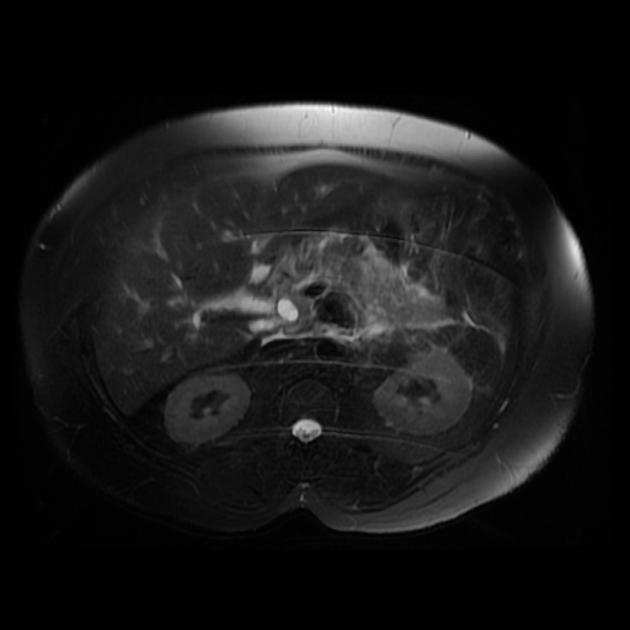
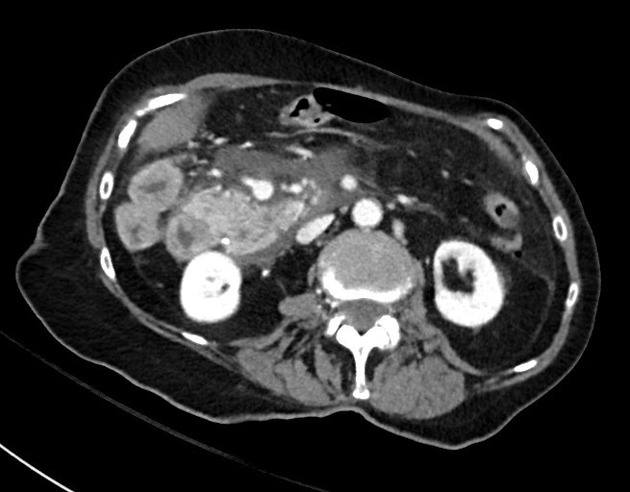
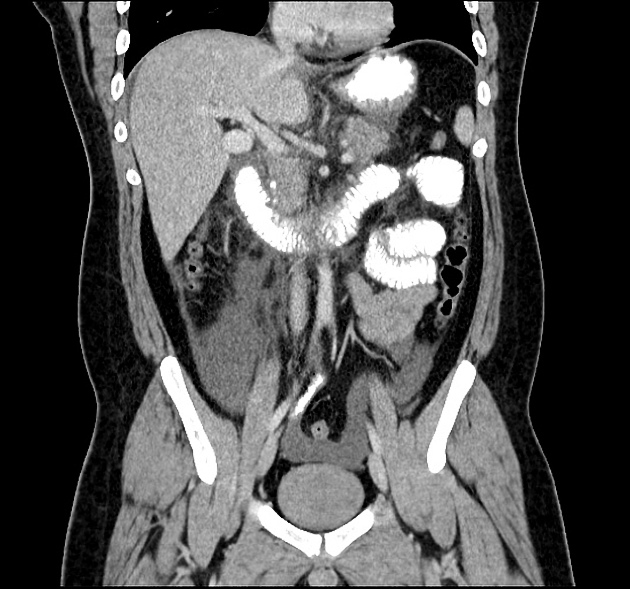
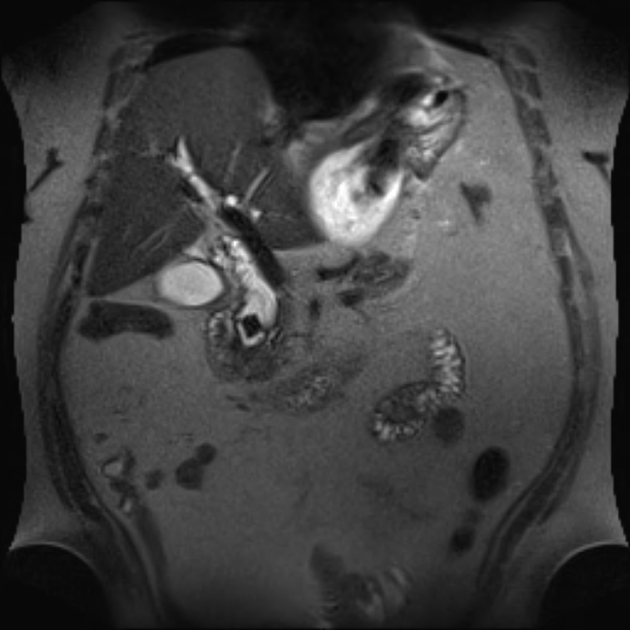
Gallstone pancreatitis
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Knipe H, Worsley C, Elfeky M, et al. Gallstone pancreatitis. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 20 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-35488
Permalink:
rID:
35488
Article created:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures
Revisions:
8 times, by
6 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Synonyms:
- Gallstone-induced pancreatitis
- Biliary pancreatitis
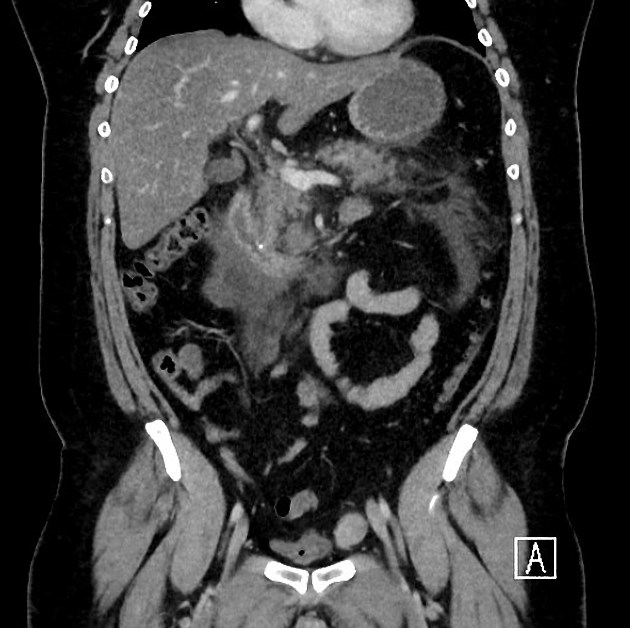
Gallstone pancreatitis refers to pancreatitis caused by gallstones, specifically distal choledocholithiasis. Gallstones are the cause for 35-40% of acute pancreatitis but this number has a wide regional variance.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Gallstone pancreatitis has a higher incidence in women (compared to alcohol-induced pancreatitis, which has a higher incidence in men) 4.
Pathology
The exact pathophysiology of gallstone pancreatitis remains unclear. There are a number of theories 2,3:
- distal gallstone obstruction results in pancreatic duct obstruction, this results in increased pancreatic duct pressure and unregulated pancreatic enzyme activity
- acinar cell hyperstimulation has also been implicated
- infected bile reflux inducing pancreatic enzyme action
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment options vary but include:
- conservative management
-
cholecystectomy
- may be performed acutely during the index admission, or after a short interval after discharge
- If gallstones are not treated, recurrence occurs in ~45% (range 32-61%) 4
-
ERCP
- Meta-analysis show no benefit of routine ERCP in gallstone pancreatitis in the absence of biliary obstruction or cholangitis 5
References
- 1. Vitale G. Early Management of Acute Gallstone Pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 2007;245(1):18-9. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000250967.32581.c9 - Pubmed
- 2. Wang GJ, Gao CF, Wei D et-al. Acute pancreatitis: etiology and common pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009;15 (12): 1427-30. Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 3. Hazem ZM. Acute biliary pancreatitis: diagnosis and treatment. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2009;15 (3): 147-55. doi:10.4103/1319-3767.54740 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 4. Sekimoto M, Takada T, Kawarada Y et-al. JPN Guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis: epidemiology, etiology, natural history, and outcome predictors in acute pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006;13 (1): 10-24. doi:10.1007/s00534-005-1047-3 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 5. Tse F, Yuan Y. Early routine endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography strategy versus early conservative management strategy in acute gallstone pancreatitis. (2012) The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009779.pub2 - Pubmed
- 6. Bortoff G, Chen M, Ott D, Wolfman N, Routh W. Gallbladder Stones: Imaging and Intervention. Radiographics. 2000;20(3):751-66. doi:10.1148/radiographics.20.3.g00ma16751 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- benign epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumors
- primary malignant epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumors
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumors
- hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumors
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumors
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic hemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumor
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumor
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumor
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumors
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumors
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.