Torus fracture
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Calum Worsley had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Calum Worsley's current disclosures- Buckle fracture
- Cortical buckle fracture
- Torus fractures
- Buckle fractures
- Cortical buckle fractures
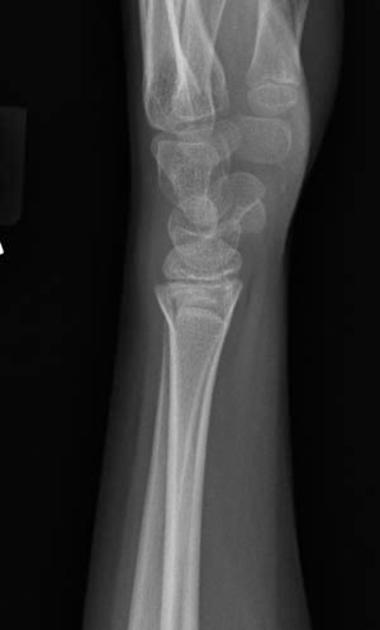
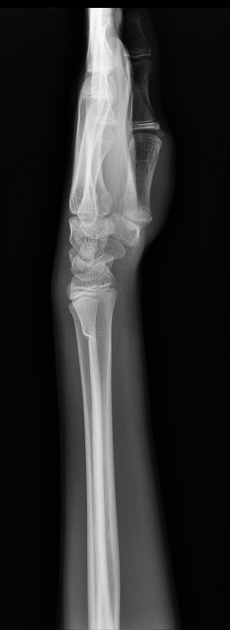
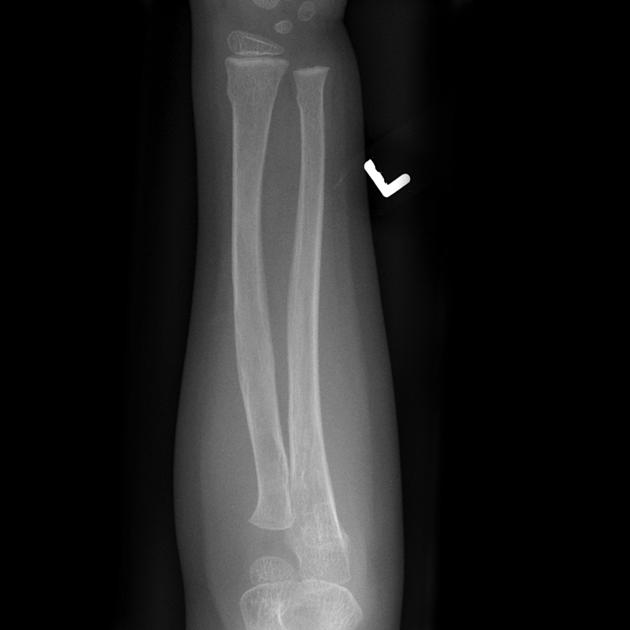
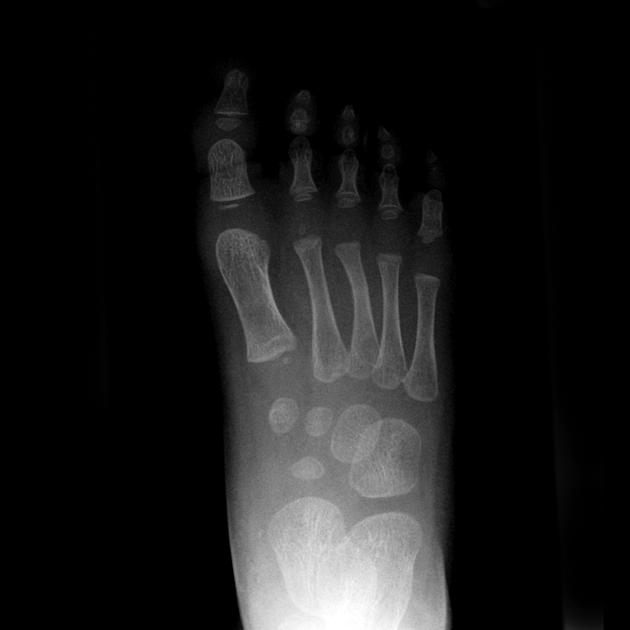
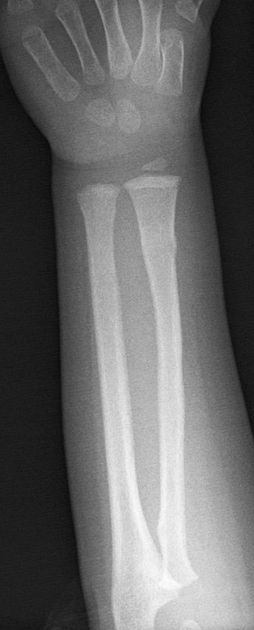
