Broca's area
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Julian Maingard had no recorded disclosures.
View Julian Maingard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- Brodmann area 44
- Broca's area
- Broca's areas
- Brodmann area 45
- Broca area
Broca's area (Brodmann areas 44 and 45) is an area of the lateral frontal lobe in the dominant hemisphere concerned with the production of speech.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
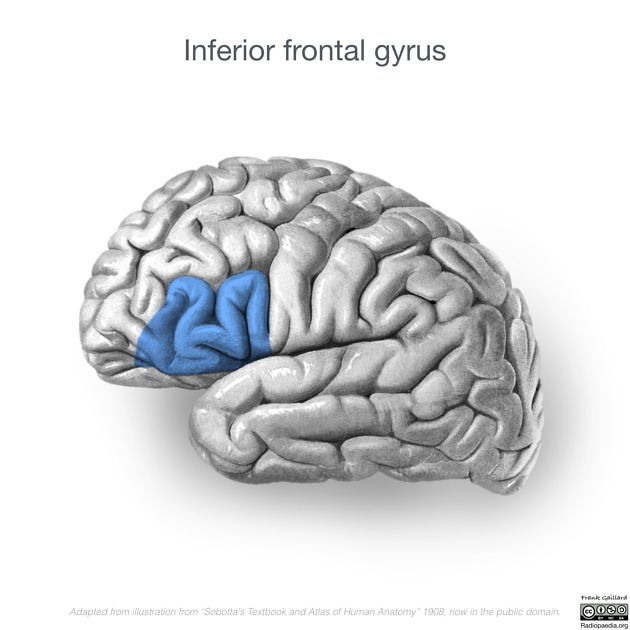
Broca's area is located in the posterior inferior frontal gyrus (pars opercularis (Brodmann area 44) and pars triangularis (Brodmann area 45)) of the dominant hemisphere, anterior to the anterior commissure line. It is anterior to the primary motor cortex on the precentral gyrus.
Relations
It is bounded anteriorly by the ascending ramus of the lateral (Sylvian) fissure and posteriorly by the precentral sulcus.
Arterial supply
superior division of the middle cerebral artery (MCA)
Neurophysiology
This language-eloquent area is most often located in the left hemisphere, also in left-handed individuals 4. However, right-hemispheric dominance may occur in roughly 4% of right-handed individuals and may be as high as 27% in extreme left-handers 5.
Maybe even more interestingly, there appears to be significant plasticity of organization in the brain regarding the shift of language-eloquent hemisphere 5. This has been demonstrated to occur in right-handed patients under experimental conditions with left-sided (virtually reversible) perisylvian lesions by functional MRI (fMRI) 3.
Additionally, some doubt has been cast on the role of Broca's area in long term speech production outcomes following damage to Broca's area, with other regions (e.g. anterior arcuate fasciculus) implicated as being as, if not more, important 7.
Related pathology
References
- 1. Keller SS, Roberts N, Hopkins W. A comparative magnetic resonance imaging study of the anatomy, variability, and asymmetry of Broca's area in the human and chimpanzee brain. J. Neurosci. 2009;29 (46): 14607-16. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2892-09.2009 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 2. Thomas P. Naidich, MD, Mauricio Castillo, MD, Soonmee Cha, MD et al. Imaging of the Brain. (2012) ISBN: 9781416050094 - Google Books
- 3. Krieg S, Sollmann N, Hauck T et al. Functional Language Shift to the Right Hemisphere in Patients with Language-Eloquent Brain Tumors. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e75403. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075403 - Pubmed
- 4. Robert B. Daroff. Bradley's Neurology in Clinical Practice. (2012) ISBN: 9781437704341 - Google Books
- 5. Finger S, Buckner RL, Buckingham H. Does the right hemisphere take over after damage to Broca's area? the Barlow case of 1877 and its history. Brain Lang. 2003;85 (3): 385-95. Pubmed citation
- 6. Knecht S, Dräger B, Deppe M et-al. Handedness and hemispheric language dominance in healthy humans. Brain. 2001;123 Pt 12: 2512-8. Pubmed citation
- 7. Gajardo-Vidal A, Lorca-Puls D, team P et al. Damage to Broca’s Area Does Not Contribute to Long-Term Speech Production Outcome After Stroke. Brain. 2021;144(3):817-32. doi:10.1093/brain/awaa460 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Trepanation
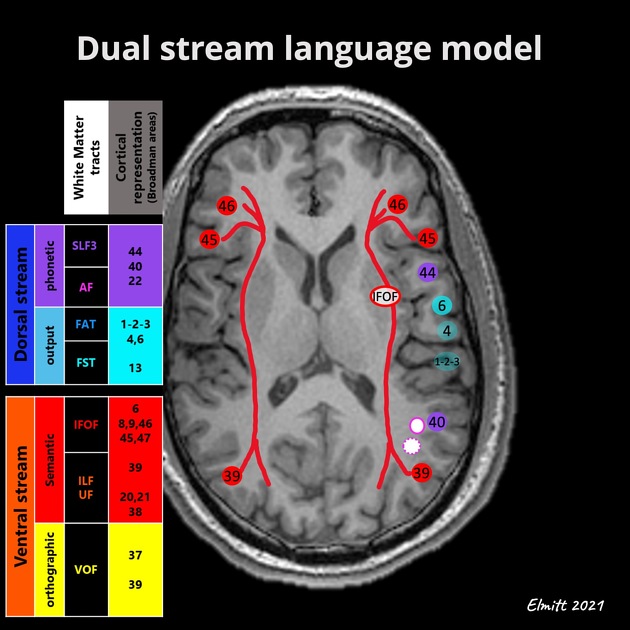
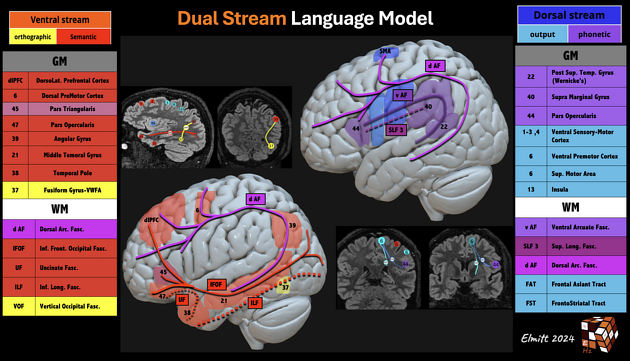
- Dual stream language processing models
- Functional neuroanatomy
- Frontotemporal lobar degeneration
- Frontal lobe
- Inferior frontal gyrus
- Brodmann areas
- Related articles (multiple choice questions)
- Middle cerebral artery
- Eloquent cortex
- Broca aphasia
- Pars opercularis
- Supratentorial intracranial mass in an adult (an approach)
- Association fibres of the brain
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.