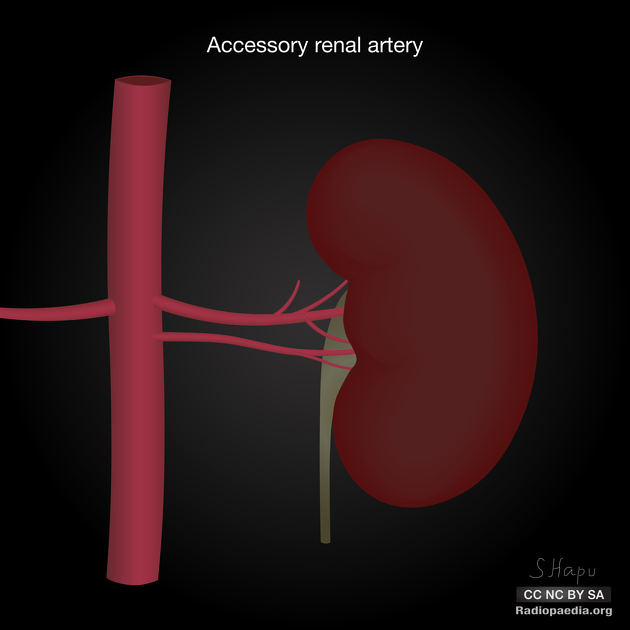
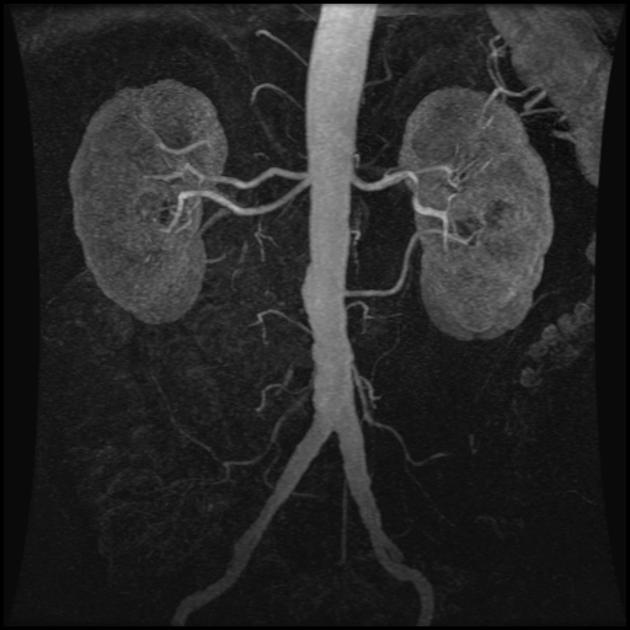
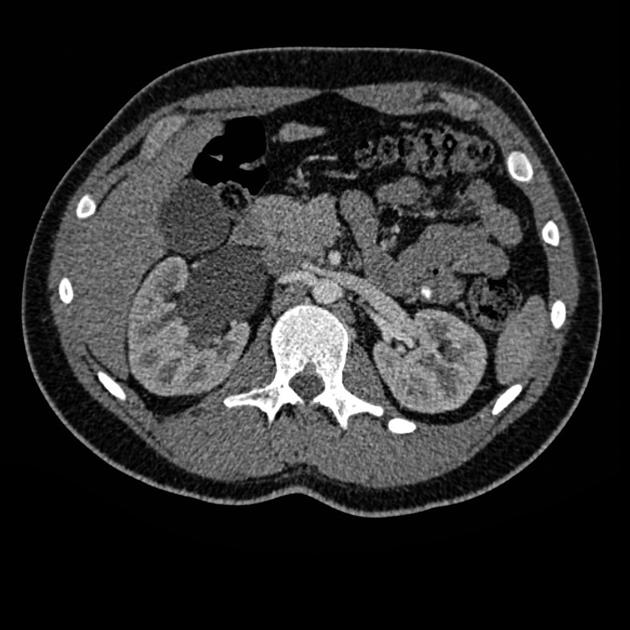
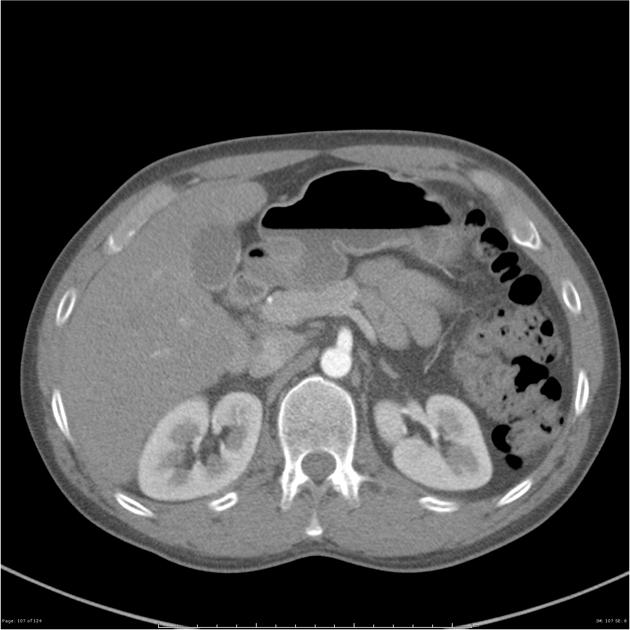
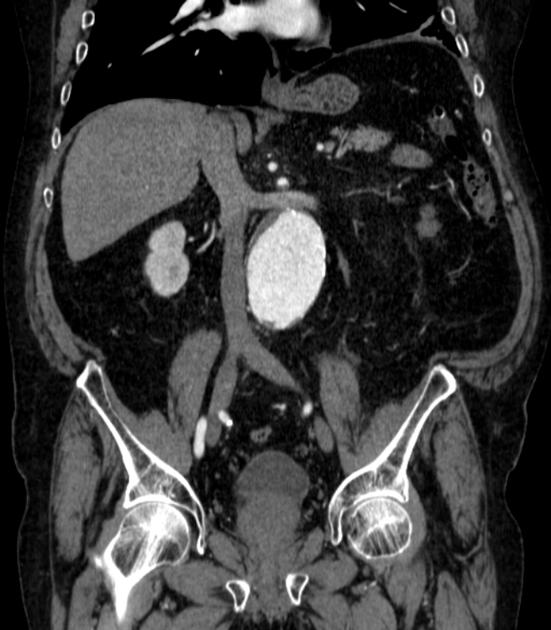
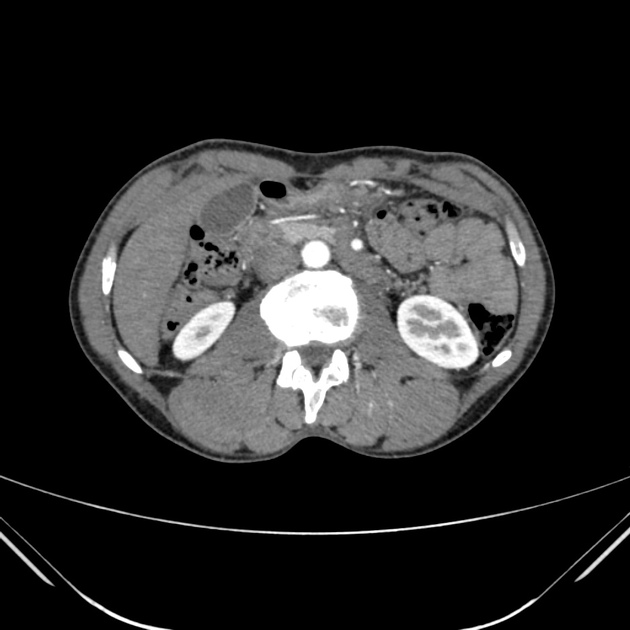
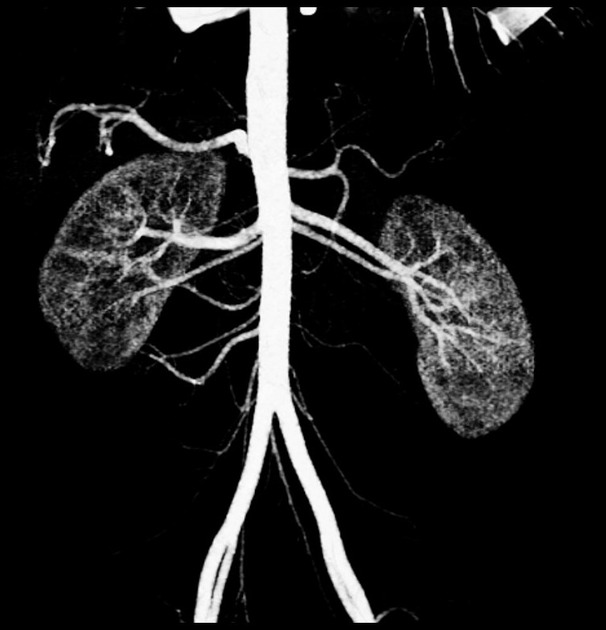
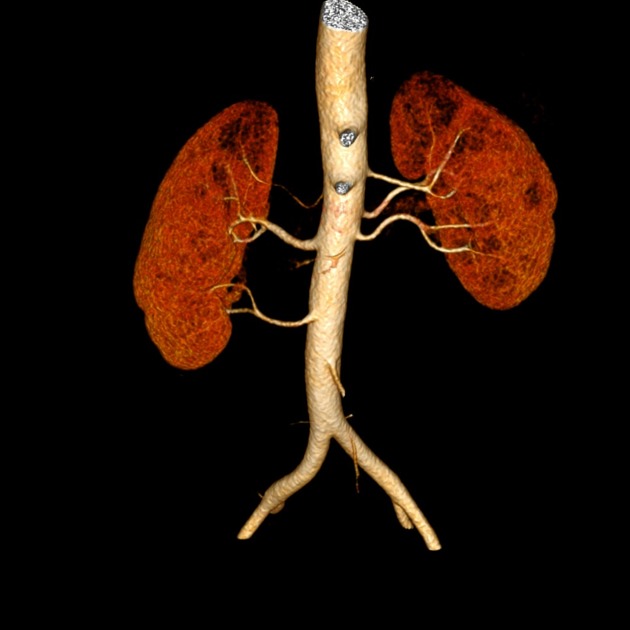
Multiple renal arteries
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Accessory renal arteries
- Extra renal areteries
- Aberrant renal artery
- Aberrant renal arteries
- Extra renal artery
- Accessory renal artery
- Additional renal artery
- Hilar supplemental artery
- Extrahilar renal artery
