Atlanto-occipital dissociation injuries
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Liz Silverstone had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Liz Silverstone's current disclosures- Atlanto-occipital dissociation (AOD)
- Atlanto-occipital dislocations
- Atlanto-occipital subluxations
- Atlanto-occipital dissociation
Atlanto-occipital dissociation injuries are severe and include both atlanto-occipital dislocations and atlanto-occipital subluxations.
On this page:
Pathology
The tectorial membrane and alar ligaments provide most of the stability to the atlanto-occipital joint, and injury to these ligaments results in instability due to low inherent osseous stability 3.
Classification
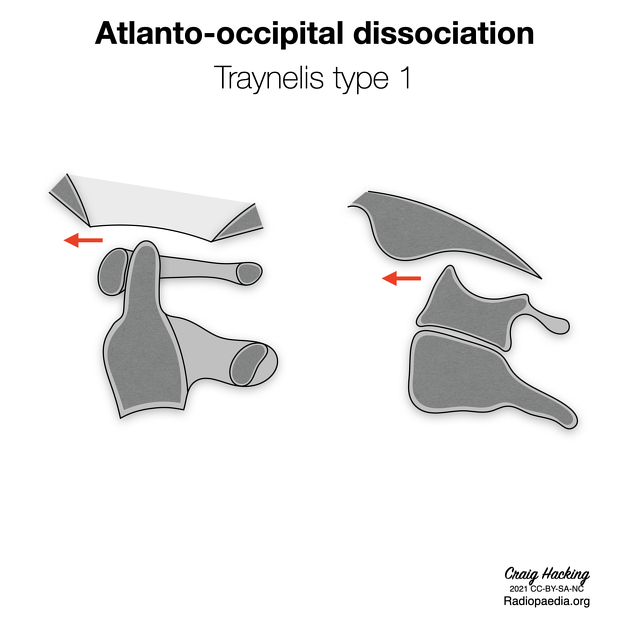
The Traynelis classification describes injuries according to the displacement of the occipital condyles relative to the atlas.
The AO Spine classification of upper cervical injuries is another classification system split into location-specific patterns and then further subdivided according to injury type and presence of neurological signs and/or modifying factors.
Radiographic features
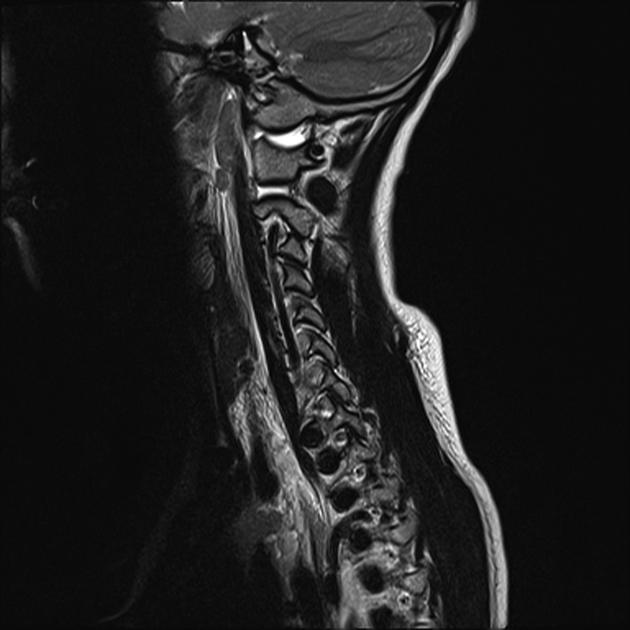
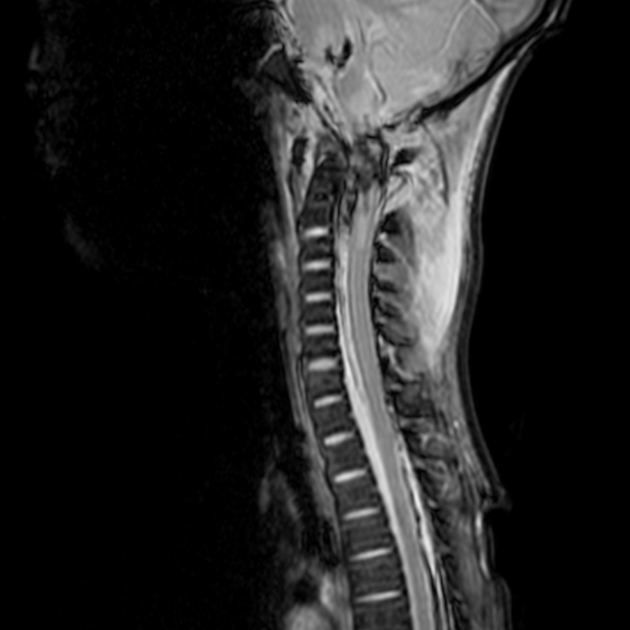
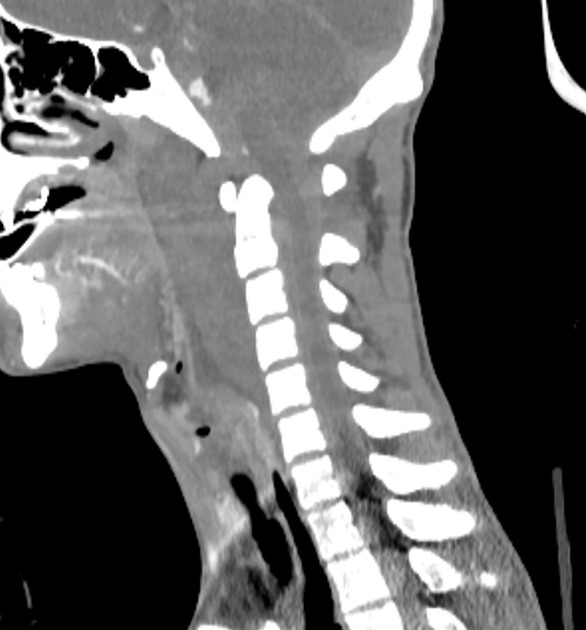
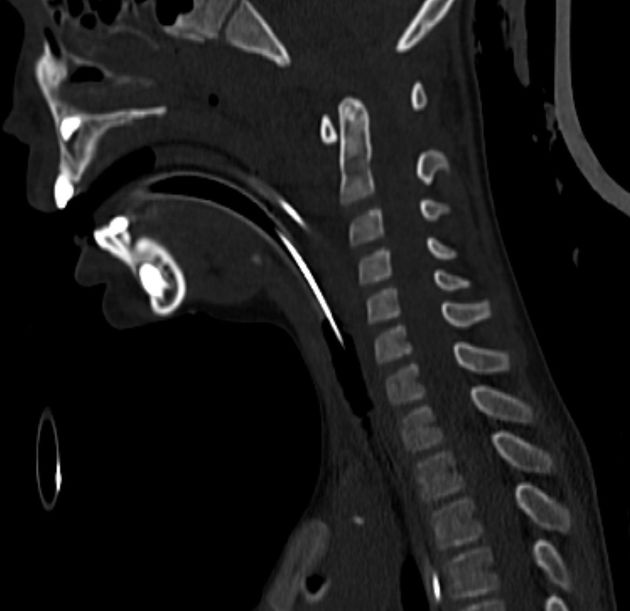
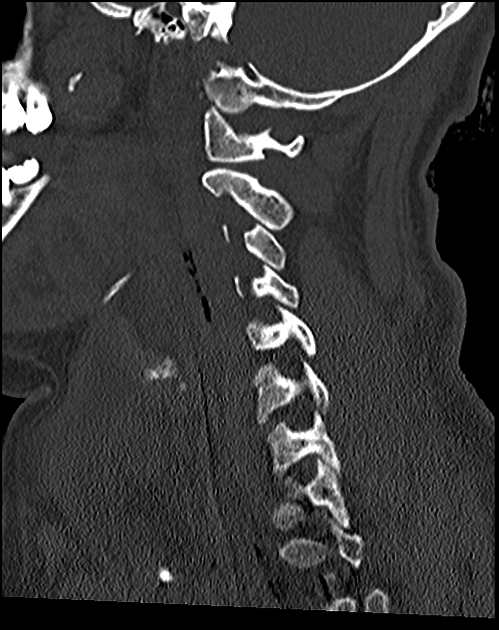
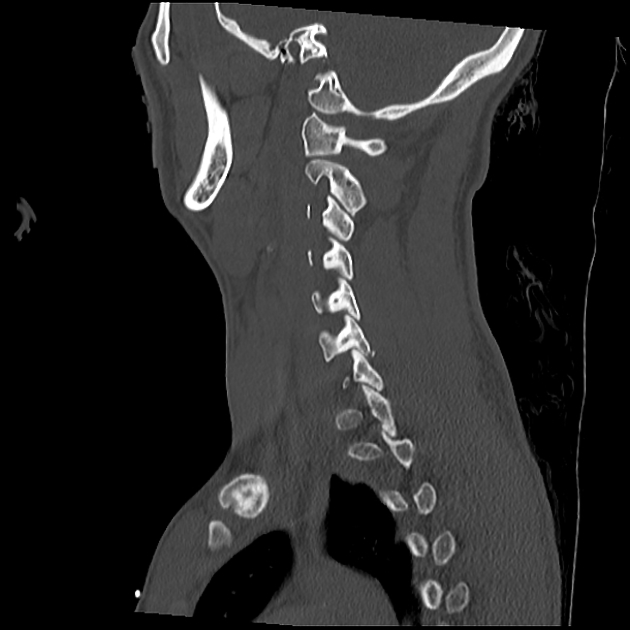
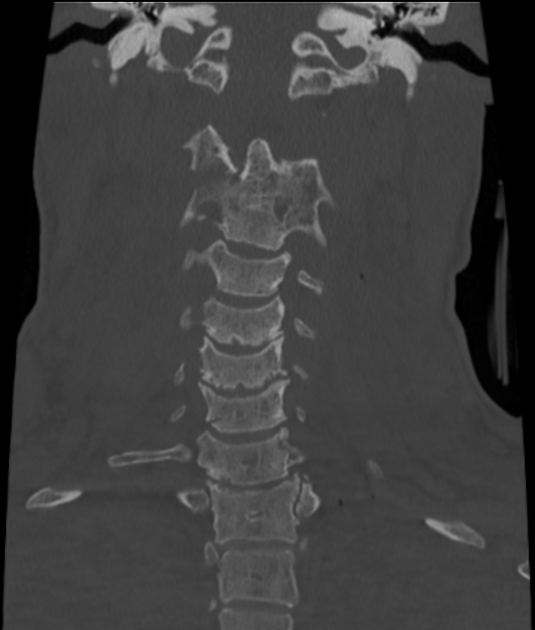
The key to the diagnosis, in addition to identifying gross disruption of the normal alignment of the atlanto-occipital joint, hinges on using a number of lines on the lateral horizontal shoot-through cervical spine film 1:
basion-dens interval (BDI) >10 mm in adults 3
basion-axial interval (BAI) >12 mm in adults
Powers ratio >1 (insensitive to a vertical distraction injury or posterior dissociation)
-
>3 mm in adult males
>2.5 mm in adult females
CT
For pediatric patients, the condyle-C1 interval (CCI) has been shown to provide the highest diagnostic accuracy 4.
condyle-C1 interval (CCI) >4 mm in children
Differential diagnosis
Jefferson fracture: anterior and posterior C1 ring fracture, possible lateral masses displacement
odontoid fracture: type 2 will cause posterior dens displacement and will disrupt Powers ratio
atlanto-axial subluxation: atlantoaxial rotatory fixation will cause C1 lateral mass asymmetry relative to the dens
Down syndrome: atlanto-occipital instability due to laxity of the alar ligament
rheumatoid arthritis: CT/MRI will show atlantooccipital instability due to pannus destabilisation of joints and ligaments, and x-ray will show erosions
References