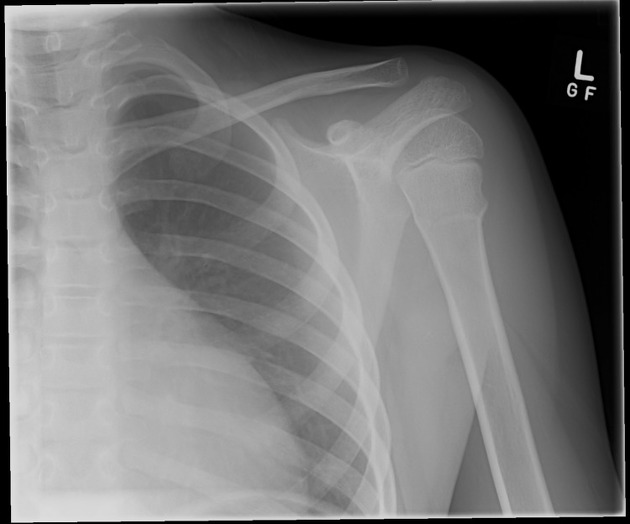
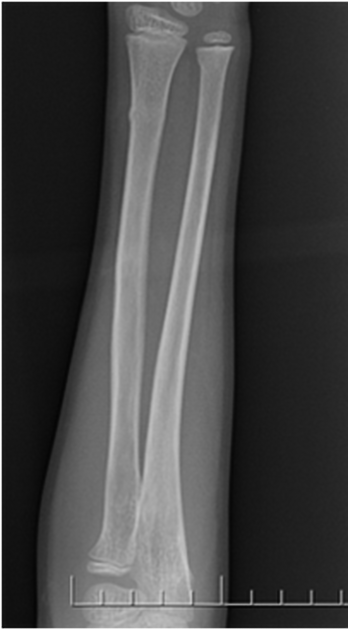
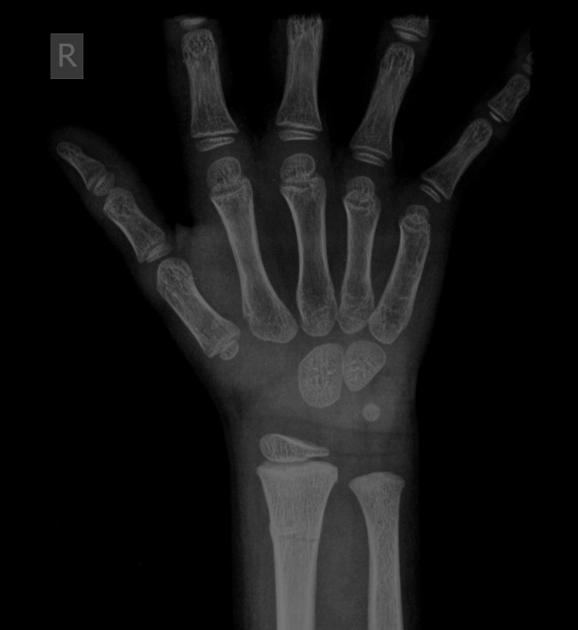
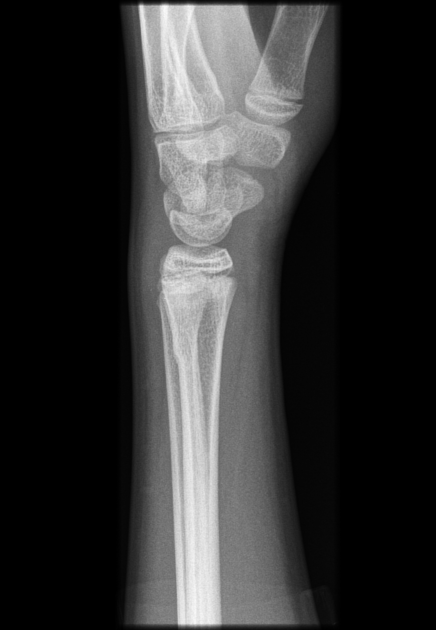
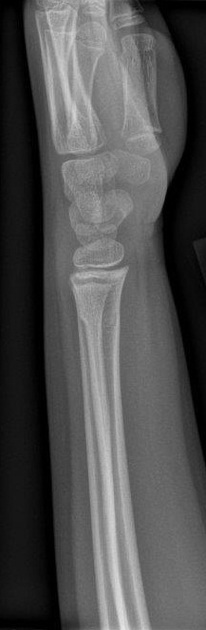
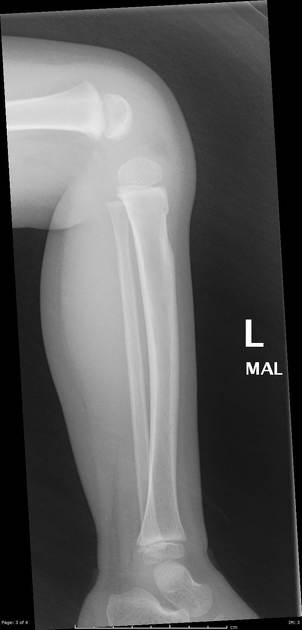
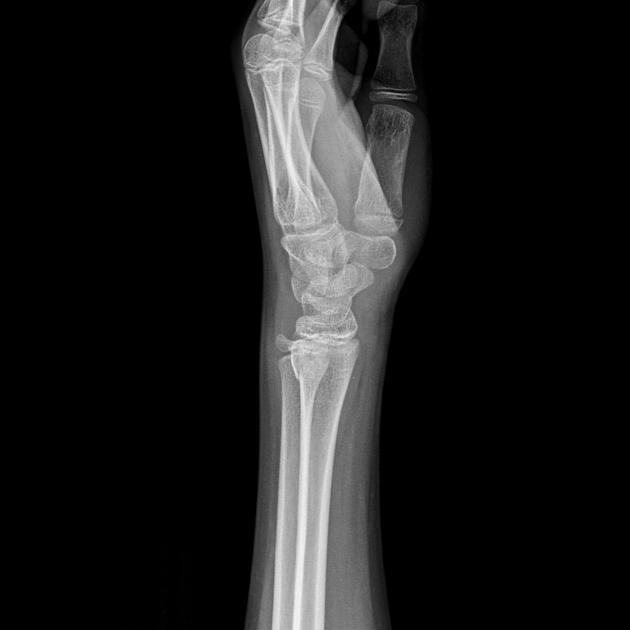
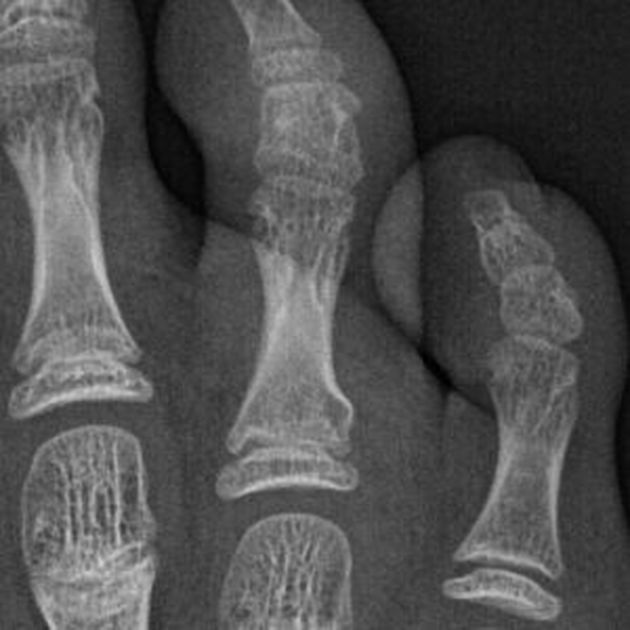
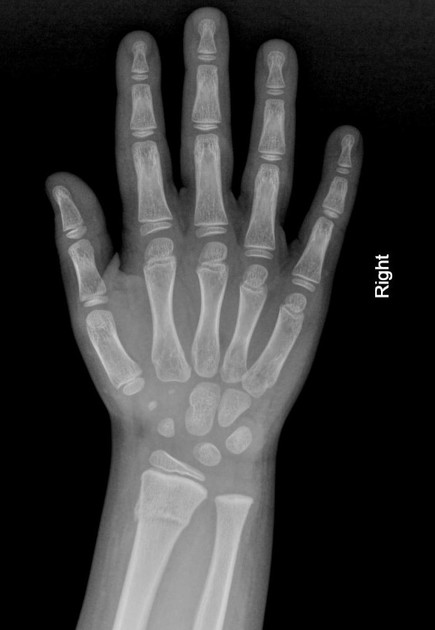
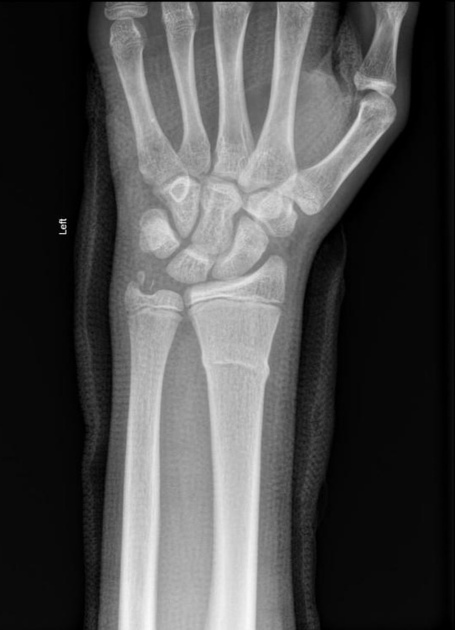
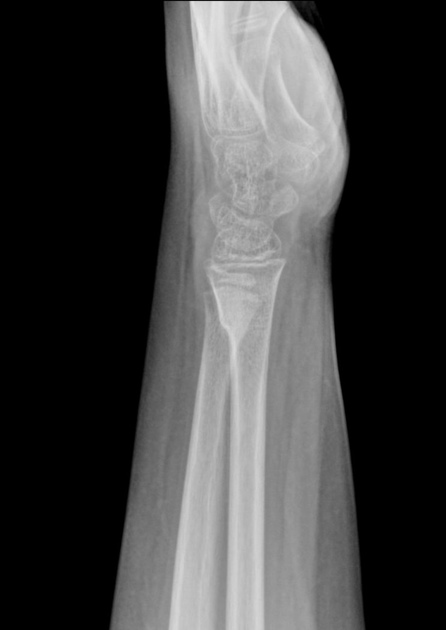
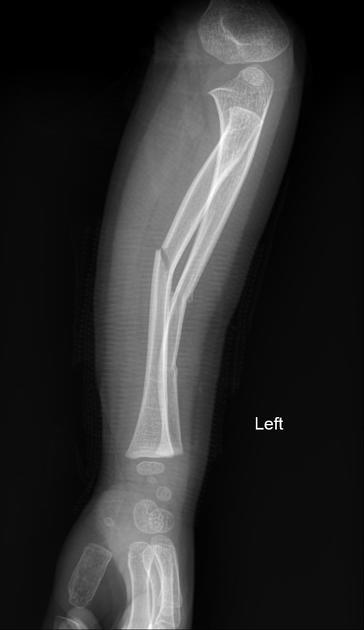
