Bifid median nerve
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Charudutt Jayant Sambhaji had no recorded disclosures.
View Charudutt Jayant Sambhaji's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
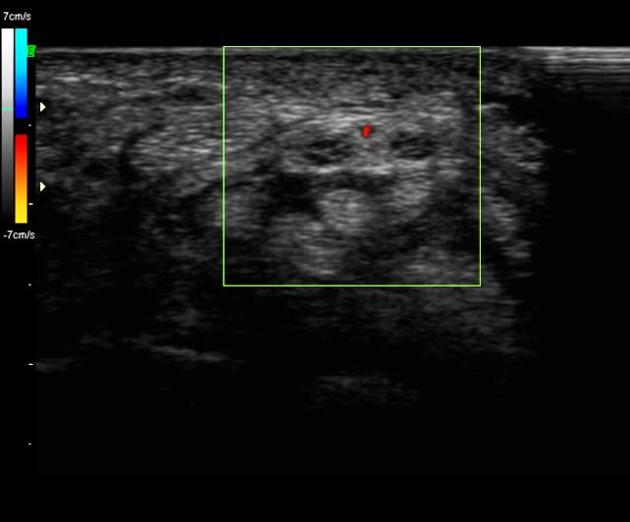
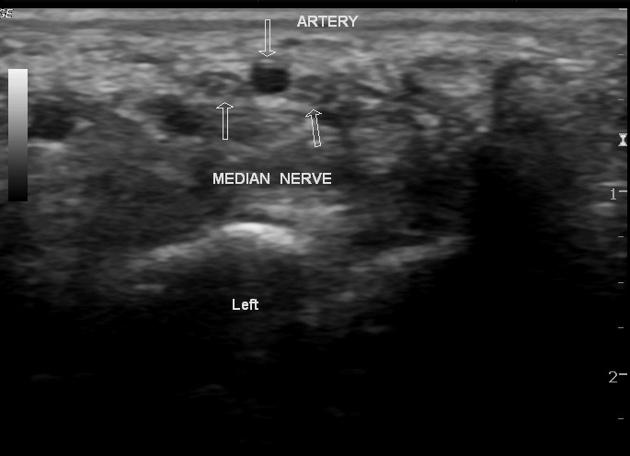
View Yoshi Yu's current disclosuresA bifid median nerve is an uncommon anatomical variation in the forearm and has an increased association with a persistent median artery 4.
On this page:
Images:
Epidemiology
It has an incidence of 9-19% 4. A persistent median artery is present in approximately half of those with a bifid median nerve 4.
Gross anatomy
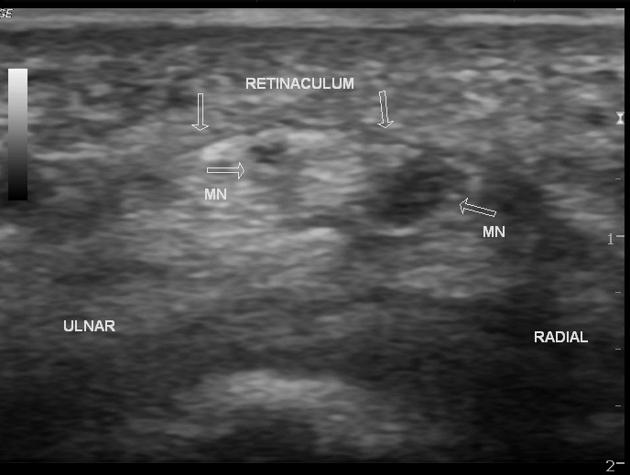
The median nerve usually divides into two or three branches after exiting the distal edge of the flexor retinaculum that covers the carpal tunnel. These subdivide into digital nerves that supply opposing sides of the digits. The median nerve may divide into two nerve bundles in the distal forearm and appear as a bifid median nerve in the carpal tunnel.
When present, the persistent median artery of the forearm lies in between the two nerve bundles. The artery and bifid nerve can be enclosed by a common epineurium.
