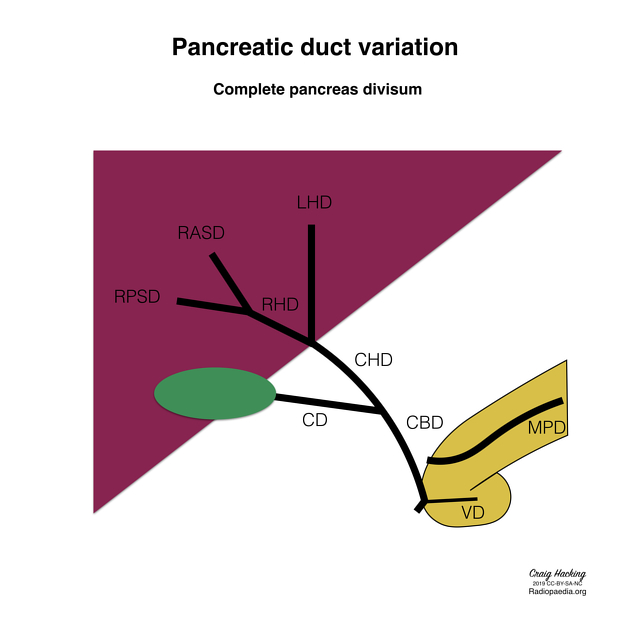
Pancreas divisum represents a variation in pancreatic ductal anatomy that can be associated with abdominal pain and idiopathic pancreatitis. It is characterized, in the majority of cases, by the dorsal pancreatic duct (i.e. main pancreatic and Santorini ducts) directly entering the minor papilla with no communication with the ventral duct (a.k.a duct of Wirsung) and thus, the major papilla.
On this page:
Terminology
The term dominant dorsal duct syndrome is sometimes used in the literature to reflect that the main pancreatic duct draining via the minor papilla does not always have the classical pancreas divisum anatomy 8.
The classic description of pancreas divisum refers to the complete form but incomplete and reverse forms have also been described.
Epidemiology