- Perforated renal artery
- Extra hilar renal artery
- Supernumerary renal arteries
- Supernumerary renal artery
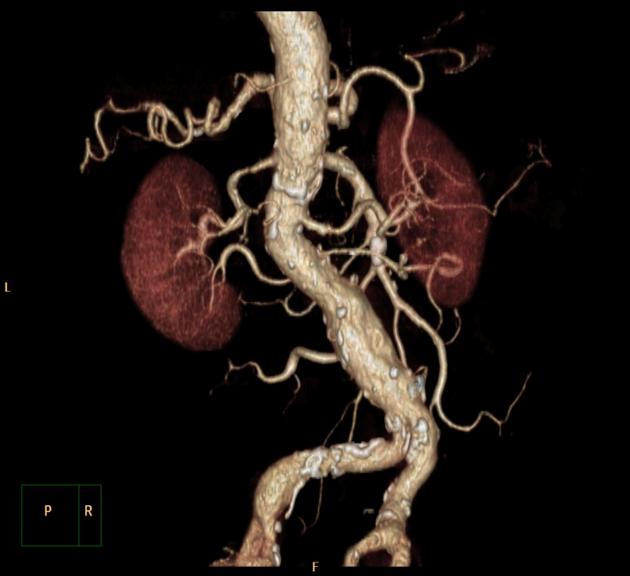
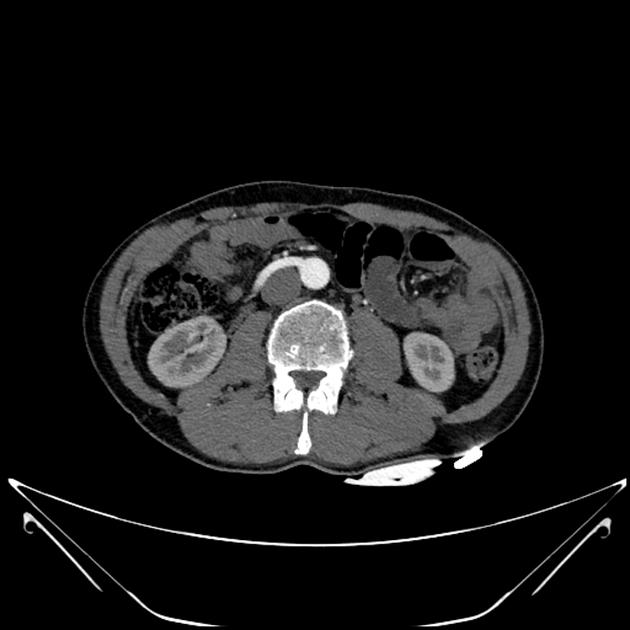
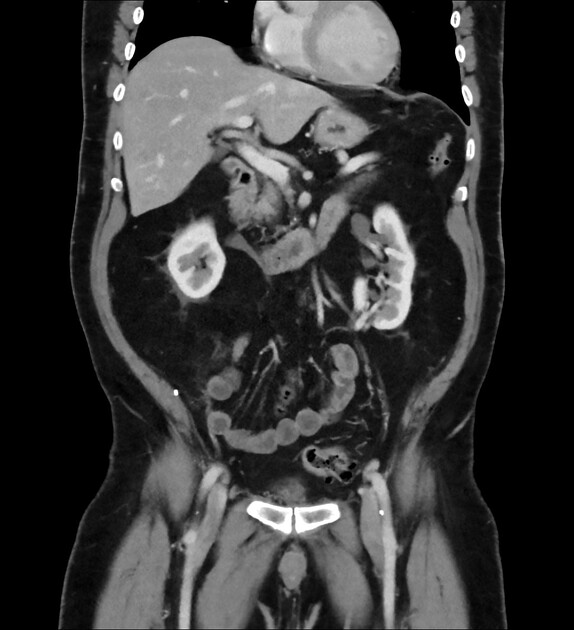
Multiple renal arteries, also known as additional or accessory renal arteries, are a common variant of the renal arteries.
On this page:
Terminology
Various terms have been proposed to describe supernumerary renal arteries, although there is no consensus 6,8,9:
-
multiple renal arteries
may be preferred as these are end-arteries, equivalent to a segmental branch of a single artery, and thus are the sole supply of a renal segment
most commonly used term in the literature 8
-
additional renal artery
arises from the abdominal aorta and enters the kidney
second most commonly used term in the literature
-
multiple renal artery
-
enter the kidney via the renal hilum
main renal artery: largest hilar artery
hilar supplemental artery: smaller hilar artery
third most commonly used term in the literature 8
-
supplementary renal artery
-
aberrant/extrahilar/perforated renal artery: enter kidney elsewhere, but at the renal hilum 8
-
superior/inferior polar artery: enters at the superior/inferior renal pole
solitary
pedicular: accompanied by polar vein and nerve plexus
false supernumerary: replaces a segmental artery
true supernumerary: does not replace a segmental artery
-
Epidemiology
Multiple renal arteries are present in ~25% (range 20-30%) of the population 1,8,9 although has considerable regional variation being reported to be more common in White and African populations, and less common in Indian and Chinese populations 8. There appears to be no gender predilection 8.
Gross anatomy
Multiple renal arteries can occur unilaterally with no clear side predilection 8 and they occur bilaterally in 10-15% of cases 1.
