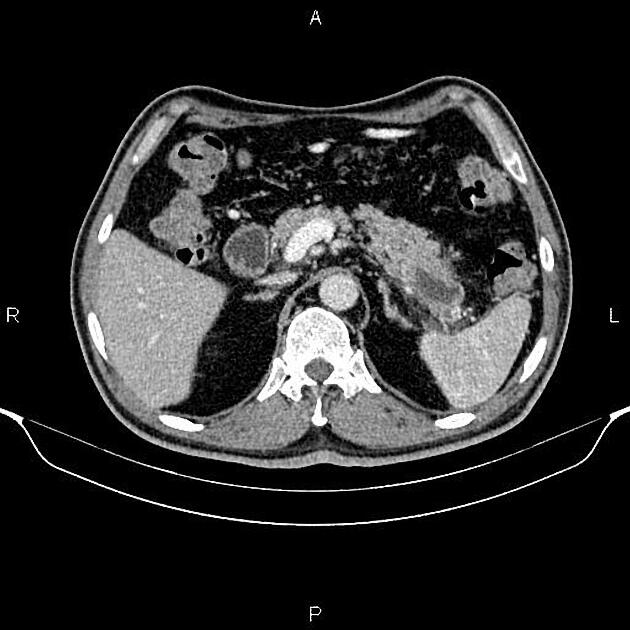
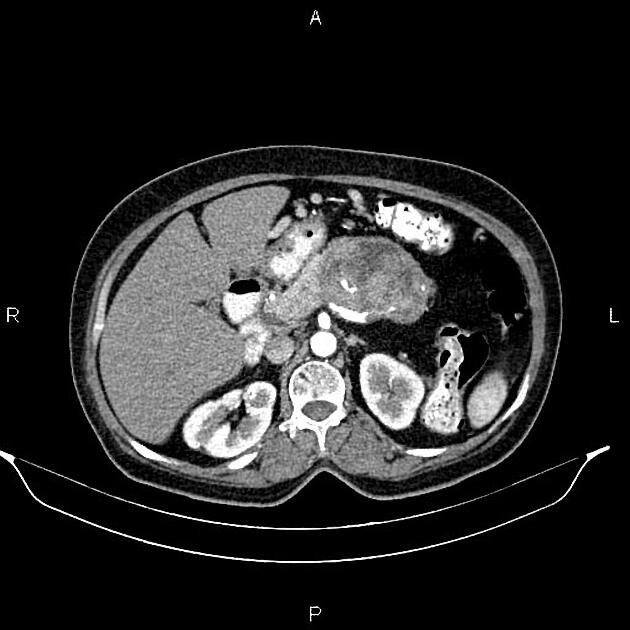
It is typically seen as a cystic pancreatic lesion with less numerous cysts and larger in size (with an average diameter of ~10-12 cm) than typically observed with serous cystadenomas/cystadenocarcinomas. Its external surface is often smooth, composed of unilocular or multilocular large (>2-4 cm) cysts with a thicker wall 5.
CT
On CT, they appear round to ovoid, externally smooth, near-water-density cystic lesions. Amorphous calcifications, septations and solid excrescences may be seen. Both mucinous cystadenomas and cystadenocarcinomas do not have central scars.
MRI
Signal characteristics of the cyst(s) can vary depending on the content. Mucin components exhibit high signal on T1 while calcific components are low signal on both T1 and T2 10. Pure cystic components show low signal on T1 and high signal on T2.
Treatment and prognosis
While surgical resection is the standard mode of treatment, even the overtly malignant mucinous cystadenocarcinomas carry a far better prognosis than solid ductal adenocarcinomas 1.
Differential diagnosis
On ultrasound or CT, consider:
serous cystadenoma of the pancreas: can sometimes be indistinguishable on imaging 3
See also
References
- 1. Curry CA, Eng J, Horton KM et-al. CT of primary cystic pancreatic neoplasms: can CT be used for patient triage and treatment? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;175 (1): 99-103. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Inceoglu R, Dosluoglu H, Okboy N et-al. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas: an uncommon presentation with anaemia and upper gastrointestinal bleeding. J R Soc Med. 1991;84 (3): 171-2. - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 3. Itai Y, Moss AA, Ohtomo K. Computed tomography of cystadenoma and cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Radiology. 1982;145 (2): 419-25. Radiology (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 4. Buetow PC, Rao P, Thompson LD. From the Archives of the AFIP. Mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 18 (2): 433-49. Radiographics (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 5. Kalra MK, Maher MM, Mueller PR et-al. State-of-the-art imaging of pancreatic neoplasms. Br J Radiol. 2003;76 (912): 857-65. doi:10.1259/bjr/16642775 - Pubmed citation
- 6. Thompson LD, Becker RC, Przygodzki RM et-al. Mucinous cystic neoplasm (mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of low-grade malignant potential) of the pancreas: a clinicopathologic study of 130 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1999;23 (1): 1-16. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. (link) - Pubmed citation
- 7. Ros PR, Mortele KJ. CT and MRI of the abdomen and pelvis, a teaching file. Philadelphia, PA : Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, c2007. (2006) ISBN:0781772370. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- benign epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumors
- primary malignant epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumors
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumors
- hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumors
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumors
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic hemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumor
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumor
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumor
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumors
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumors
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.