It is the most common variation of pancreatic duct formation and may be present in ~5% (range 4-10%) of the general population 3,4,6. Its MRCP prevalence is ~9% with autopsy prevalence up to 14% 7.
Clinical presentation
Most people with a pancreas divisum are asymptomatic, but this variant is found more frequently in patients with chronic abdominal pain and idiopathic pancreatitis than in the general population 4. Of those with recurrent idiopathic pancreatitis, ~20% (range 12-26%) of patients are thought to have pancreas divisum compared with ~5% (range 3-9%) of the general population 13.
Pathology
It results from failure of fusion of dorsal and ventral pancreatic anlages. As a result, the dorsal pancreatic duct drains most of the pancreatic glandular parenchyma via the minor papilla. Although controversial, this variant is considered a cause of pancreatitis.
Pancreatic divisum can result in a santorinicele, which is a cystic dilatation of the distal dorsal duct (duct of Santorini), immediately proximal to the minor papilla.
Three subtypes are known:
type 1 (classic): no connection at all; occurs in the majority of cases; 70%
type 2 (absent ventral duct): minor papilla drains all of pancreas while major papilla drains bile duct; 20-25%
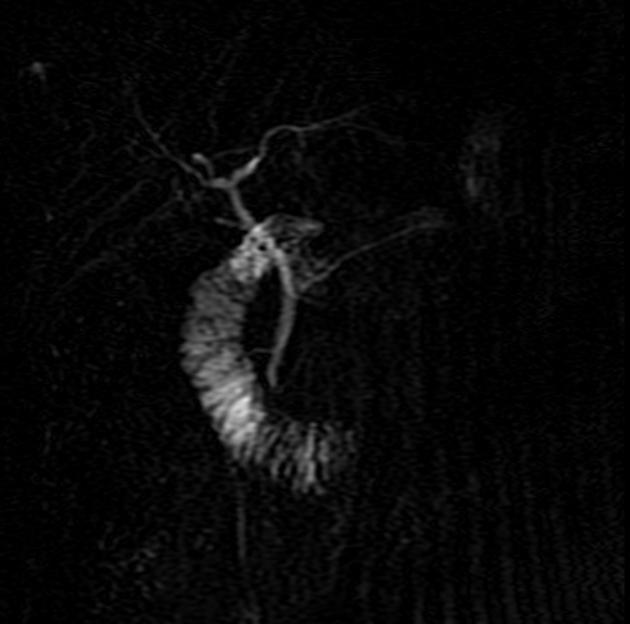
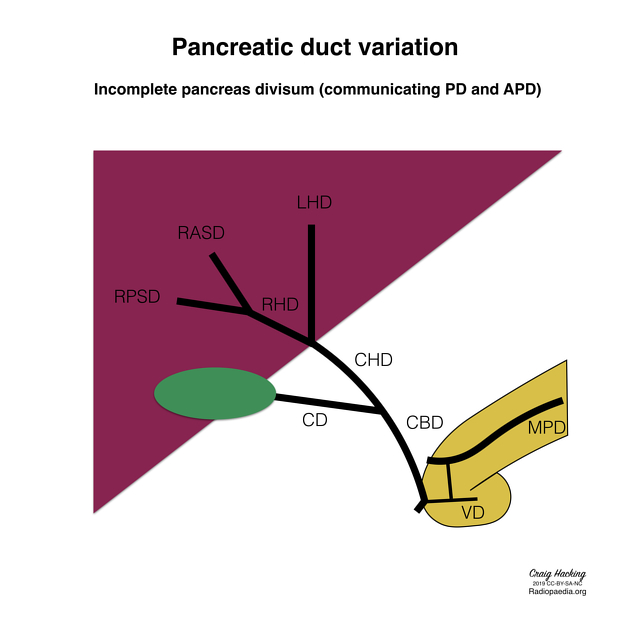
type 3 (functional): filamentous or inadequate connection between dorsal and ventral ducts; 5-6%
Reverse pancreas divisum has been described where the main duct fuses with the ventral duct and a small residual dorsal duct does not communicate with the main duct and drains separately into the minor papilla 9,10.
