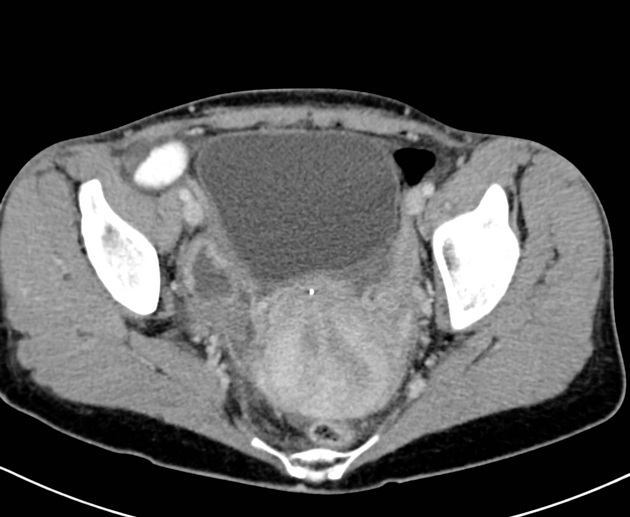
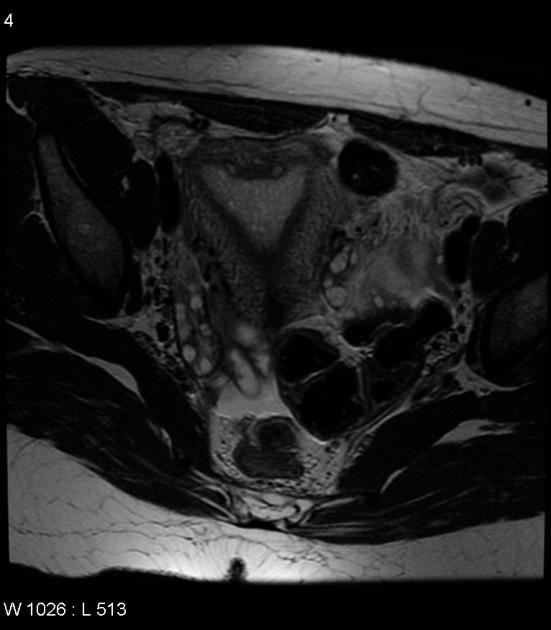
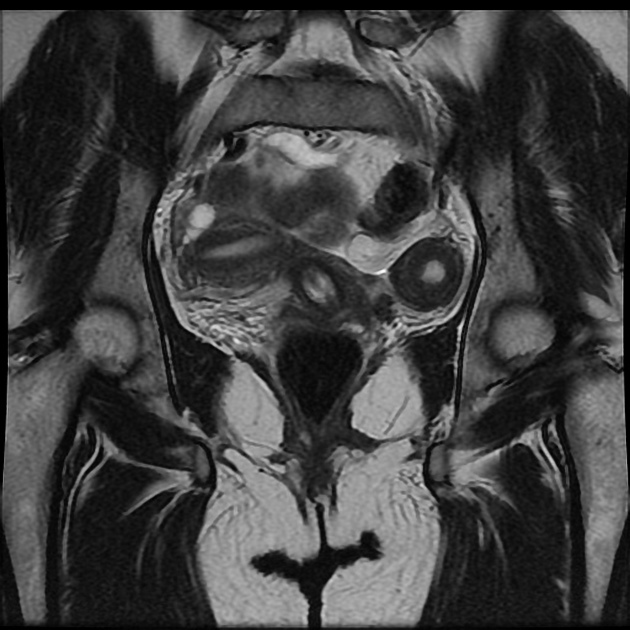
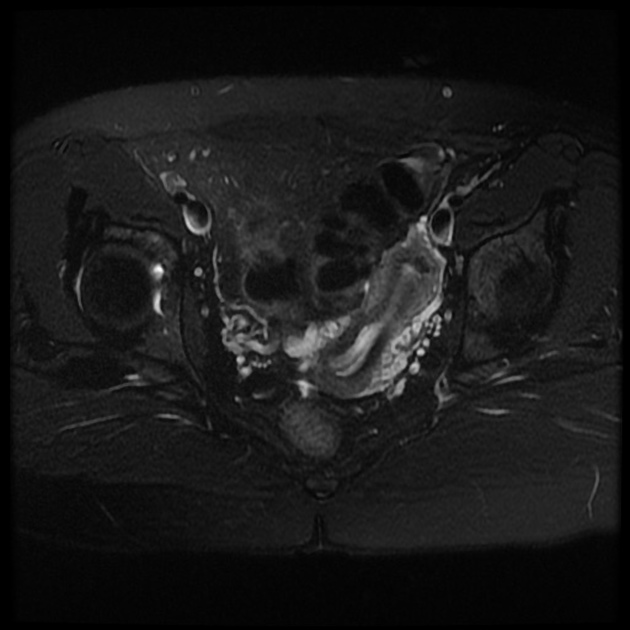
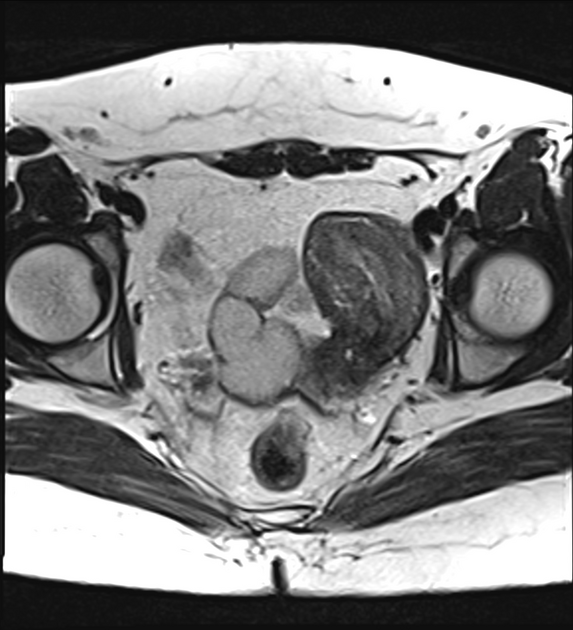
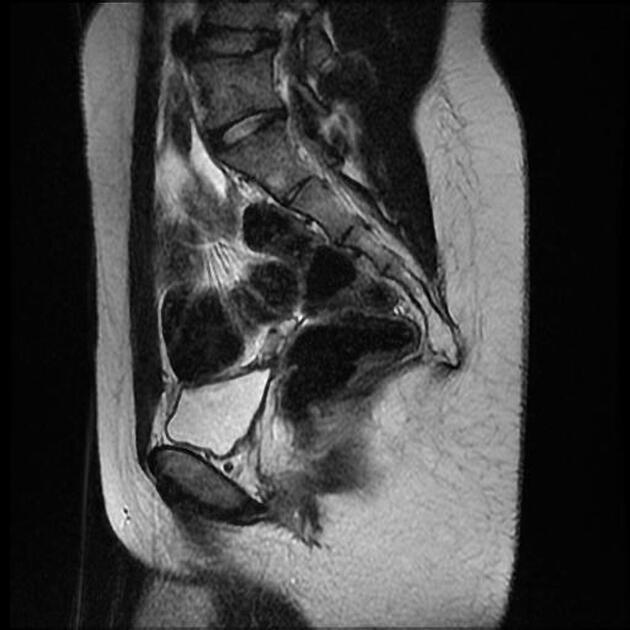
Müllerian duct anomalies
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mohamed R Nouh had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mohamed R Nouh's current disclosures- Uterine anomalies
- Müllerian duct anomaly (MDA)
- Mullerian duct anomaly
- Anomalies of uterine development
- Uterine anomaly
- Mulleran duct anomalies
- Congenital uterine anomalies
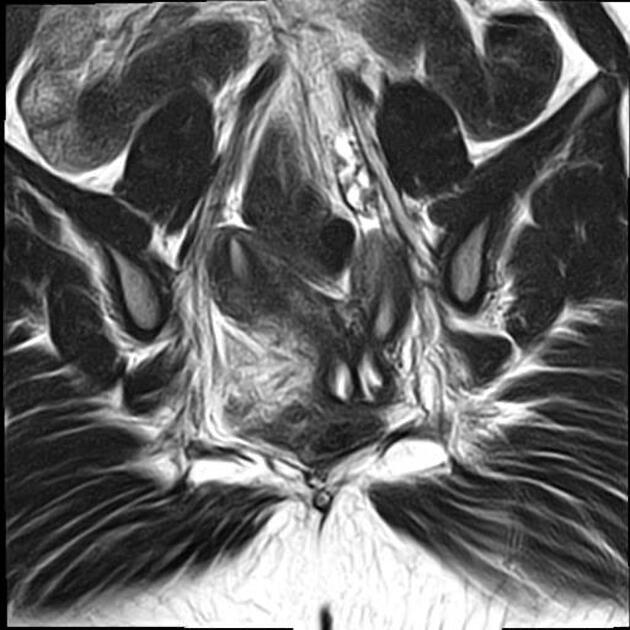
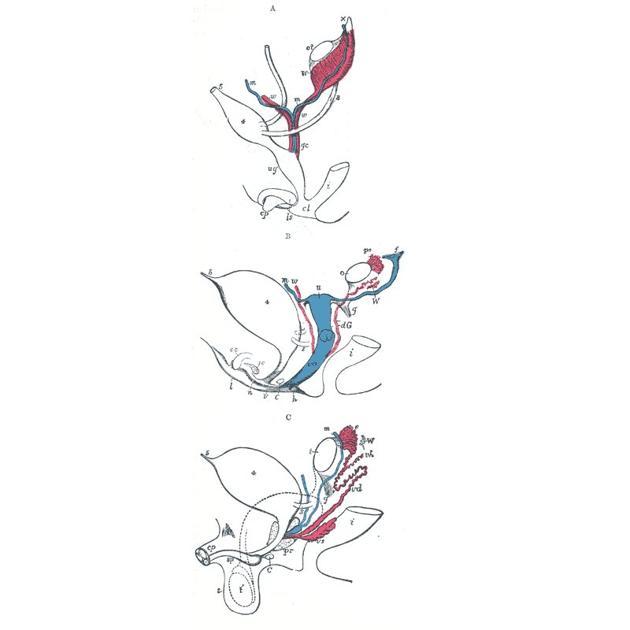