- 1. Rojas C, Bertozzi J, Martinez C, Whitlow J. Reassessment of the Craniocervical Junction: Normal Values on CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(9):1819-23. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0660 - Pubmed
- 2. Hall G, Kinsman M, Nazar R et al. Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation. World J Orthop. 2015;6(2):236-43. doi:10.5312/wjo.v6.i2.236 - Pubmed
- 3. Riascos R, Bonfante E, Cotes C, Guirguis M, Hakimelahi R, West C. Imaging of Atlanto-Occipital and Atlantoaxial Traumatic Injuries: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Radiographics. 2015;35(7):2121-34. doi:10.1148/rg.2015150035 - Pubmed
- 4. Pang D, Nemzek W, Zovickian J. Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation--Part 2: The Clinical Use of (Occipital) Condyle-C1 Interval, Comparison with Other Diagnostic Methods, and the Manifestation, Management, and Outcome of Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation in Children. Neurosurgery. 2007;61(5):995-1015; discussion 1015. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000303196.87672.78 - Pubmed
- 5. Kasliwal M, Fontes R, Traynelis V. Occipitocervical Dissociation-Incidence, Evaluation, and Treatment. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2016;9(3):247-54. doi:10.1007/s12178-016-9347-6 - Pubmed
- 6. Divi S, Schroeder G, Oner F et al. AOSpine-Spine Trauma Classification System: The Value of Modifiers: A Narrative Review With Commentary on Evolving Descriptive Principles. Global Spine J. 2019;9(1 Suppl):77S-88S. doi:10.1177/2192568219827260 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Atlas (C1)
- Occipital condyle fracture
- Basion
- Opisthion
- Basion-dens interval
- Atlanto-occipital articulation
- Torticollis
- AO Spine classification of upper cervical injuries
- Cervical spine fractures
- Cervical spine injury
- Powers ratio
- Wackenheim line
- Basion-axial interval
- Musculoskeletal curriculum
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (A)
- Traynelis classification of atlanto-occipital dislocations
- Condyle-C1 interval (CCI)
- Atlantodental interval
- Atlanto-occipital dissociation
- Craniocervical dissociation
- Atlanto-occipital dissociation with vertebral artery transection
- Atlanto-occipital dissociation (Traynelis type 1), C2 teardrop fracture, C6/7 facet joint dislocation
- Atlanto-occipital dissociation - Traynelis type 1
- Traynelis classification of atlanto-occipital dissociation (diagrams)
- Craniocervical dissociation with basilar artery transection
- Atlanto-occipital and atlantoaxial distraction
- Craniocervical dissociation
- Hypoxic ischaemic injury, diffuse axonal injury and atlanto-occipital dislocation
