Hepatic peliosis is a rare benign vascular condition characterized by dilatation of sinusoidal blood-filled spaces within the liver. There may be involvement of other organs, most commonly the spleen and bone marrow. It can be seen in a variety of settings and is important as appearances may mimic malignancy.
On this page:
Epidemiology
As the causes of peliosis are varied, the demographics will reflect the underlying cause.
Clinical presentation
Patients are usually asymptomatic 6 and thus the condition is discovered incidentally on imaging or autopsy. In some instances, lesions may be complicated by hemorrhage presenting acutely or result in hepatomegaly or liver impairment.
Pathology
The pathogenesis remains uncertain, with possible etiologies including the breakdown of the sinusoidal borders, hepatic outflow obstruction and dilatation of the central vein of the hepatic lobule.
Histologically, hepatic peliosis is characterized by multiple mottled blood-filled cyst-like spaces within the liver with associated sinusoidal dilatation 1,2. These vary in size from <1 mm to several centimeters in diameter.
Macroscopically, the liver appears dark or even purple, and usually, the entire liver is involved to a greater or lesser degree. Focal lesions may demonstrate central areas of hemorrhage.
Etiology
idiopathic: 20-50%
-
toxins
arsenic
polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
thorium oxide
-
drugs
anabolic steroids
azathioprine
corticosteroids
diethylstilbestrol (DES)
immunoglobulin therapy
methotrexate
oral contraceptives
tamoxifen
6-thioguanine (6-TG)
6-mercaptopurine (6-MP)
-
chronic illness
malignancy, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma
necrotizing vasculitis
hematologic disorders: Hodgkin disease, multiple myeloma
-
infection in AIDS
bacillary peliosis caused by Bartonella henselae, Bartonella quintana and Rochalimaea henselae
-
other
renal or cardiac transplantation
Radiographic features
Unfortunately, appearances are non-specific with variable enhancement patterns. Typically, there are multiple lesions, ranging from a few large lesions to innumerable small lesions.
Ultrasound
Sonographic appearances are non-specific, usually demonstrating an irregular hypoechoic region/mass 2.
CT
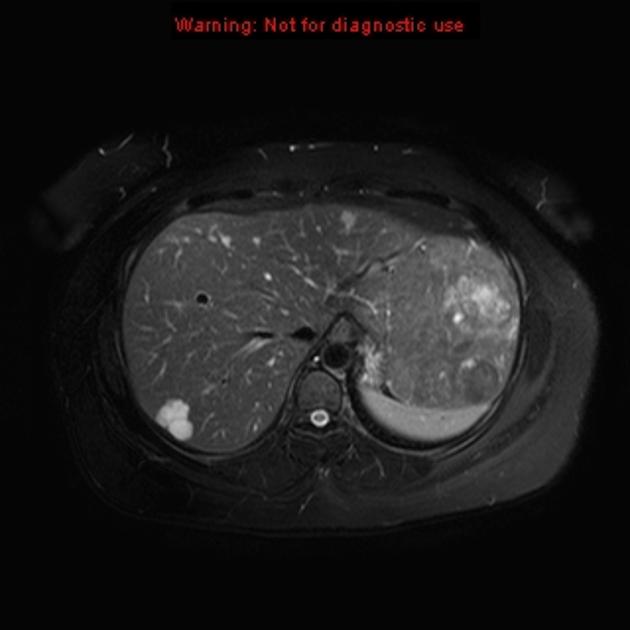
Appearance on pre-contrast CT is variable, depending on liver density, but is usually of multiple hypoattenuating lesions of variable size. Central hemorrhage may lead to areas of hyperattenuation and even dystrophic calcification 1.
Following contrast administration, there is usually globular centrifugal (more common) or centripetal arterial enhancement with no washout, the lesion remaining slightly hyperattenuating compared to surrounding liver on portal venous phase 1. Enhancement may be uniform or peripheral or irregular, but in contrast to cavernous hemangioma, it is usually continuous. There is no mass effect on neighboring hepatic vessels 6.