Müllerian duct anomalies (MDAs) are congenital abnormalities that occur when the Müllerian ducts (paramesonephric ducts) do not develop correctly. This may be due to complete agenesis, defective vertical or lateral fusion, or resorption failure.
On this page:
Epidemiology
MDAs are estimated to occur in 1-5% of all women. There is a higher rate of women with repeated miscarriages (3-15%) 2,5.
Associations
Renal anomalies are frequently associated, most commonly renal agenesis but also crossed fused renal ectopia, and duplex kidney 2.
Müllerian anomalies are associated with higher rates of endometriosis, particularly in obstructive cases. Surgical removal of uterine remnants or blockages has been shown to alleviate symptoms of endometriosis 6.
Clinical presentation
Despite these anomalies being common 1, the majority are asymptomatic. Obstruction of the Müllerian duct may occur, and patients present with an abdominal mass and dysmenorrhea. Delayed treatment may result in severe consequences and potentially infertility. Patients may also present with recurrent miscarriages and infertility 2,5.
Pathology
Subtypes
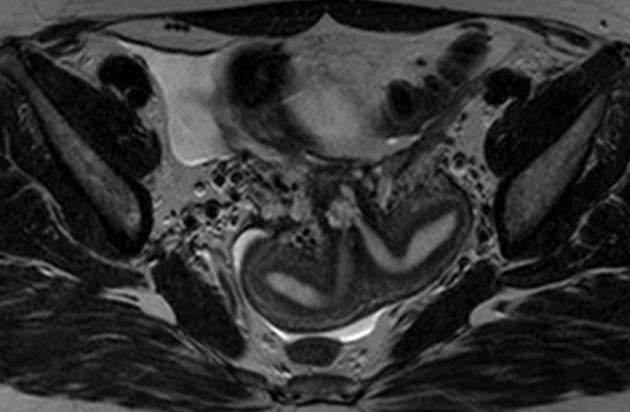
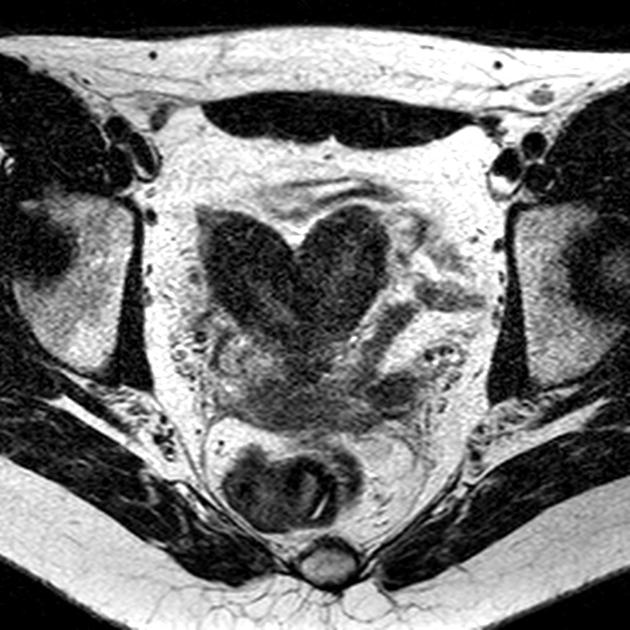
The Müllerian duct anomaly classification system divides them according to clinical manifestations, prognosis, and treatment. Accurate diagnosis is essential since management varies according to the type of malformation.
