Pancreatic lipoma
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Matt A. Morgan had no recorded disclosures.
View Matt A. Morgan's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yuichiro Hirano had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yuichiro Hirano's current disclosures- Pancreatic lipomas
- Lipoma of the pancreas
- Lipomas of the pancreas
Pancreatic lipomas are uncommon mesenchymal tumors of the pancreas.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Rarely symptomatic, they are most often detected incidentally on cross-sectional imaging for another purpose. If they do cause symptoms, it will typically be those related to regional mass effect from the mass.
Pathology
Pancreatic lipomas are composed of mature fat cells with thin internal fibrous septa. They differ from pancreatic lipomatosis in that they have well-defined margins covered by a thin collagen capsule.
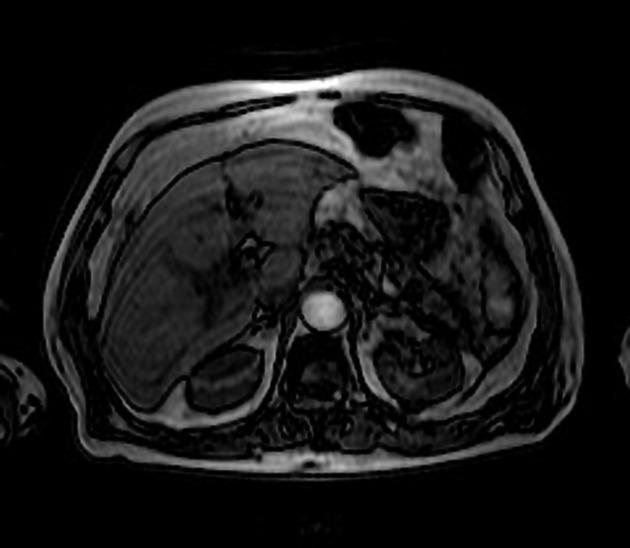
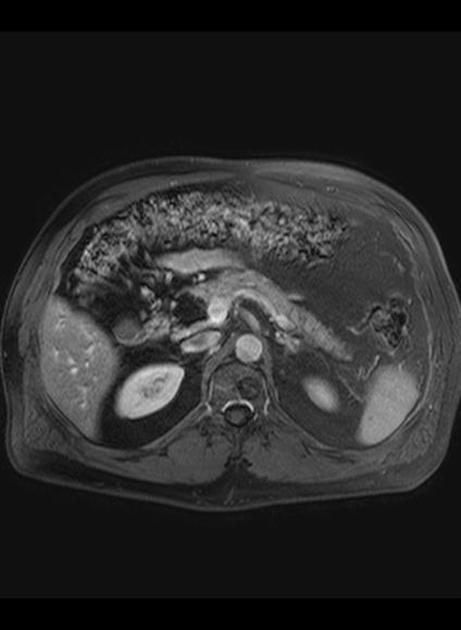
Radiographic features
Correct diagnosis is important to avoid confusion with a neoplastic process. Most contain macroscopic fat.
Ultrasound
difficult to diagnose: may be hyperechoic or hypoechoic
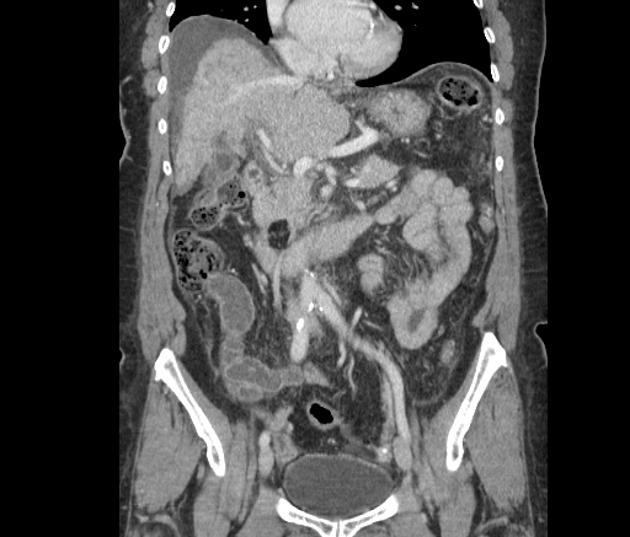
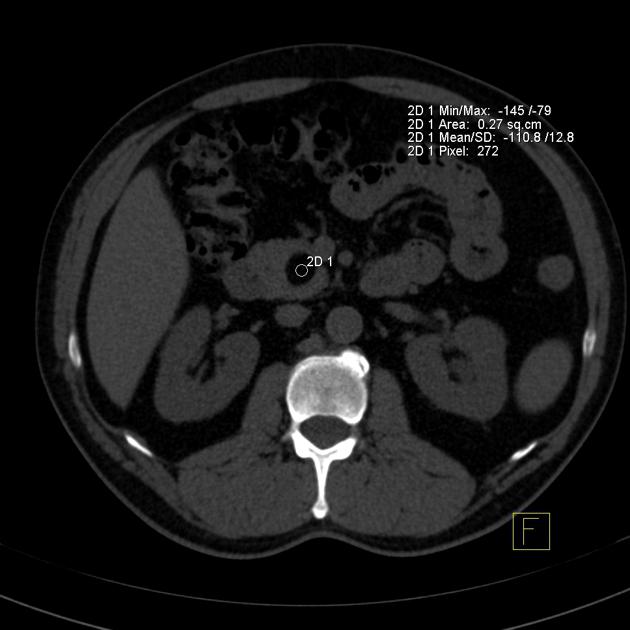
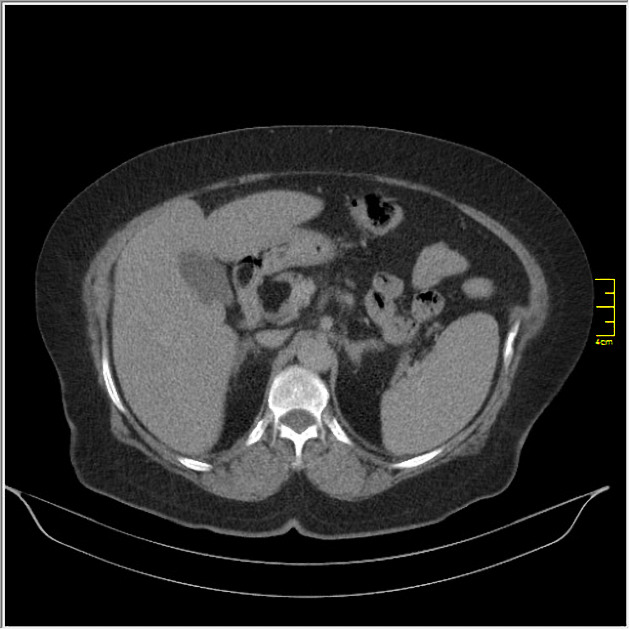
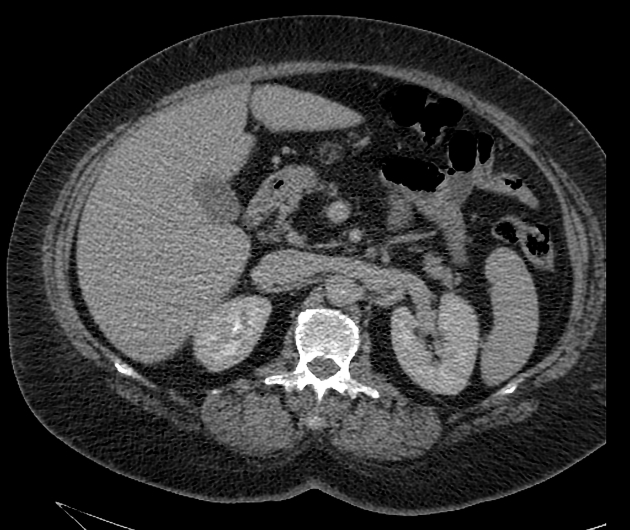
CT
well-circumscribed, lobulated lesion in the pancreas
generally fat attenuation (≤ -30 HU)
non-enhancing
MRI
well-circumscribed, lobulated lesion in the pancreas
T1 and T2 hyperintense
saturates on a fat-saturated sequence
may not be hypointense on an out-of-phase sequence (edge may show "india-ink" artifact)
Treatment and prognosis
They are benign lesions, and only rarely require resection.
Differential diagnosis
pancreatic mature cystic teratoma (dermoid): even more rare; may have associated calcifications
liposarcoma: should be considered if there are atypical findings such as an infiltrative lesion, a large lesion, or solid enhancing elements
focal fatty infiltration: there is overall decrease in pancreatic volume with preserved lobular contour and replacement of the pancreatic parenchyma by fat density 3