Radiographic features
Fluoroscopy
ERCP
This was the traditional method of diagnosis where a pancreas divisum was suspected when there was no contrast extending towards the pancreatic tail when administered through the ampulla of Vater.
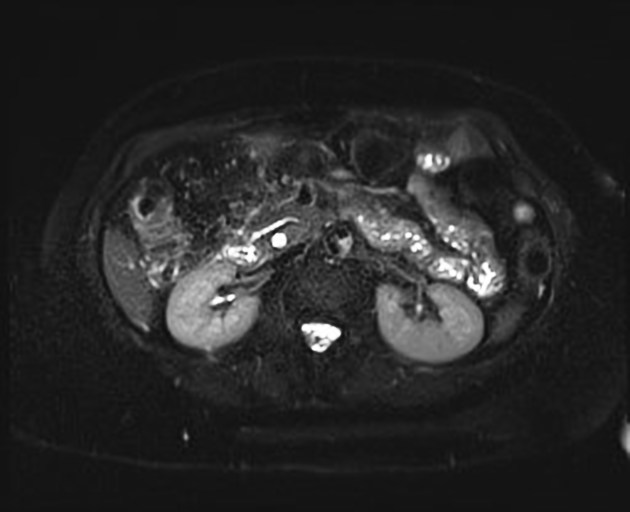
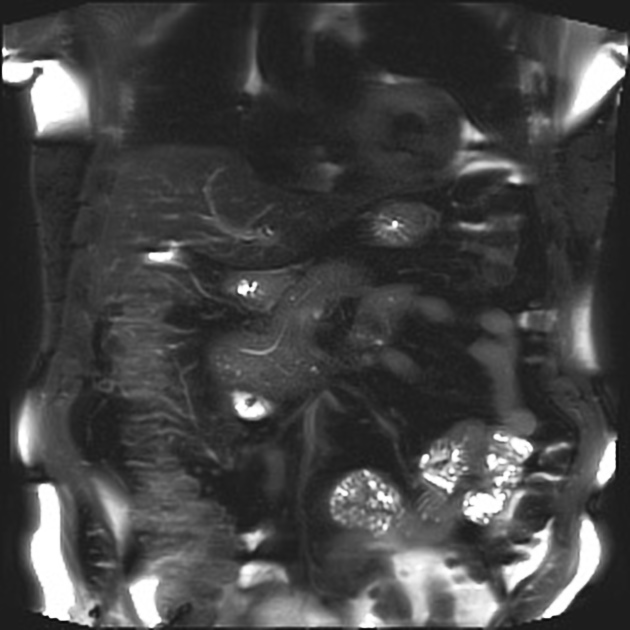
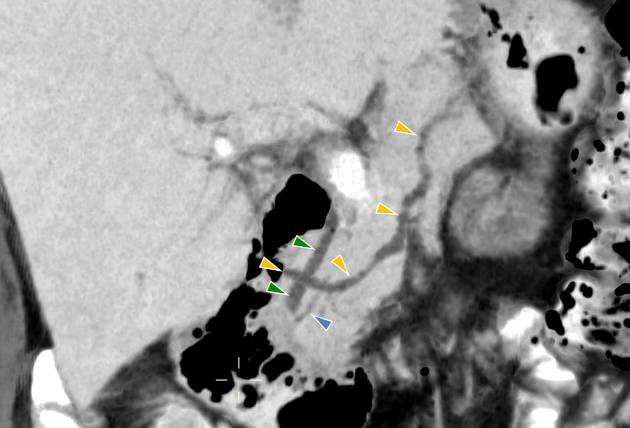
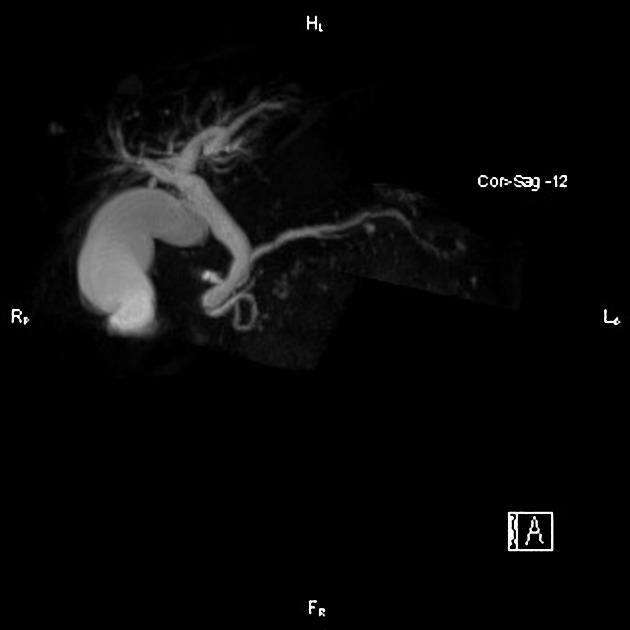
MRI
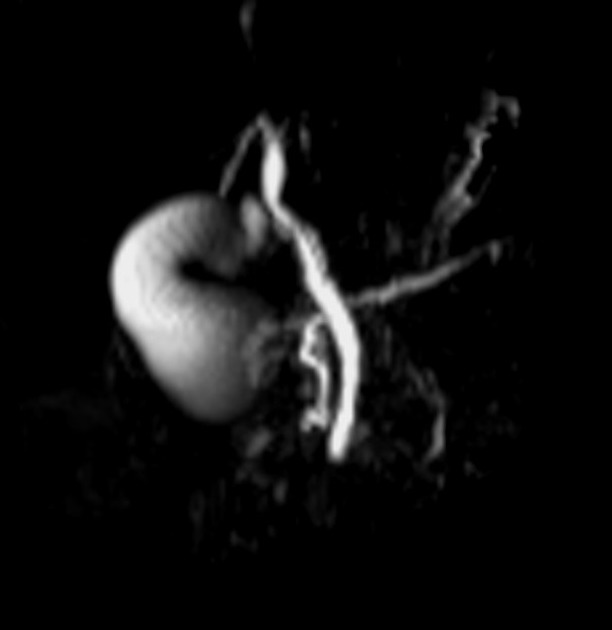
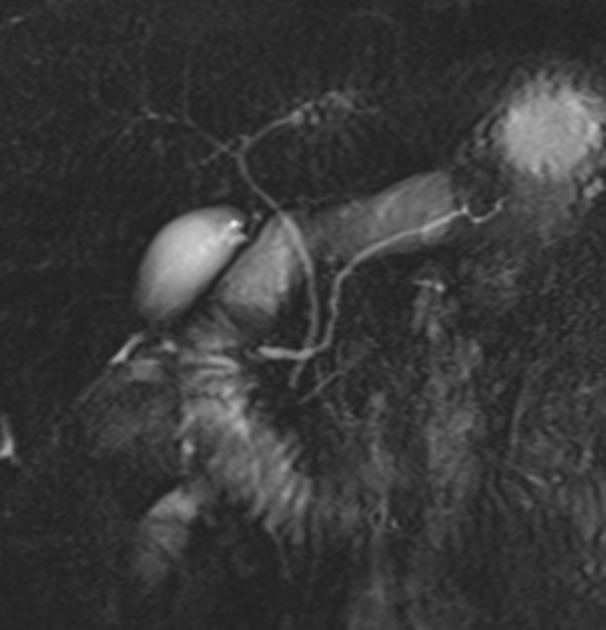
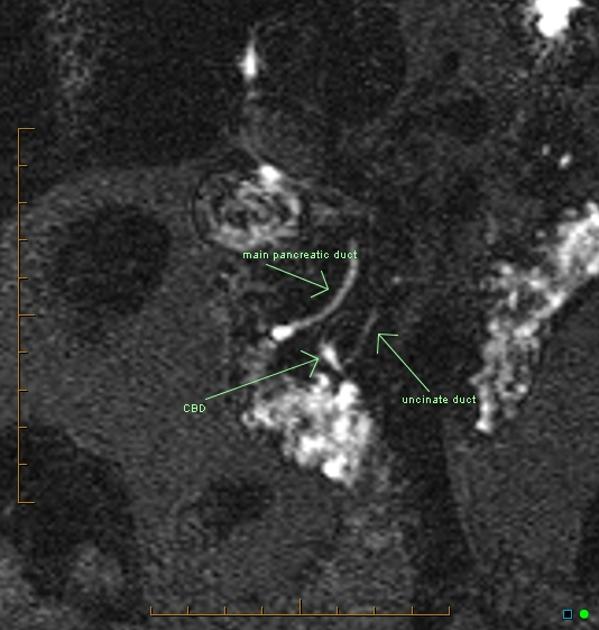
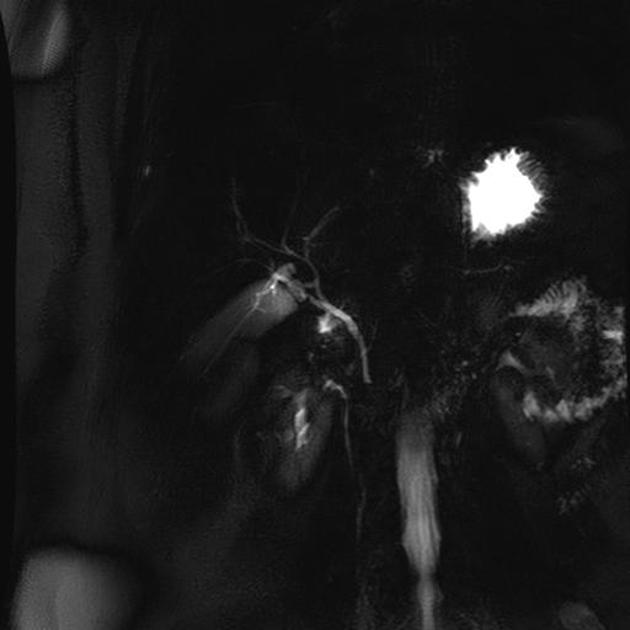
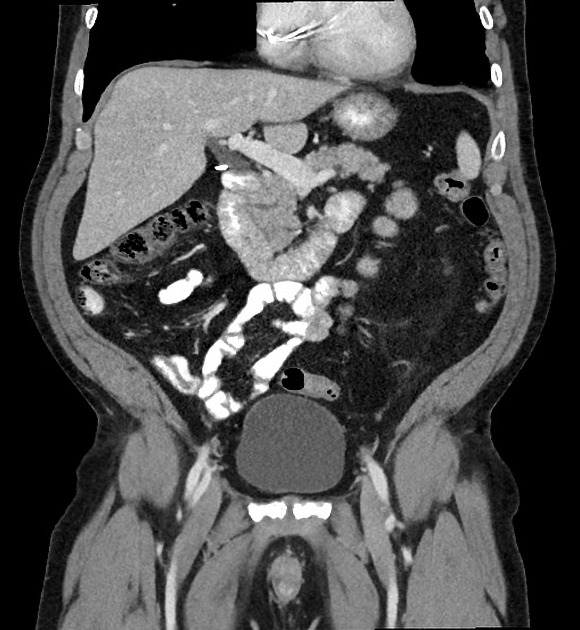
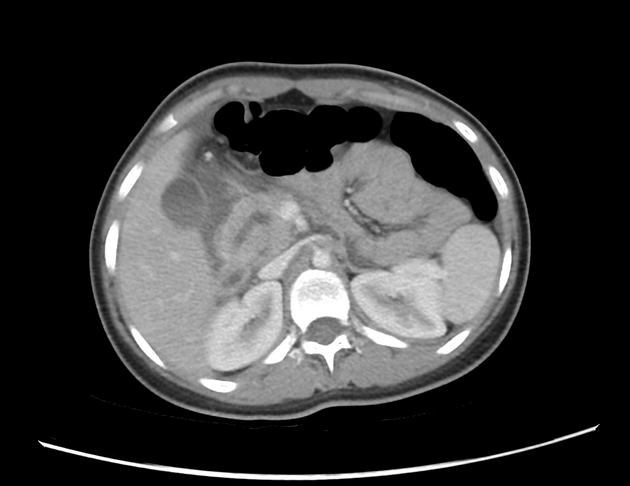
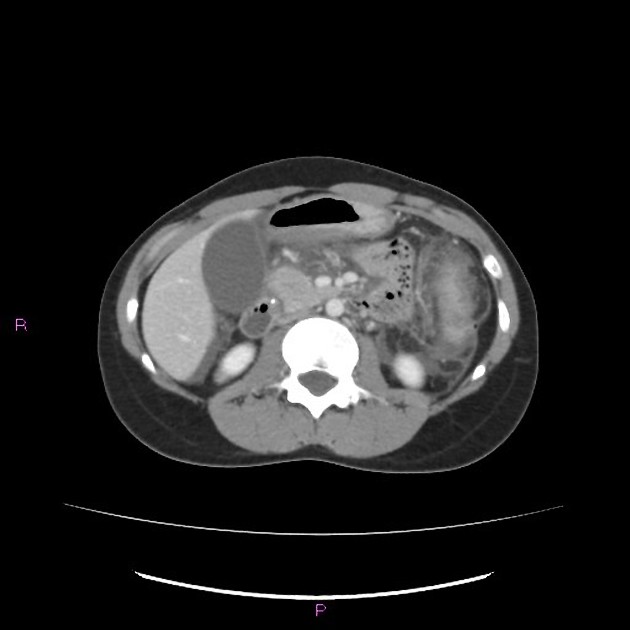
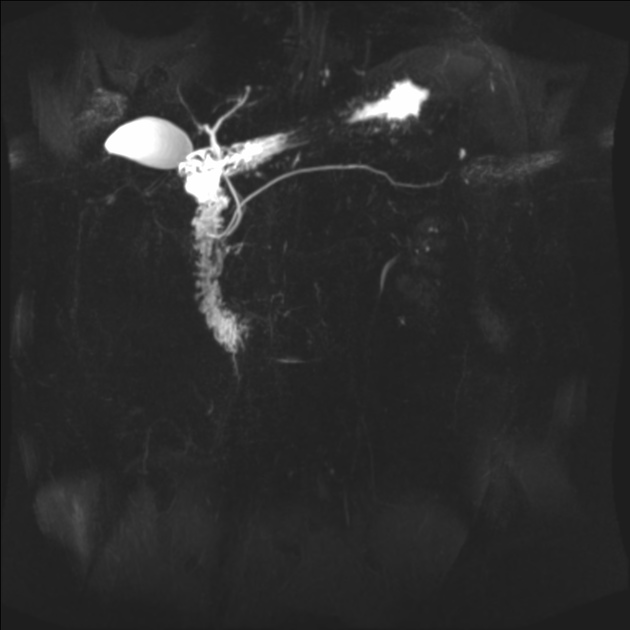
MRI is the gold standard method of evaluation. The key imaging features:
the dorsal pancreatic duct is in direct continuity with the duct of Santorini, which drains into the minor papilla
the ventral pancreatic duct (duct of Wirsung) does not communicate with the dorsal pancreatic duct but joins with the distal common bile duct to enter the major papilla
Some authors claim increased sensitivity of secretin MRCP (S-MRCP) in detection of pancreas divisum 2.
Treatment and prognosis
A diagnosis of pancreas divisum does not routinely warrant treatment, especially when incidental and asymptomatic. In symptomatic patients (e.g. recurrent pancreatitis), management options may include 6:
conservative, non-operative treatment +/- pancreatic enzyme supplements
minor papillotomy
minor papilla stenting
balloon dilatation of any associated stricture












 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.