uterine agenesis: ~10%
arcuate uterus: often considered as part of normal anatomical variation, ~7%
unicornuate uterus: ~15% (range 5-25%)
-
uterus didelphys: ~7.5 % (range 5-11%)
bicornuate uterus: ~25% (range 10-39%)
-
septate uterus: ~45% (range 34-55%)
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
should be performed initially
confirms any structural abnormalities of the genital tract
sometimes cannot help to identify the type of MDA (especially on 2D imaging alone)
3D coronal transvaginal imaging has a high degree of diagnostic accuracy and ideally should be performed in the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle
MRI
valuable non-invasive technique
evaluation of the female pelvic anatomy
accurate Müllerian duct anomaly classification
Treatment and prognosis
Many patients are asymptomatic and require no treatment. However, where obstruction occurs, surgical intervention is usually required and may result in permanent infertility - counseling is required.
See also
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Junqueira B, Allen L, Spitzer R, Lucco K, Babyn P, Doria A. Müllerian Duct Anomalies and Mimics in Children and Adolescents: Correlative Intraoperative Assessment with Clinical Imaging. Radiographics. 2009;29(4):1085-103. doi:10.1148/rg.294085737 - Pubmed
- 2. Troiano R & McCarthy S. Mullerian Duct Anomalies: Imaging and Clinical Issues. Radiology. 2004;233(1):19-34. doi:10.1148/radiol.2331020777 - Pubmed
- 3. Steinkeler J, Woodfield C, Lazarus E, Hillstrom M. Female Infertility: A Systematic Approach to Radiologic Imaging and Diagnosis. Radiographics. 2009;29(5):1353-70. doi:10.1148/rg.295095047 - Pubmed
- 4. Saleem S. MR Imaging Diagnosis of Uterovaginal Anomalies: Current State of the Art. Radiographics. 2003;23(5):e13. doi:10.1148/rg.e13 - Pubmed
- 5. Behr S, Courtier J, Qayyum A. Imaging of Müllerian Duct Anomalies. Radiographics. 2012;32(6):E233-50. doi:10.1148/rg.326125515 - Pubmed
- 6. Bhamidipaty-Pelosi S, Kyei-Barffour I, Volpert M et al. Müllerian Anomalies and Endometriosis: Associations and Phenotypic Variations. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024;22(1):157. doi:10.1186/s12958-024-01336-1 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Habitual miscarriage
- Longitudinal vaginal septum
- Fetal akinesia sequence
- Cord presentation
- Female infertility
- Placenta increta
- Cervical ectopic pregnancy
- Septate uterus
- Müllerian duct anomaly classification
- Placenta percreta
- Haematometrocolpos
- Herlyn-Werner-Wunderlich syndrome
- Androgen insensitivity syndrome
- Müllerian duct
- Uterus
- Streak ovaries
- Uterus didelphys
- Paediatric curriculum
- Cystic lesions around vagina and female urethra
- Cervical incompetence
- Herlyn-Werner-Wunderlich syndrome
- Septate uterus
- Renal agenesis
- Uterine didelphys
- Undescended fallopian tubes
- Unicornuate uterus
- Uterine hypoplasia with partial vaginal agenesis
- Bicornuate uterus
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome
- Uterus didelphys with obstructed hemivagina
- Septate uterus
- Hernia uterine inguinale
- Robert's uterus
- Uterus didelphys
- Uterus didelphys
- Unicornuate uterus with haematometra in non-communicating contralateral rudimentary horn
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome
- Uterine hypoplasia
- Septate uterus
- Bicornuate uterus
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.