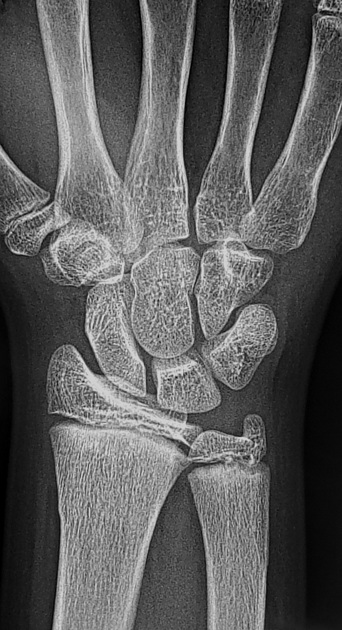
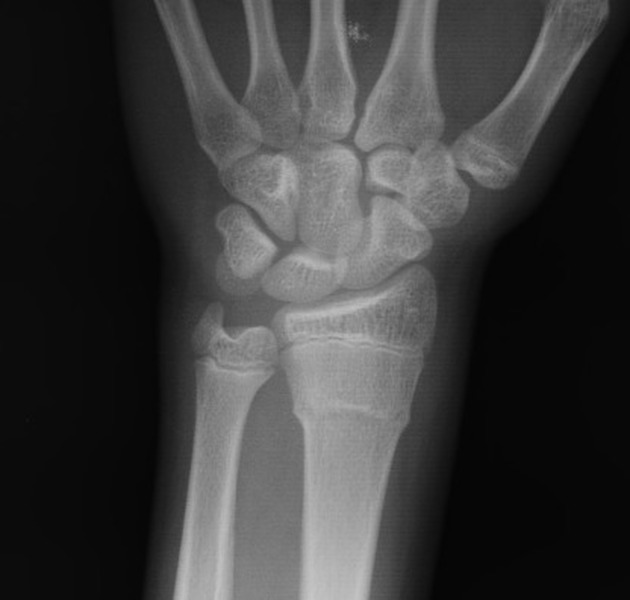
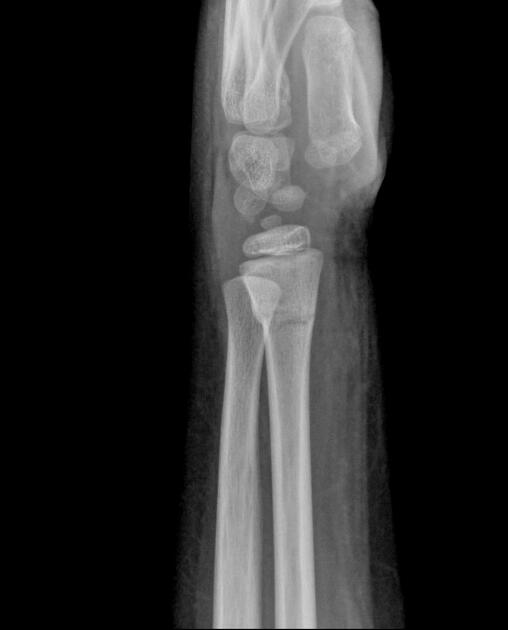
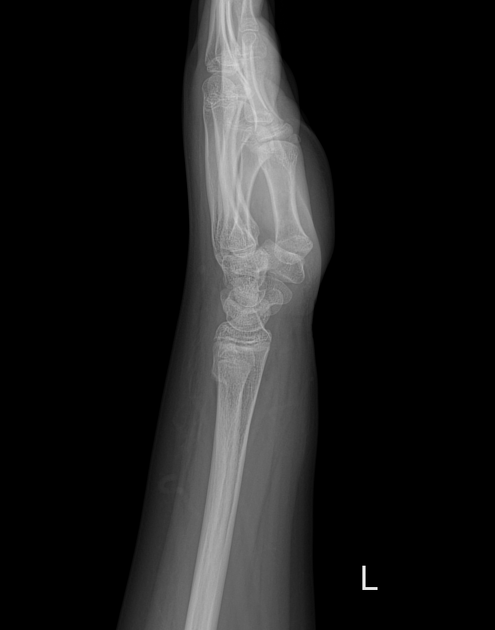
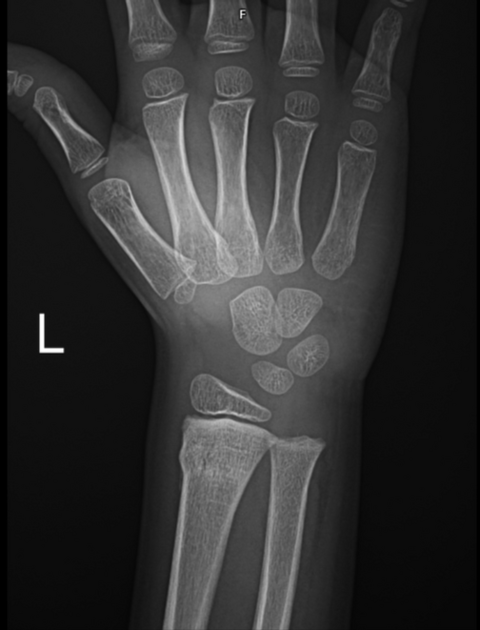
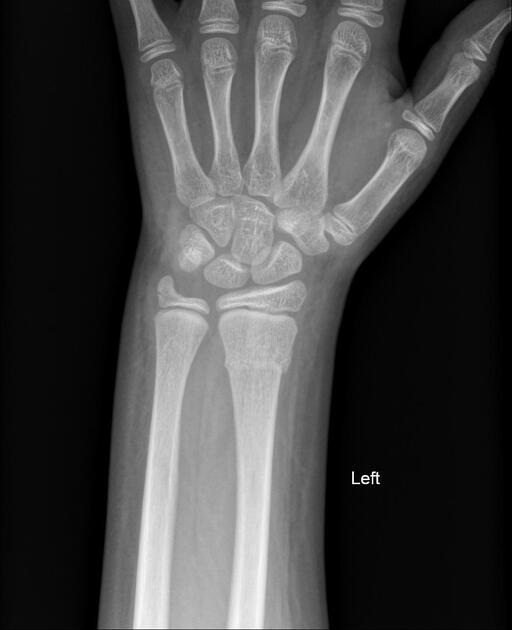
Torus fractures, also known as buckle fractures, are incomplete fractures of the shaft of a long bone that is characterized by bulging of the cortex. They result from trabecular compression due to an axial loading force along the long axis of the bone. They are usually seen in children, frequently involving the distal radial metaphysis.
On this page:
Terminology
Strictly speaking, a torus fracture refers to a circumferential buckle fracture 7. However, the terms are often used interchangeably.
Rarely, a torus fracture may refer to the fracture of an oral torus, and there is potential for the two terms to be confused 10.
Epidemiology
These type of fractures are more common in children, especially aged 5-10 years, due to the elasticity of their bones. In adults, the commonest form of torus fracture by far is a buckle fracture of the ribs.
There has been a single case report of a torus fracture of the distal radius in an adult 9.
Pathology
Cortical buckle fractures occur when there is axial loading of a long bone. This most commonly occurs at the distal radius following a fall on an outstretched arm; the force is transmitted from carpus to the distal radius and the point of least resistance fractures, usually the dorsal cortex of the distal radius.
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
distinct fracture lines are not seen
subtle deformity or buckle of the cortex may be evident
in some cases, angulation is the only diagnostic clue
Treatment and prognosis
They are self-limiting and typically do not require operative intervention, although a manipulation may be required if the angulation is severe. Sometimes a cast may be applied, but often a splint is all that is required with a period of rest and immobilization.