A single supernumerary renal artery is most prevalent (~15%; range 9-22%) although two supernumerary renal arteries are also common (~5%; range 3-7%) with 3 or more uncommon (<1-2%) 8,9.
Supernumerary arteries most commonly arise from the abdominal aorta and rarely from a wide number of other arteries 8.
Supernumerary renal arteries most common enter the kidney at the hilum (~60%) followed by the inferior pole (~30%) then superior pole (~10%) 8.
History and etymology
The first recorded case of multiple renal arteries was described by Eustachius in the sixteenth century 7,8.
Clinical importance
Accurate identification is of utmost importance for surgical planning prior to live donor transplantation 2,3 and renal artery embolization for various reasons 4,5.
Related pathology
multiple renal arteries are associated with and may be contributory to essential hypertension 10
References
- 1. Gray's Anatomy. (2015) ISBN: 9780702052309 - Google Books
- 2. Urban B, Ratner L, Fishman E. Three-Dimensional Volume-Rendered CT Angiography of the Renal Arteries and Veins: Normal Anatomy, Variants, and Clinical Applications. Radiographics. 2001;21(2):373-86; questionnaire 549. doi:10.1148/radiographics.21.2.g01mr19373 - Pubmed
- 3. Sahani D, Rastogi N, Greenfield A et al. Multi-Detector Row CT in Evaluation of 94 Living Renal Donors by Readers with Varied Experience. Radiology. 2005;235(3):905-10. doi:10.1148/radiol.2353040496 - Pubmed
- 4. Kiron Varghese, Srilakshmi Adhyapak. Therapeutic Embolization. (2016) ISBN: 9783319424941 - Google Books
- 5. Türkvatan A, Ozdemir M, Cumhur T, Olçer T. Multidetector CT Angiography of Renal Vasculature: Normal Anatomy and Variants. Eur Radiol. 2009;19(1):236-44. doi:10.1007/s00330-008-1126-3 - Pubmed
- 6. Ozkan U, Oğuzkurt L, Tercan F, Kizilkiliç O, Koç Z, Koca N. Renal Artery Origins and Variations: Angiographic Evaluation of 855 Consecutive Patients. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2006;12(4):183-6. - Pubmed
- 7. Graves F. The Arterial Anatomy of the Congenitally Abnormal Kidney. Br J Surg. 1969;56(7):533-41. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800560717 - Pubmed
- 8. Gulas E, Wysiadecki G, Szymański J et al. Morphological and Clinical Aspects of the Occurrence of Accessory (Multiple) Renal Arteries. Arch Med Sci. 2018;14(2):442-53. doi:10.5114/aoms.2015.55203 - Pubmed
- 9. Pradhay G, Gopidas G, Karumathil Pullara S et al. Prevalence and Relevance of Multiple Renal Arteries: A Radioanatomical Perspective. Cureus. 2021;13(10):e18957. doi:10.7759/cureus.18957 - Pubmed
- 10. Wu F, Yuan X, Sun K et al. Effect of Accessory Renal Arteries on Essential Hypertension and Related Mechanisms. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024;13(4):e030427. doi:10.1161/JAHA.123.030427 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Aberrant extra renal artery and vein arising from common iliac vessels
- Precaval accessory right renal artery
- Retroaortic left renal vein - type I
- Type IV left renal vein
- Right-sided triplex and left-sided duplex horseshoe kidney
- Thoracic origin of renal artery
- Duplex kidney with triple renal arteries
- Unilateral partial renal atrophy
- Bilateral accessory renal arteries with mild pelvi-ureteric junction (PUJ) obstruction
- Pelviureteric junction obstruction with aberrant accessory lower pole renal artery
- Duplex kidney with obstructed lower moiety
- Renal arterial supply variants (illustrations)
- Accessory renal artery
- Malrotated duplex kidney
- Precaval accessory renal artery
- Aberrant renal artery
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Bilateral accessory renal arteries
- Abnormal renal vascular impression on intravenous pyelogram
- Accessory renal arteries
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.