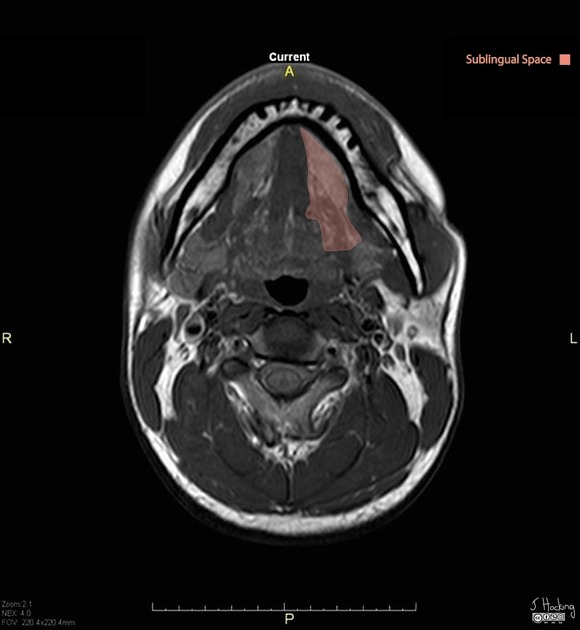
Sublingual space
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Sagar H S had no recorded disclosures.
View Sagar H S's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosuresThe sublingual spaces are paired suprahyoid deep spaces of the head and neck located below the tongue.
Gross anatomy
The sublingual space is a part of the floor of mouth 1.
As the sublingual space is not bounded by fascia posteriorly, some authors consider the sublingual space a component of the submandibular space 2. More commonly, however, the sublingual and submandibular spaces are discussed separately 3-5.
Each sublingual space communicates with contralateral sublingual space via a small isthmus just below the frenulum.
Boundaries
It is like an inverted V with its apex pointing anteriorly and is located between:
superiorly: intrinsic muscles of the tongue
inferolaterally: mylohyoid muscle
posteriorly: freely communicates along the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle with the submandibular and parapharyngeal spaces
anteriorly: mandible
medially: geniohyoid/genioglossus complex
Contents
sublingual gland and duct
lingual artery and vein
glossopharyngeal (CN IX) and hypoglossal (CN XII) nerves
deep portion of the submandibular gland and duct
Related pathology
References
- 1. La'porte SJ, Juttla JK, Lingam RK. Imaging the floor of the mouth and the sublingual space. (2011) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 31 (5): 1215-30. doi:10.1148/rg.315105062 - Pubmed
- 2. Som PM, Curtin HD. Head and Neck Imaging. (2011) ISBN: 9780323053556
- 3. Mukherji SK, Castillo M. A simplified approach to the spaces of the suprahyoid neck. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 1998;36 (5): 761-80, v. Pubmed citation
- 4. Harnsberger HR. Handbook Of Head And Neck Imaging: Handbooks in Radiology Series, 2e. Mosby. ISBN:0815142331. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 5. Otonari-Yamamoto M, Nakajima K, Tsuji Y et-al. Imaging of the mylohyoid muscle: separation of submandibular and sublingual spaces. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194 (5): W431-8. doi:10.2214/AJR.09.3516 - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Ranula
- Mylohyoid boutonniere
- Ludwig angina
- Ludwig angina progressing to necrotising deep soft tissue infection
- Plunging ranula
- Cervical cystic lymphangioma
- Submandibular gland main duct sialolith
- Ranula
- Lingual abscess
- Plunging ranula
- Mylohyoid boutonniere
- Submandibular gland haemangioma
- Tongue and floor of mouth neoplasm
- Ludwig angina
- Sublingual space: annotated MRI
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.