- Atlanto-occipital dislocation
- Base of skull lines (annotated images)
- Atlanto-occipital dissociation
- Craniocervical junction distraction injury
- Atlantooccipital dissociation
- Atlanto-occipital disassociation
Related articles: Fractures
-
fracture
- terminology[+][+]
- fracture location
- diaphyseal fracture
- metaphyseal fracture
- physeal fracture
- epiphyseal fracture
- fracture types
- avulsion fracture
- articular surface injuries
- complete fracture
- incomplete fracture
- infraction
- compound fracture
- pathological fracture
- stress fracture
- fracture displacement
- fracture location
- fracture healing[+][+]
- skull fractures
-
facial fractures[+][+]
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
- alveolar process fractures
- frontal sinus fracture
- isolated zygomatic arch fractures
- mandibular fracture
- nasal bone fracture
- orbital blow-out fracture
- paranasal sinus fractures
- complex fractures
- dental fractures
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
-
spinal fractures[+][+]
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- AO classification of upper cervical injuries
- AO classification of subaxial injuries
- Anderson and D'Alonzo classification (odontoid fracture)
- Roy-Camille classification (odontoid process fracture)
- Gehweiler classifcation (atlas fractures)
- Levine and Edwards classification (hangman fracture)
- Allen and Ferguson classification (subaxial spine injuries)
- subaxial cervical spine injury classification (SLIC)
- thoracolumbar spinal fracture classification systems
- three column concept of spinal fractures (Denis classification)
- classification of sacral fractures
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- spinal fractures by region
- spinal fracture types
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
- rib fractures[+][+]
- sternal fractures
-
upper limb fractures[+][+]
- classification
- Rockwood classification (acromioclavicular joint injury)
- AO classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO/OTA classification of distal humeral fractures
- Milch classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Weiss classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Bado classification of Monteggia fracture-dislocations (radius-ulna)
- Mason classification (radial head fracture)
- Frykman classification (distal radial fracture)
- Mayo classification (scaphoid fracture)
- Hintermann classification (gamekeeper's thumb)
- Eaton classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- Keifhaber-Stern classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- upper limb fractures by region
