Cuneus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Daniel Loh had no recorded disclosures.
View Daniel Loh's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tim Luijkx had no recorded disclosures.
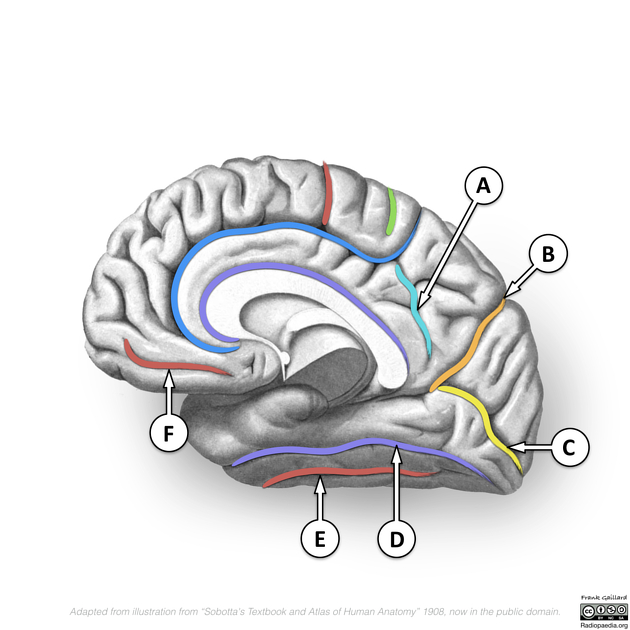
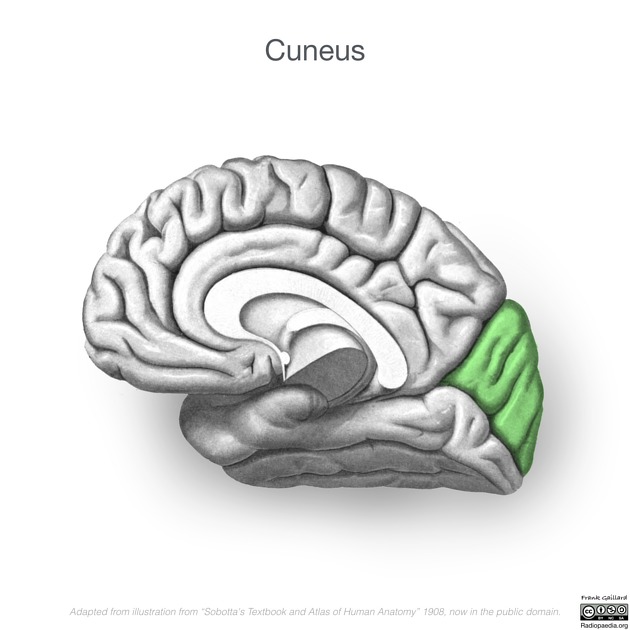
View Tim Luijkx's current disclosuresThe cuneus (plural: cunei) is a wedge-shaped region on the medial surface of the occipital lobe.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Relations
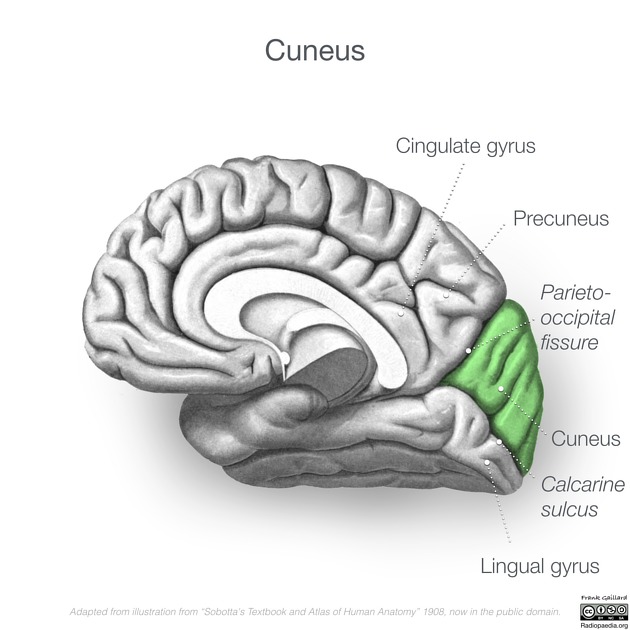
Anterosuperiorly the parieto-occipital sulcus separates the cuneus from the precuneus of the parietal lobe.
Posteroinferiorly the cuneus abuts the calcarine sulcus which separates it from the lingual gyrus 1.
The parieto-occipital sulcus and calcarine sulcus join to form a "Y".
Blood supply
Blood supply to the cuneus is via the calcarine artery and parieto-occipital artery. The proportion varies from person to person and either artery can be the major source of perfusion 2.
Function
Fibers of the superior optic radiation corresponding to the inferior quadrant of the visual field synapse on the cuneus 3.
Magneto encephalographic (MEG) measurements of occipital cortical signals have shown that the anteromedial cuneus activates almost simultaneously with the primary visual cortex (3-4 ms delay) in response to a visual stimulus and may act to modulate signals traveling from the primary visual cortex to the extrastriate cortices 4.
Related pathology
Lesions of the cuneus result in an inferior contralateral quadrantanopia 3.
Beyond its role in vision, a reduction of cortical thickness of the cuneus has also been associated with the pathogenesis of trigeminal neuralgia 5, as well as the development of psychosis in patients with a history of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection 6.
An MRI study found that thinning of posterior cortical regions, including the cuneus, is closely correlated with the occurrence and severity of visual hallucinations in dementia with Lewy bodies 7.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Standing S. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 41e. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:0702052302. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Marinković SV, Milisavljević MM, Lolić-Draganić V et-al. Distribution of the occipital branches of the posterior cerebral artery. Correlation with occipital lobe infarcts. Stroke. 1987;18 (4): 728-32. Pubmed citation
- 3. Haines DE. Fundamental Neuroscience for Basic and Clinical Applications: with STUDENT CONSULT Online Access, 4e. Saunders. ISBN:1437702945. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Vanni S, Tanskanen T, Seppä M et-al. Coinciding early activation of the human primary visual cortex and anteromedial cuneus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2001;98 (5): 2776-80. doi:10.1073/pnas.041600898 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 5. Parise M, Kubo TT, Doring TM et-al. Cuneus and fusiform cortices thickness is reduced in trigeminal neuralgia. J Headache Pain.15 (1): 17. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-15-17 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 6. Whitford TJ, Wood SJ, Yung A et-al. Structural abnormalities in the cuneus associated with Herpes Simplex Virus (type 1) infection in people at ultra high risk of developing psychosis. Schizophr. Res. 2012;135 (1-3): 175-80. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2011.11.003 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 7. Delli Pizzi S, Franciotti R, Tartaro A et-al. Structural Alteration of the Dorsal Visual Network in DLB Patients with Visual Hallucinations: A Cortical Thickness MRI Study. PLoS ONE. 2014;9 (1): . doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086624
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.