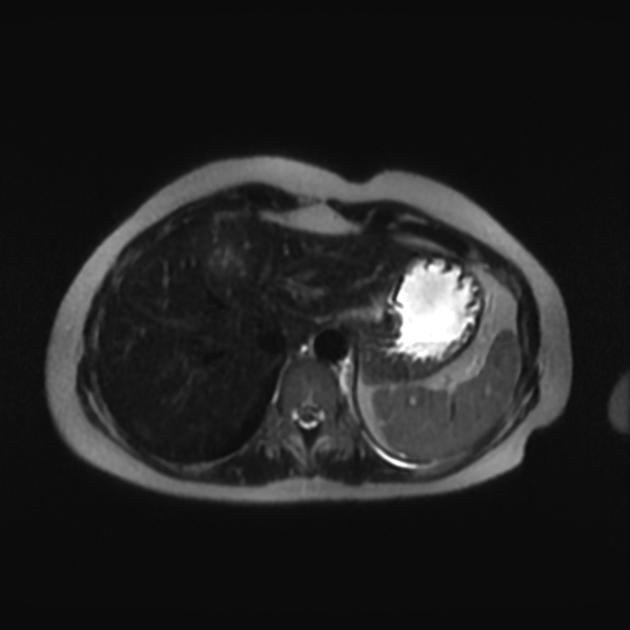
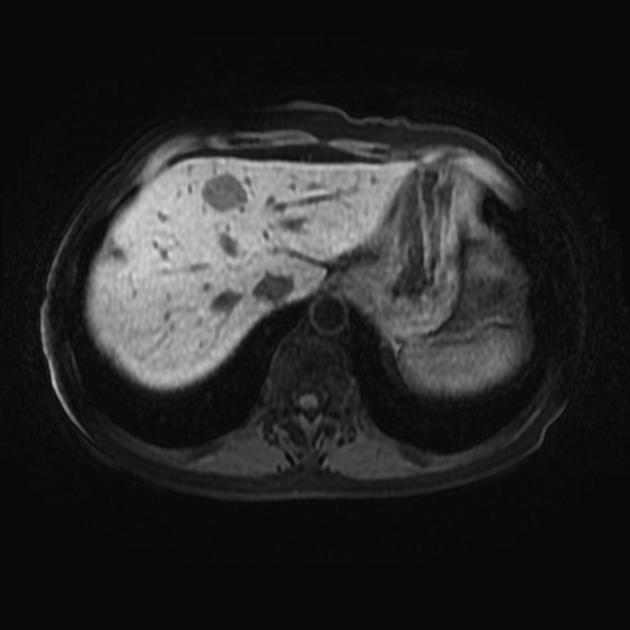
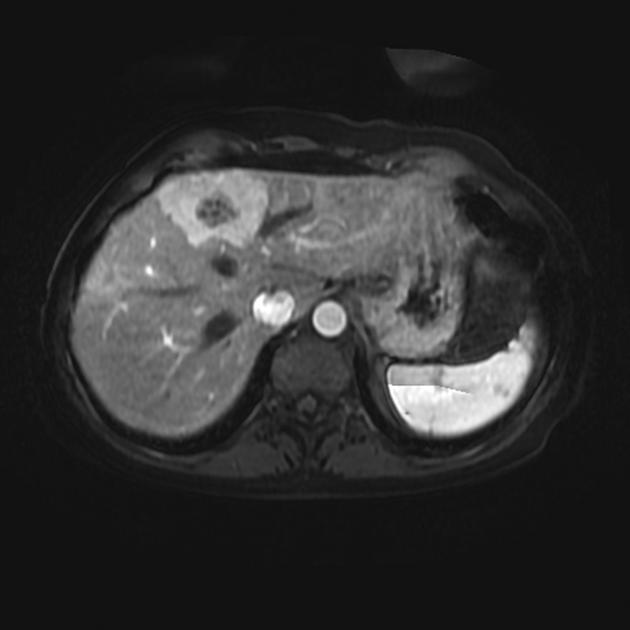
MRI
Signal characteristics may be altered due to the presence of hemorrhage; however, in general:
T1: typically hypointense (unless complicated by recent hemorrhage)
T2: hyperintense
T1 C+ (Gd): enhancement is typical, and is usually centrifugal (from center outward)
Angiography (DSA)
hypervascular with multiple vascular nodules
Treatment and prognosis
It is important not to drain peliosis, having mistaken it for a hepatic abscess, as hemorrhage can be life threatening 7.
Treatment depends on the cause. When a causative drug/toxin is suspected, withdrawal of that agent may result in resolution. If seen in the setting of HIV/AIDS, antibiotic treatment may be effective in eradicating B. henselae. If focal and hemorrhagic, resection may also be beneficial 1.
Complications
rupture and hemorrhage
History and etymology
From the Greek word pelios, meaning "dusky" or "purple" 1.
Differential diagnosis
General imaging differential considerations include:
-
globular discontinuous contrast enhancement tends to be centripetal (periphery first) rather than centrifugal (center first)
-
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
usually bright arterial enhancement with early washout
-
fluid component does not enhance
-
focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)
when typical, are easy to distinguish: central scar; homogeneous arterial enhancement (except for scar); delayed enhancement of the scar; isoattenuating on portal venous phase; strong enhancement on hepatobiliary phase
-
may contain fat
hypervascular metastases
hepatic sinusoidal dilation: usually the enhancement pattern is different on CT/MRI 5




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.