Choroid plexus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Margaret Nguyen had no recorded disclosures.
View Margaret Nguyen's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosuresThe choroid plexus is located within the cerebral ventricles and is made of choroidal epithelial cells (type of ependymal cell), loose connective tissue (tela choroidea), and permeable capillaries. It produces cerebrospinal fluid.
The choroid plexuses also form the blood-CSF barrier alongside arachnoid and arachnoid villi 2.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Location
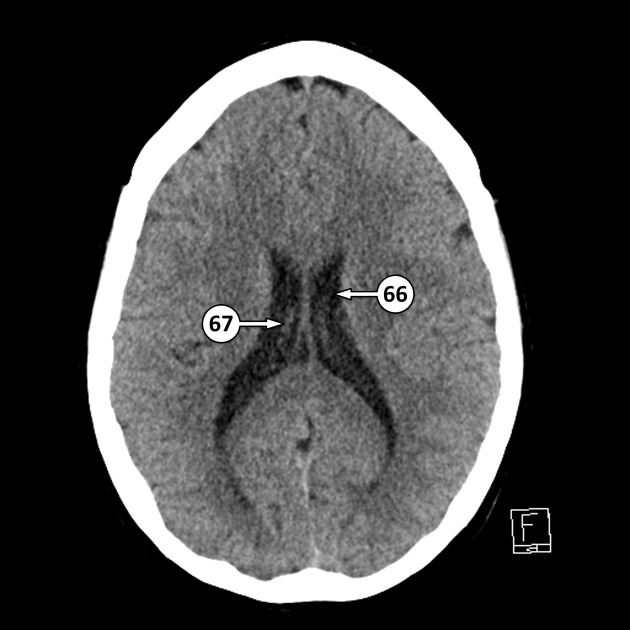
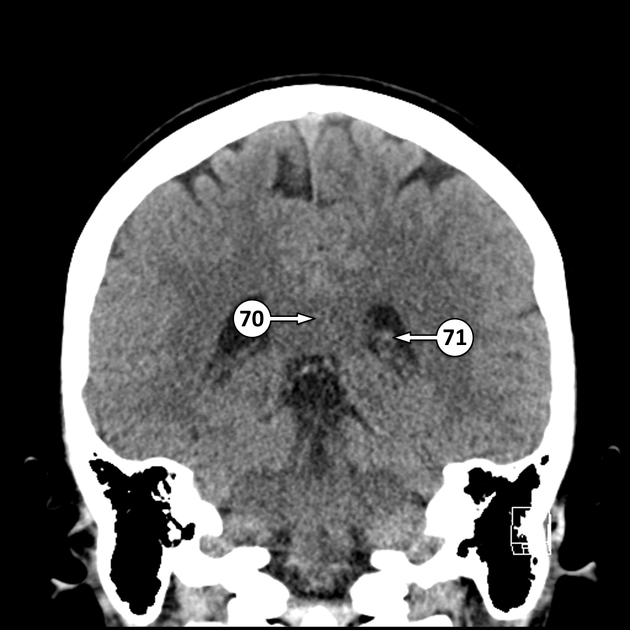
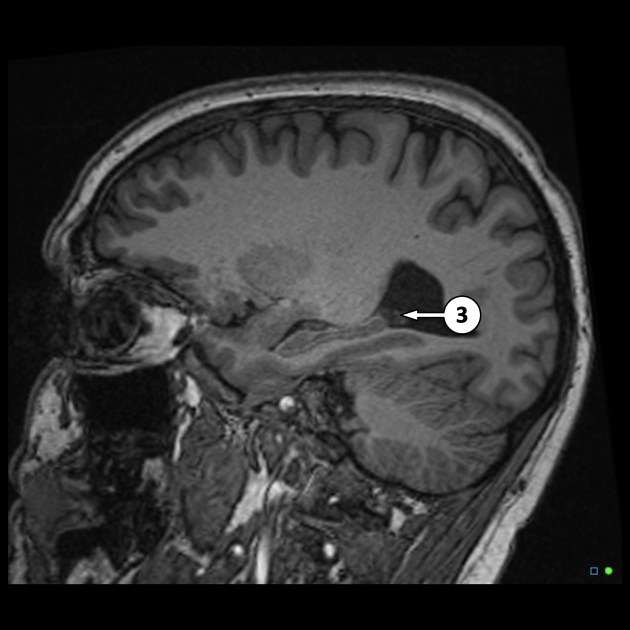
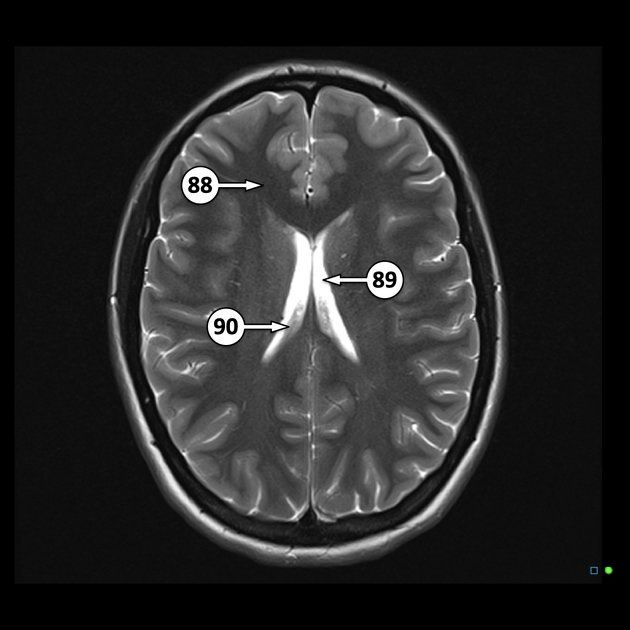
the roof of the temporal horns of the lateral ventricles, extending along the floor of the body of the lateral ventricles, through the interventricular foramen of Monro, and along the roof of the third ventricle. They typically do not extend into the frontal or occipital horns of the lateral ventricles
the medullary part of the fourth ventricle, extending into the lateral apertures (of Luschka)
Radiographic features
CT and MRI
Rich in blood supply and lack of blood-brain barrier lead to avid enhancement of a normal choroid plexus after contrast administration. However, the enhancement may appear asymmetrical on both sides of the brain or mass-like, leading to false interpretations of tumor 4.
On the other hand, choroid plexus can be entirely calcified and lack enhancement which can resemble other types of non-enhancing tumors such as tuberculoma, neurocysticercorsis, non-enhancing meningioma or schwannoma 4.
Related pathology
-
vascular
-
infection and inflammation
-
neoplastic
References
