Small bowel
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Raymond Chieng had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Raymond Chieng's current disclosures- Small intestine
- Small intestines
- Small bowels
The small bowel (or small intestine) is the section of bowel between the stomach and the colon. It has distinctive mucosal folds, valvulae conniventes, and is made up of three functional units:
On this page:
Terminology
Although anatomically it is stated that the duodenum forms the first part of the small bowel/intestine, clinically it is often used to refer to the jejunum and ileum only 1.
Gross anatomy
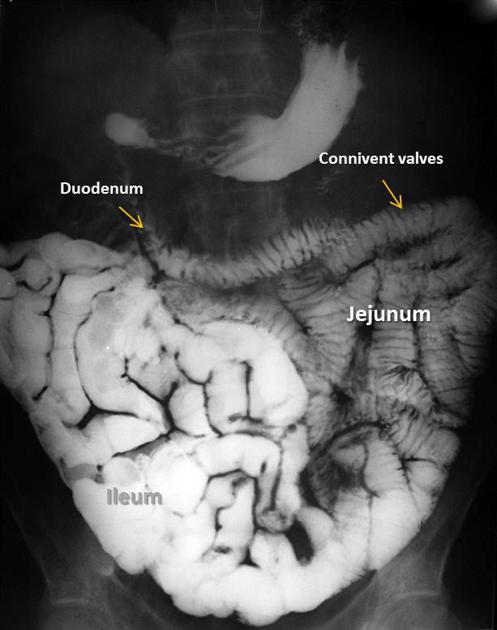
The total length of the jejunum and ileum varies from 3 to 10 m with an average length of 6 m. Both jejunum and ileum are attached to mesentery. The root of mesentery extends from the left of L2 vertebrae to the right sacroiliac joint, measuring 15 cm. Jejunum occupies proximal two-fifths while the ileum occupies the distal three-fifths of the small intestine. The mucosal folds in small intestine are known as valvulae conniventes (or plica semilunaris). Lymphoid follicles in the small intestine become progressively more numerous as they go into the distal ileum. In the distal ileum, these lymphoid follicles clump together to form Peyer's patches and are located at the antimesenteric border of the small intestine 2.
Arterial supply
The small intestine is supplied by superior mesenteric artery (arise from abdominal aorta at the level of L1 vertabra) from middle portion of the second part of the duodenum until terminal ileum. Jejunal and ileum branches arise from the left side of the main trunk of the superior mesenteric artery. These branches are linked to each other through a series of arcades (single arcade in jejunum and multiple arcades in ileum). They terminated as vasa recta (end arteries) within the intestinal wall 2.
Venous drainage
Veins from the small intestine drains into superior mesenteric vein which in turns drain into portal vein 2.
Lymphatic drainage
Lymph from small intestine drains into the superior mesenteric group of pre-aortic nodes 2.
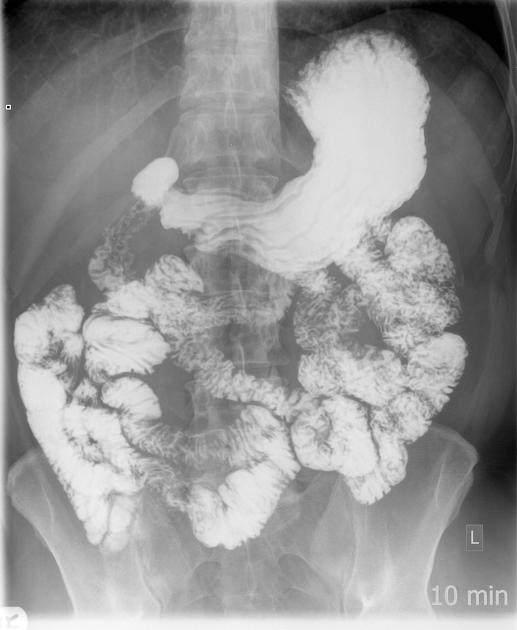
Radiographic features
Fluoroscopy
See main article: barium studies of small bowel.
Related pathology
References
- 1. Chummy S. Sinnatamby. Last's Anatomy. (2018) ISBN: 9780702033940
- 2. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2011) Page 167-168. ISBN: 9780702029714 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Dumping syndrome
- MR enteroclysis
- Organomegaly
- Terminal ileum
- Normal radiological reference values
- Jejunoileal bypass
- Ileum
- CT enterography (protocol)
- Caecal bascule
- Incompetent ileocaecal valve
- Intestinal angioedema
- Ascending colon
- Ilium vs ileum
- Descending colon
- Femoral hernia
- Ileovesicostomy
- Root of the mesentery
- Leiomyosarcoma
- Cecum
- Roux limb
- Small bowel obstruction
- Meckel’ s diverticulitis complicated by acute small intestinal obstruction
- Stages of embryonic rotation of the gut
- Small bowel peristalsis - normal (ultrasound)
- Small bowel intussusception due to sarcoma metastasis
- Gallstone ileus within a hernia sac
- Submucosal jejunal haematoma with haemoperitoneum
- Small bowel obstruction
- Spontaneous intramural small bowel haemorrhage
- Small bowel (ultrasound)
- Small bowel obstruction
- Small bowel obstruction due to incarcerated femoral hernia
- Meckel diverticulitis
- Traumatic small bowel perforation
- Hereditary angioedema - small bowel
- Small bowel obstruction attributed to adhesions
- Inguinal hernia
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.