pseudohypertrophic lipomatosis: enlarged pancreatic size with fat density 4
References
- 1. Manning M, Srivastava A, Paal E, Gould C, Mortele K. Nonepithelial Neoplasms of the Pancreas: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation, Part 1--Benign Tumors: From the Radiologic Pathology Archives. Radiographics. 2016;36(1):123-41. doi:10.1148/rg.2016150212 - Pubmed
- 2. Lee S, Thng C, Chow P. Lipoma of the Pancreas, a Case Report and a Review of the Literature. World J Radiol. 2011;3(10):246-8. doi:10.4329/wjr.v3.i10.246 - Pubmed
- 3. Stadnik A, Cieszanowski A, Bakoń L, Grodzicka A, Rowiński O. Pancreatic Lipoma: An Incydentaloma Which Can Resemble Cancer - Analysis of 13 Cases Studied with CT and MRI. Pol J Radiol. 2012;77(3):9-13. doi:10.12659/pjr.883368 - Pubmed
- 4. Bhatt S, Ahmad M, Tandon A, Mandal S, Garg D. Pancreatic Lipoma and Its Differentiation from Various Fat Containing Lesions in the Pancreas: An Imaging Guide. IJRRT. 2017;4(5):62-5. doi:10.15406/ijrrt.2017.04.00112
- 5. Aithal Sitharama S, Bashini M, Gunasekaran K, Barathi Subramania D. Pancreatic Lipoma: A Pancreatic Incidentaloma; Diagnosis with Ultrasound, Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. BJR Case Rep. 2016;2(4):20150507. doi:10.1259/bjrcr.20150507 - Pubmed
- 6. Sato K, Takagi H, Ishibashi A, Koyama Y, Mori M. Small Pancreatic Lipoma: Case Report and Literature Review. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007;54(77):1582-4. - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- benign epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumors
- primary malignant epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumors
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumors
- hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumors
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumors
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic hemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumor
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumor
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumor
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumors
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumors
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.