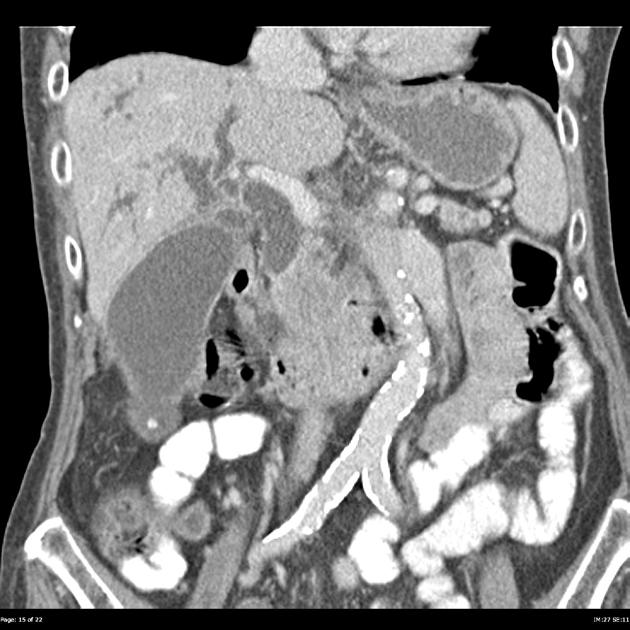
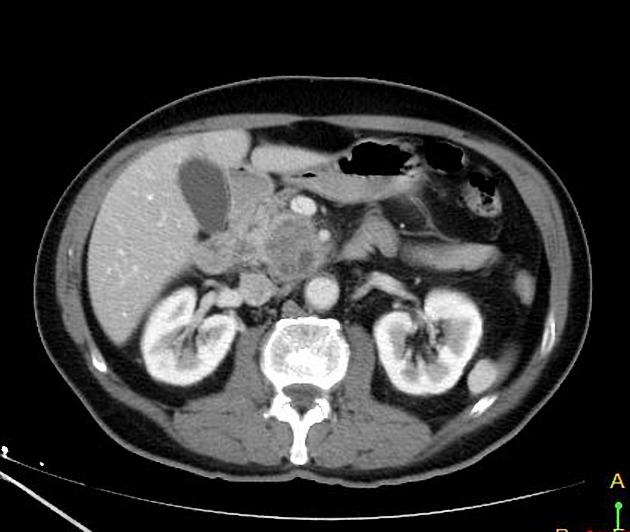
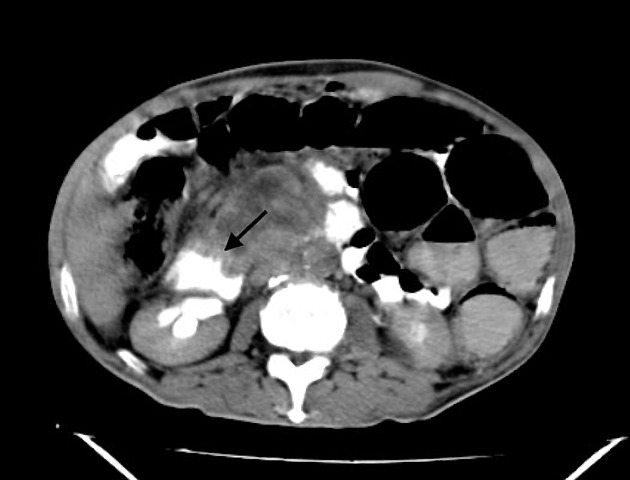
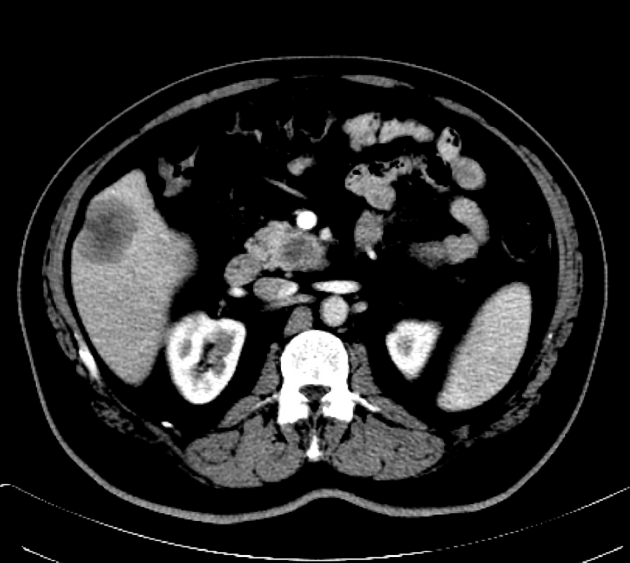
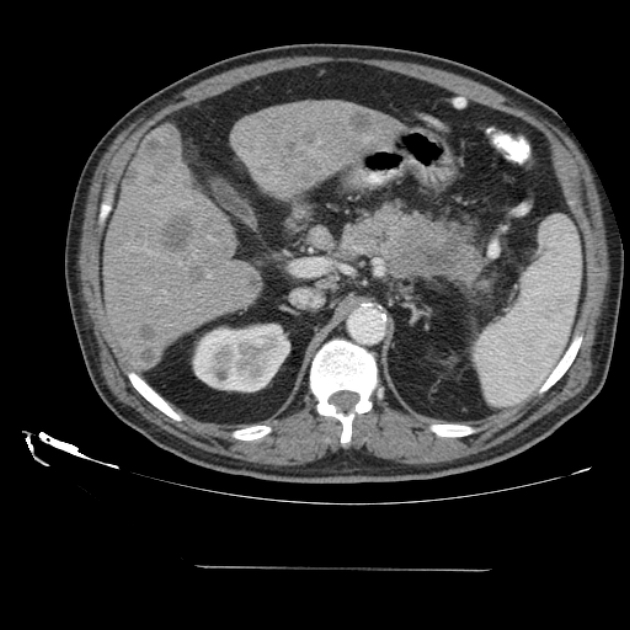
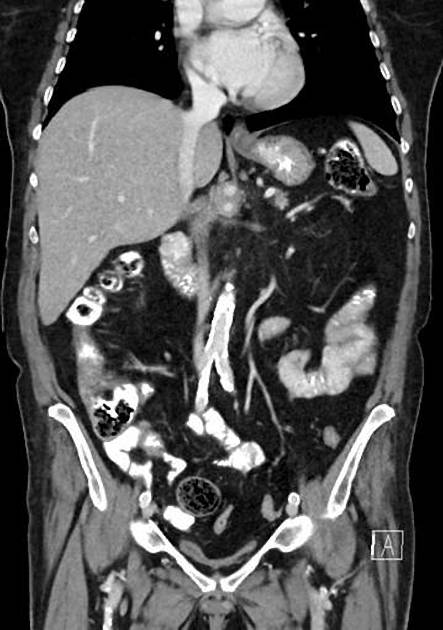
Pancreatic cancer (staging)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- Staging of pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Staging of pancreatic adenocarcinomas
- Pancreatic tumours staging system
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (staging)
Staging of pancreatic cancer (i.e. ductal adenocarcinoma) is traditionally performed according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) / Union for International Cancer Control (IUCC) TNM system.
In the 2017 new edition (8th edition) AJCC published various major changes including exocrine and endocrine tumors of the pancreas are now staged using different staging systems. The following is for the staging of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. In the 8th edition of AJCC, T staging has become more size-based rather than descriptive-based, resectability has been omitted from T4 category, and the number and not just the presence of the regional lymph nodes defines the N stage of disease 1,3.
As the majority of tumors are non-resectable, staging is primarily achieved with imaging, although laparoscopy is often required to confirm resectability. CT is the preferred modality for assessing resectability 2.
Primary tumor staging (T)
Tx, T0, Tis: see TNM system
-
T1: tumor ≤2 cm in greatest dimension
T1a: tumor ≤0.5 cm in greatest dimension
T1b: tumor >0.5 cm and <1 cm in greatest dimension
T1c: tumor 1-2 cm in greatest dimension
T2: tumor >2 cm in greatest dimension but less than ≤4 cm
T3: tumor >4 cm in greatest dimension
T4: involvement of celiac axis, superior mesenteric artery and/or common hepatic artery
Regional lymph nodes (N)
Nx: nodes cannot be assessed
N0: no evidence of nodal involvement
N1: 1-3 regional node metastases present
N2: 4 or more regional node metastases present
Metastases (M)
Mx: presence of metastases cannot be assessed
M0: no evidence of metastases
M1: distant metastases present
Stage groupings
stage 0: Tis N0 M0
stage Ia: T1 N0 M0
stage Ib: T2 N0 M0
stage IIa: T3 N0 M0
stage IIb: T1, T2, or T3 with N1 M0
stage III: N2 M0 with any T, or T4 with any N M0
stage IV: M1 with any T and N