History and etymology
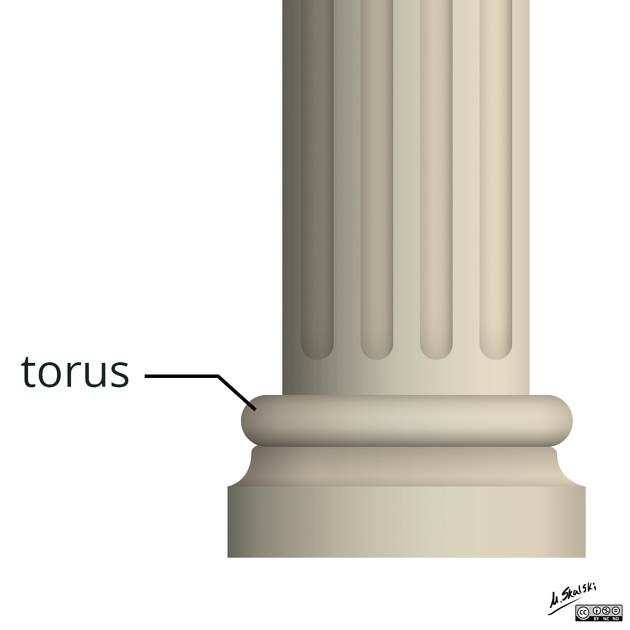
The term torus is the Latin word meaning protuberance. A torus is the convex portion of the upper part of the base of a Greek column and resembles the appearance of the cortical buckling seen in the "column" of bone which has been fractured in the pattern discussed in this article.
Practical points
in children ≥7 years, a distance of <1 cm between the fracture and physis means a potentially unstable distal radius fracture is more likely than a buckle fracture 8
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Bennett DL, Mencio GA, Hernanz-schulman M et-al. Buckle fractures in children: Is urgent treatment necessary? J Fam Pract. 2009;58 (10): E1-6. J Fam Pract (link) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Jadhav SP, Swischuk LE. Commonly missed subtle skeletal injuries in children: a pictorial review. Emerg Radiol. 2008;15 (6): 391-8. doi:10.1007/s10140-008-0733-2 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Plint AC, Perry JJ, Tsang JL. Pediatric wrist buckle fractures. Should we just splint and go? CJEM. 2004;6 (6): 397-401. CJEM (link) - Pubmed citation
- 4. Hernandez JA, Swischuk LE, Yngve DA et-al. The angled buckle fracture in pediatrics: a frequently missed fracture. Emerg Radiol. 2003;10 (2): 71-5. doi:10.1007/s10140-003-0288-1 - Pubmed citation
- 5. Solan MC, Rees R, Daly K. Current management of torus fractures of the distal radius. Injury. 2002;33 (6): 503-5. Injury (link) - Pubmed citation
- 6. Uzelac A, Davis R. Blueprints Radiology. LWW. ISBN:1405104600. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 7. B. J. Manaster, David A. May, David G. Disler. Musculoskeletal Imaging,The Requisites (Expert Consult - Online and Print), 4th ed (2013). ISBN: 9780323081771
- 8. Benjamin W. Iles, Julie B. Samora, Satbir Singh, Lynne Ruess. Differentiating stable buckle fractures from other distal radius fractures: the 1-cm rule. (2018) Pediatric Radiology. doi:10.1007/s00247-018-4316-4 - Pubmed
- 9. García-Mata S & Hidalgo-Ovejero A. Distal Radial Torus Fracture in an Adult. A New Type of Occult Wrist Fracture? An Sist Sanit Navar. 2019;42(1):69-73. doi:10.23938/ASSN.0386 - Pubmed
- 10. Saura-Ingles A, Garcia-Ballesta C, Pérez-Lajarin L, López-Jornet P. Fracture in the Chin Area: An Unusual Case of Mandibular Torus Fracture. Br Dent J. 2005;199(1):27-9. doi:10.1038/sj.bdj.4812536 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Greenstick and buckle fractures - distal radius and ulna
- Buckle fracture - distal radius
- Distal radial and ulnar buckle fractures
- Buckle fracture
- Torus fracture
- Buckle fracture
- Torus fracture
- Buckle fracture of the tibia
- Torus fracture - second metacarpal
- Distal radius fracture
- Os triangulare
- Torus fracture
- Torus fracture of the radius
- Torus fracture of the radius
- Tibial torus fracture and fibular bowing
- Torus fracture of the radius
- Torus fracture of the radius
- Torus fracture
- Buckle fracture - distal radius
- Torus fracture
Related articles: Fractures
-
fracture
- terminology
- fracture location[+][+]
- diaphyseal fracture
- metaphyseal fracture
- physeal fracture
- epiphyseal fracture
- fracture types
- avulsion fracture
- articular surface injuries[+][+]
- complete fracture[+][+]
-
incomplete fracture
- bowing fracture
- buckle fracture (torus)
- greenstick fracture
- infraction
- compound fracture[+][+]
- pathological fracture
- stress fracture[+][+]
- fracture displacement[+][+]
- fracture location[+][+]
- fracture healing[+][+]
- skull fractures[+][+]
-
facial fractures[+][+]
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
- alveolar process fractures
- frontal sinus fracture
- isolated zygomatic arch fractures
- mandibular fracture
- nasal bone fracture
- orbital blow-out fracture
- paranasal sinus fractures
- complex fractures
- dental fractures
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
-
spinal fractures[+][+]
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- AO classification of upper cervical injuries
- AO classification of subaxial injuries