- shoulder
- clavicular fracture
-
scapular fracture
- acromion fracture
- coracoid process fracture
- glenoid fracture
- humeral head fracture
- proximal humeral fracture
- humeral neck fracture
- arm
- elbow
- forearm
- wrist
-
carpal bones
- scaphoid fracture
- lunate fracture
- capitate fracture
- triquetral fracture
- pisiform fracture
- hamate fracture
- trapezoid fracture
- trapezium fracture
- hand
- shoulder
- classification
- lower limb fractures[+][+]
- classification by region
- pelvic fractures
- hip fractures
- Pipkin classification (femoral head fracture)
- Garden classification (hip fracture)
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Cooke and Newman classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Johansson classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Vancouver classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- femoral
- knee
- Schatzker classification (tibial plateau fracture)
- AO classification of distal femur fractures
- Meyers and McKeevers classification (anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture)
- tibia/fibula
- Watson-Jones classification (tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture)
- ankle
- foot
- Berndt and Harty classification (osteochondral lesions of the talus)
- Sanders CT classification (calcaneal fracture)
- Hawkins classification (talar neck fracture)
- Myerson classification (Lisfranc injury)
- Nunley-Vertullo classification (Lisfranc injury)
- pelvis and lower limb fractures by region
- pelvic fracture
- sacral fracture
- coccygeal fracture
-
hip
- acetabular fracture
- femoral head fracture
-
femoral neck fracture
- subcapital fracture
- transcervical fracture
- basicervical fracture
-
trochanteric fracture
- pertrochanteric fracture
- intertrochanteric fracture
- subtrochanteric fracture
- femur
- mid-shaft fracture
- bisphosphonate-related fracture
- distal femoral fracture
- knee
- avulsion fractures
- Segond fracture
- reverse Segond fracture
- anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- arcuate complex avulsion fracture (arcuate sign)
- biceps femoris avulsion fracture
- iliotibial band avulsion fracture
- semimembranosus tendon avulsion fracture
- Stieda fracture (MCL avulsion fracture)
- patellar fracture
- tibial plateau fracture
- avulsion fractures
- leg
- tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture
- tibial shaft fracture
- fibular shaft fracture
- Maisonneuve fracture
- ankle
- foot
- tarsal bones
- metatarsal bones
- phalanges
- classification by region
- terminology[+][+]








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.