References
- 1. Stephen Edge, David R. Byrd, Carolyn C. Compton et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Handbook. (2011) ISBN: 9780387884424 - Google Books
- 2. Bipat S, Phoa S, van Delden O et al. Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis and Determining Resectability of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2005;29(4):438-45. doi:10.1097/01.rct.0000164513.23407.b3 - Pubmed
- 3. Chun Y, Pawlik T, Vauthey J. 8th Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Pancreas and Hepatobiliary Cancers. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25(4):845-7. doi:10.1245/s10434-017-6025-x - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma with liver cirrhosis
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma - liver metastases
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma - staging teaching case
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma with preoperative staging and postoperative Whipple images
- Locally advanced pancreatic cancer
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Focal fat infiltration mimicking liver metastasis
- Pancreatic cancer
- Gastric outlet obstruction - pancreatic cancer
- Pancreas adenocarcinoma - uncinate process
- Metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma of the tail with colon obstruction
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (unresectable)
- Hepatic metastases from pancreatic cancer
- Pancreatic carcinoma
- Pancreatic carcinoma
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Pancreatic head adenocarcinoma with choledocoduodenal fistula
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- benign epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumors
- primary malignant epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumors
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumors
- hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumors
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumors
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic hemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumor
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumor
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumor
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumors
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumors
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.