- Anderson and D'Alonzo classification (odontoid fracture)
- Roy-Camille classification (odontoid process fracture)
- Gehweiler classifcation (atlas fractures)
- Levine and Edwards classification (hangman fracture)
- Allen and Ferguson classification (subaxial spine injuries)
- subaxial cervical spine injury classification (SLIC)
- thoracolumbar spinal fracture classification systems
- three column concept of spinal fractures (Denis classification)
- classification of sacral fractures
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- spinal fractures by region
- spinal fracture types
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
- rib fractures[+][+]
- sternal fractures
-
upper limb fractures[+][+]
- classification
- Rockwood classification (acromioclavicular joint injury)
- AO classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO/OTA classification of distal humeral fractures
- Milch classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Weiss classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Bado classification of Monteggia fracture-dislocations (radius-ulna)
- Mason classification (radial head fracture)
- Frykman classification (distal radial fracture)
- Mayo classification (scaphoid fracture)
- Hintermann classification (gamekeeper's thumb)
- Eaton classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- Keifhaber-Stern classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- upper limb fractures by region
- shoulder
- clavicular fracture
-
scapular fracture
- acromion fracture
- coracoid process fracture
- glenoid fracture
- humeral head fracture
- proximal humeral fracture
- humeral neck fracture
- arm
- elbow
- forearm
- wrist
-
carpal bones
- scaphoid fracture
- lunate fracture
- capitate fracture
- triquetral fracture
- pisiform fracture
- hamate fracture
- trapezoid fracture
- trapezium fracture
- hand
- shoulder
- classification
- lower limb fractures[+][+]
- classification by region
- pelvic fractures
- hip fractures
- Pipkin classification (femoral head fracture)
- Garden classification (hip fracture)
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Cooke and Newman classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Johansson classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Vancouver classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- femoral
- knee
- Schatzker classification (tibial plateau fracture)
- AO classification of distal femur fractures
- Meyers and McKeevers classification (anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture)
- tibia/fibula
- Watson-Jones classification (tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture)
- ankle
- foot
- Berndt and Harty classification (osteochondral lesions of the talus)
- Sanders CT classification (calcaneal fracture)
- Hawkins classification (talar neck fracture)
- Myerson classification (Lisfranc injury)
- Nunley-Vertullo classification (Lisfranc injury)
- pelvis and lower limb fractures by region
- pelvic fracture
- sacral fracture
- coccygeal fracture
-
hip
- acetabular fracture
- femoral head fracture
-
femoral neck fracture
- subcapital fracture
- transcervical fracture
- basicervical fracture
-
trochanteric fracture
- pertrochanteric fracture
- intertrochanteric fracture
- subtrochanteric fracture
- femur
- mid-shaft fracture
- bisphosphonate-related fracture
- distal femoral fracture
- knee
- avulsion fractures
- Segond fracture
- reverse Segond fracture
- anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- arcuate complex avulsion fracture (arcuate sign)
- biceps femoris avulsion fracture
- iliotibial band avulsion fracture
- semimembranosus tendon avulsion fracture
- Stieda fracture (MCL avulsion fracture)
- patellar fracture
- tibial plateau fracture
- avulsion fractures
- leg
- tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture
- tibial shaft fracture
- fibular shaft fracture
- Maisonneuve fracture
- ankle
- foot
- tarsal bones
- metatarsal bones
- phalanges
- classification by region
- terminology






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.