- 1. Strazielle N & Ghersi-Egea J. Choroid Plexus in the Central Nervous System: Biology and Physiopathology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2000;59(7):561-74. doi:10.1093/jnen/59.7.561 - Pubmed
- 2. Liddelow S. Development of the Choroid Plexus and Blood-CSF Barrier. Front Neurosci. 2015;9:32. doi:10.3389/fnins.2015.00032 - Pubmed
- 3. Last RJ, McMinn RMH. Last's Anatomy Regional and Applied. 9th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 2003. p. 589-590.
- 4. McKinney A. Choroid Plexus: Normal Locations and Appearances. Atlas of Normal Imaging Variations of the Brain, Skull, and Craniocervical Vasculature. 2017;:177-237. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-39790-0_11
Incoming Links
- Choroidal epithelial cells
- Medial posterior choroidal artery
- Haemochromatosis (CNS manifestations)
- Atypical choroid plexus papilloma
- Germinal matrix haemorrhage
- Cerebrospinal fluid
- Ventricular system
- Lateral ventricle
- Ventriculitis
- Cerebellopontine angle mass
- Head ultrasound
- Choroid plexus hyperplasia
- Internal cerebral vein
- Ependymal cells
- Caudothalamic groove
- Transcranial Doppler sonography (ultrasound)
- Hydranencephaly
- Transthyretin amyloidosis
- Pia mater
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis (CNS manifestations)
- Choroid plexus xanthogranulomata
- Choroid plexus lipoma
- Bilateral choroid plexus xanthogranuloma
- Intracranial ventricular anatomy
- Benign miliary osteoma cutis
- Choroid plexus xanthogranulomas
- Bochdalek's flower basket
- Atypical choroid plexus papilloma
- Choroid plexus carcinoma
- Tela choroidea and choroid plexus of lateral ventricles (Gray's illustration)
- Choroid plexus cyst
- Choroid plexus xanthogranuloma
- Choroid plexus xanthogranuloma
- Large choroid plexus xanthogranuloma
- Choroid plexus xanthogranuloma
- Aicardi syndrome
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.