The ulnar artery is a terminal branch of the brachial artery, arising at the proximal aspect of the forearm. Along with the radial artery, it is one of the main arteries of the forearm.
On this page:
Summary
origin: terminal branch of the brachial artery
location: inferior aspect of the cubital fossa
supply: elbow joint, medial and central forearm muscles, median and ulnar nerves, and common flexor sheath
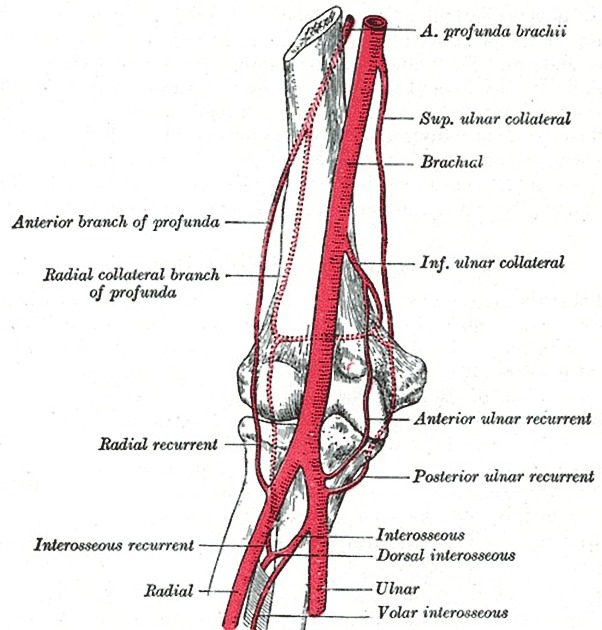
main branches: anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries, common interosseous artery, palmar carpal arch, superficial palmar arch, and dorsal carpal branch
Gross anatomy
Origin
The ulnar artery arises as a large terminal branch of the brachial artery at the inferior aspect of the cubital fossa 1.
Course
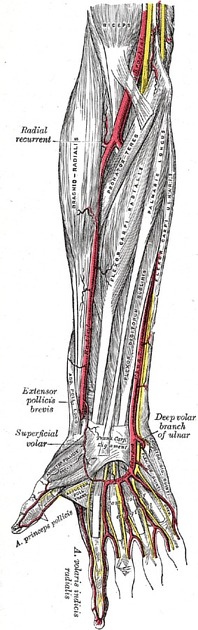
The ulnar artery courses along the ulnar aspect of the forearm deep to the flexor digitorum superficialis, pronator teres and flexor carpi radialis muscles. Proximally it is superficial to brachialis and flexor digitorum profundus but it then courses between flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor carpi ulnaris for the majority of its course.
It enters the hand with the ulnar nerve and vein by passing through the Guyon canal (ulnar canal) located between the pisiform and the hook of hamate. It then divides into its terminal branches at the carpal region of the hand 1,3.
Branches
The main branches of the ulnar artery include the anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries, the common interosseous, the palmar carpal arch, the superficial palmar arch, and the dorsal carpal branch 1.
See: mnemonic.
Termination
The ulnar artery terminates at the hand via its branches; the palmar carpal arch, the superficial palmar arch, and the dorsal carpal branch 1.
Supply
The ulnar artery supplies the periarticular anastomoses of the elbow via the anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries. It also supplies the medial and central forearm muscles, the median and ulnar nerves, and the common flexor sheath 1.
Variant anatomy
persistent median artery from the common or anterior interosseous arteries which accompanies the median nerve through the carpal tunnel
high division of the brachial artery where the brachial division occurs in the mid or upper arm, or sometime as high as the axilla. The radial and ulnar arteries therefore will have a long course in the arm.








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.