Falx cerebri
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Julian Maingard had no recorded disclosures.
View Julian Maingard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Falxes cerebrorum
- Falces cerebrorum
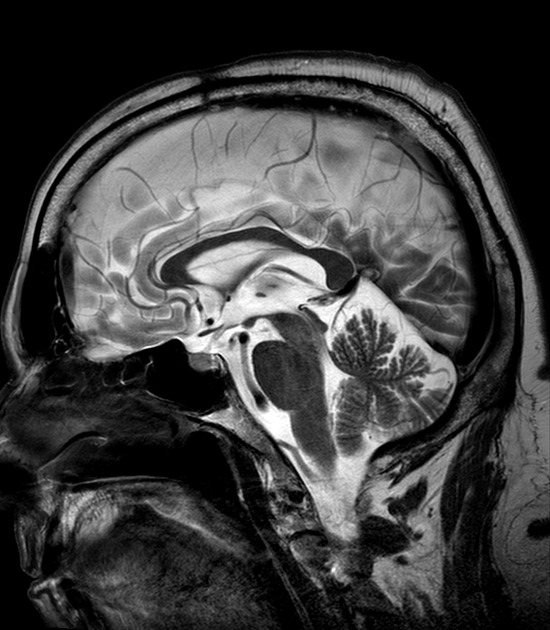
The falx cerebri (plural: falxes/falces cerebrorum) is the largest of the four main folds (or septa) of the intracranial dura mater, separating the cerebral hemispheres 1.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The falx cerebri is a double-fold of dura mater that descends through the interhemispheric fissure in the midline of the brain to separate the two cerebral hemispheres.
The falx cerebri is relatively thin anteriorly where it attaches to the crista galli of the ethmoid bone, but is broader posteriorly where it attaches to the superior surface of the tentorium cerebelli inferiorly 1,2. It attaches superiorly to the midline of the cranium and extends posteriorly to attach to the internal occipital protuberance 3.
For blood supply and innervation, see dura.
Relations
superior margin contains the superior sagittal sinus
free edge between its attachments inferiorly closely related to the superior surface of the corpus callosum and contains the inferior sagittal sinus 2,3
straight sinus is included in the line of attachment between the falx cerebri and the tentorium cerebelli 3
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Variant anatomy
The falx is rarely abnormal as an isolated variant; rather it is usually deficient as part of a broader congenital abnormality such as holoprosencephaly 6. The most common variants are seen anteriorly where the falx may be deficient or fenestrated 6. Abnormalities of the falx are frequently associated with abnormalities of the superior sagittal sinus 6.
Radiographic features
CT
anterior midline linear density near the vertex
triangular density inferiorly and posteriorly on axial sections 4
partially calcified in 7% of individuals
MRI
thin membrane on T1W and T2W images
calcifications visible on T1W imaging as hyperintensities and hypointensities on T2W imaging 5
History and etymology
The word originates from the Latin falx meaning sickle, due to its sickle-like shape.
Related pathology
References
- 1. Jinkins JR. Atlas of Neuroradiologic Embryology, Anatomy, and Variants. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (2000) ISBN:0781716527. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Pradyumna Herle, Akshat Saxena, Rudy Ambikaipalan. Basic and Clinically Relevant Anatomy. (2019) ISBN: 9781922078025
- 3. Standring S. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 40th Ed. Elsevier 2008.
- 4. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012) ISBN:0521766664. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 5. Berry. Diagnostic Radiology. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. ISBN:8180616363. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 6. Gupta SK, Aggarwal A. The missing falx: a potential surgical pitfall during interhemispheric transcallosal approach. (2017) Acta neurochirurgica. 159 (10): 1909-1911. doi:10.1007/s00701-017-3292-z - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Semilobar holoprosencephaly
- Posterior meningeal artery
- Post-hydrocephalus corpus callosum damage
- Superior sagittal sinus
- Falciform ligament
- Gorlin-Goltz syndrome
- Hyperostosis frontalis interna
- Subdural hemorrhage
- Tentorium cerebelli
- Corpus callosum
- Alobar holoprosencephaly
- Dura mater
- Schwannomatosis
- Interhemispheric fissure
- Interdigitation of gyri
- Fatty falx cerebri
- Hydranencephaly
- Frontal lobe
- Subdural haemorrhage (summary)
- Midline shift (summary)
- Alobar holoprosencephaly
- Secondary abdominal pregnancy after uterine expulsion
- Falcine meningioma
- Alobar holoprosencephaly
- Extradural spinal CSF leak
- Subdural haemorrhage
- Cranial meninges and falx (Gray's illustration)
- Alobar holoprosencephaly
- Semilobar holoprosencephaly
- Von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Neurofibromatosis type 2
- Alobar holoprosencephaly
- Acute right MCA M1 occlusion
- Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) in a toddler
- Intracranial meningioma with extracranial propagation
- Anoxic brain injury secondary to cardiac arrest
- Neurofibromatosis type 2
- Meningioma - inferior edge of falx
- Calcification of the falx cerebri
- Semilobar holoprosencephaly
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.