Superior cerebellar peduncle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Charlie Chia-Tsong Hsu had no recorded disclosures.
View Charlie Chia-Tsong Hsu's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- Superior cerebellar peduncle (SCP)
- Superior cerebellar peduncles
- Brachium conjunctivum
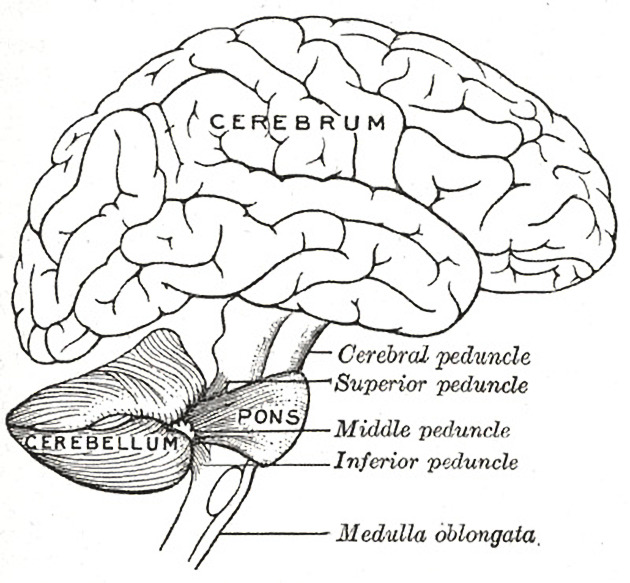
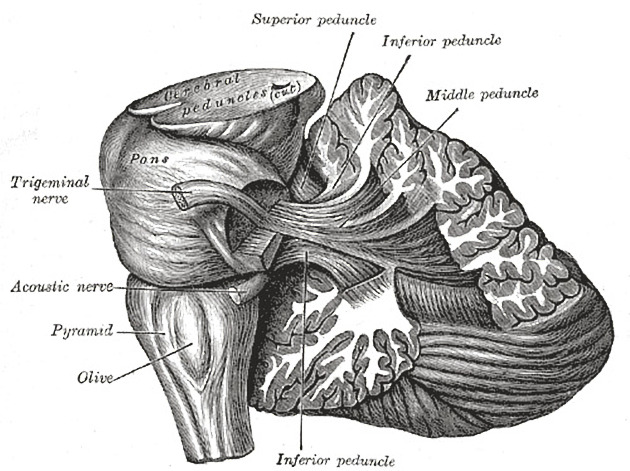
The superior cerebellar peduncles, also known as the brachium conjunctivum, are paired white matter fiber tracts that connect the cerebellum with the midbrain. The superior cerebellar peduncle contains vital afferent and efferent fibers including cerebellothalamic, cerebellorubral and ventrospinocerebellar tracts.
On this page:
Radiographic features
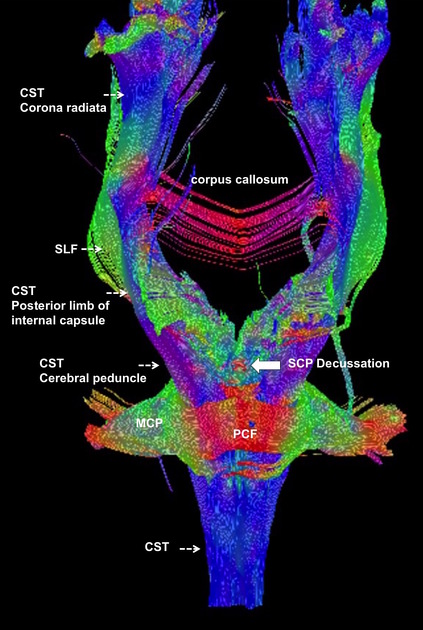
The superior cerebellar peduncles decussate centrally (decussation of Wernekinck) in the ventral midbrain at the level of the inferior colliculi. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) enables depiction of the superior cerebellar peduncle decussation and on the color-coded fractional anisotropy map this is seen as a red dot in the ventral midbrain (conventionally, red denote transversely-oriented fibers).
The thin superior medullary velum is suspended between the two peduncles.
Arterial supply
The superior cerebellar peduncles receive their arterial blood supply through branches of the superior cerebellar artery.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Related pathology
Joubert syndrome: there is absence of superior cerebellar peduncle decussation, giving the characteristic molar tooth sign
Wernekinck commissure syndrome: syndrome caused by a lesion to the superior cerebellar peduncle decussation, usually from ischemic stroke
References
- 1. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Elsevier. ISBN:B01434QBDI. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Last's anatomy, regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:044304662X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Cerebellum
- Central control of respiration
- Hypertrophic olivary degeneration
- Wernekinck commissure syndrome
- Hypomyelination with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and leg spasticity
- Leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Syndrome of the trigone
- Joubert syndrome
- Nothnagel syndrome
- Progressive supranuclear palsy
- Dentate nucleus
- Spinocerebellar tract
- Diffuse axonal injury (grading)
- Molar tooth sign (CNS)
- Superior medullary velum
- Spetzler-Martin arteriovenous malformation grading system
- Double panda sign
- Joubert syndrome
- Wernekinck commissure syndrome
- Guineafowl (Rorschach radiology)
- Joubert syndrome related disorders (JSRD)
- Hypertrophic olivary degeneration
- Pontocerebellar hypoplasia
- Joubert syndrome
- Pontocerebellar hypoplasia
- Joubert syndrome with schizencephaly and posterior fossa cyst
- Chronic lymphocytic inflammation with pontine perivascular enhancement responsive to steroids (CLIPPERS)
- Joubert syndrome
- Cerebellar peduncles (Gray's illustration)
- Cerebellar peduncles (Gray's illustration)
- Decussation of fibres in the brainstem (Gray's illustration)
- Wernekink commissure syndrome
- Cerebellar mutism syndrome and pilocytic astrocytoma
- Decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle on diffusion tensor imaging
- Decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle on diffusion tensor imaging
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.