Practical points
As the median artery can be easily detected on ultrasound, it is essential that this be mentioned in the radiologist's report to avoid inadvertent injury to the nerve and artery during surgical release of the transverse carpal ligament.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Propeck T, Quinn T, Jacobson J, Paulino A, Habra G, Darian V. Sonography and MR Imaging of Bifid Median Nerve with Anatomic and Histologic Correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;175(6):1721-5. doi:10.2214/ajr.175.6.1751721 - Pubmed
- 2. Gassner E, Schocke M, Peer S, Schwabegger A, Jaschke W, Bodner G. Persistent Median Artery in the Carpal Tunnel: Color Doppler Ultrasonographic Findings. J Ultrasound Med. 2002;21(4):455-61. doi:10.7863/jum.2002.21.4.455 - Pubmed
- 3. Bayrak I, Bayrak A, Kale M, Turker H, Diren B. Bifid Median Nerve in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J Ultrasound Med. 2008;27(8):1129-36. doi:10.7863/jum.2008.27.8.1129 - Pubmed
- 4. Eyer B. Persistent Median Artery - Radsource. Radsource. Radsource
Incoming Links
- Trifid median nerve
- Persistent median artery of the forearm with bifid median nerve - bilateral
- Bifid median nerve and persistent median artery of the forearm
- Bifid median nerve
- Bifid median nerve and persistant median artery
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery of upper limb
- Carpal tunnel syndrome - with inverted notch sign
- Carpal tunnel syndrome in bifid median nerve
- Bilateral persistent median artery of the forearm with unilateral bifid median nerve
- Bifid median nerve and persistent median artery of the forearm
Related articles: Anatomy: Upper limb
-
skeleton of the upper limb
- clavicle
- scapula
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- hand
- accessory ossicles of the upper limb
- accessory ossicles of the shoulder
- accessory ossicles of the elbow
-
accessory ossicles of the wrist (mnemonic)
- os centrale carpi
- os epilunate
- os epitriquetrum
- os styloideum
- os hamuli proprium
- lunula
- os triangulare
- trapezium secondarium
- os paratrapezium
- os radiostyloideum (persistent radial styloid)
- joints of the upper limb
-
pectoral girdle
-
shoulder joint
- articulations
- associated structures
- joint capsule
- bursae
- ligaments
- movements
- scapulothoracic joint
-
glenohumeral joint
- arm flexion
- arm extension
- arm abduction
- arm adduction
- arm internal rotation (medial rotation)
- arm external rotation (lateral rotation)
- circumduction
- arterial supply - scapular anastomosis
- ossification centers
-
shoulder joint
-
elbow joint
- proximal radioulnar joint
- ligaments
- associated structures
- movements
- alignment
- arterial supply - elbow anastomosis
- development
-
wrist joint
- articulations
-
ligaments
- intrinsic ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments
- radioscaphoid ligament
- dorsal intercarpal ligament
- dorsal radiotriquetral ligament
- dorsal radioulnar ligament
- volar radioulnar ligament
- radioscaphocapitate ligament
- long radiolunate ligament
- Vickers ligament
- short radiolunate ligament
- ulnolunate ligament
- ulnotriquetral ligament
- ulnocapitate ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- associated structures
- extensor retinaculum
- flexor retinaculum
- joint capsule
- movements
- alignment
- ossification centers
-
hand joints
- articulations
- carpometacarpal joint
-
metacarpophalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
-
interphalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
- movements
- ossification centers
- articulations
-
pectoral girdle
- spaces of the upper limb
- muscles of the upper limb
- shoulder girdle
- anterior compartment of the arm
- posterior compartment of the arm
-
anterior compartment of the forearm
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
-
posterior compartment of the forearm (extensors)
- superficial
- deep
- muscles of the hand
-
accessory muscles
- elbow
- volar wrist midline
- palmaris longus profundus
- aberrant palmaris longus
- volar wrist radial-side
- accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis
- flexor indicis profundus
- flexor carpi radialis vel profundus
- accessory head of the flexor pollicis longus (Gantzer muscle, common)
- volar wrist ulnar-side
- dorsal wrist
- blood supply to the upper limb
-
arteries
- subclavian artery (mnemonic)
- axillary artery
- brachial artery (proximal portion)
- ulnar artery
- radial artery
- veins
-
arteries
- innervation of the upper limb
- intercostobrachial nerve
-
brachial plexus (mnemonic)
- branches from the roots
- branches from the trunks
- branches from the cords
- lateral cord
- posterior cord
- medial cord
- terminal branches
- lymphatic drainage of the upper limb





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.