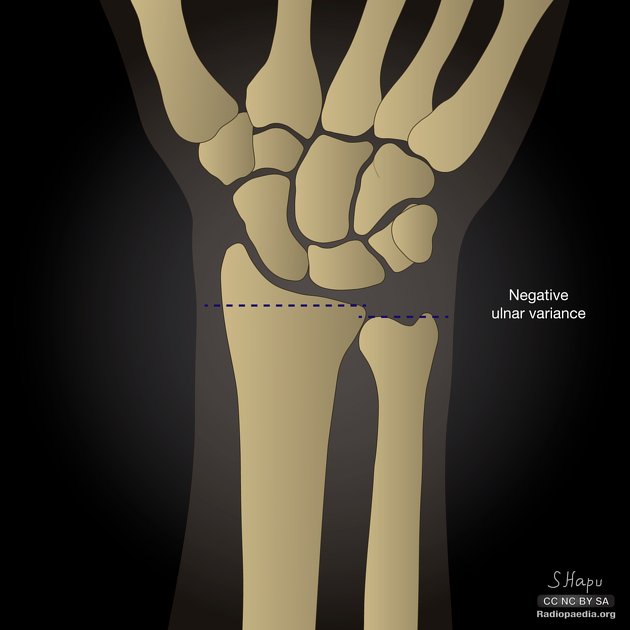
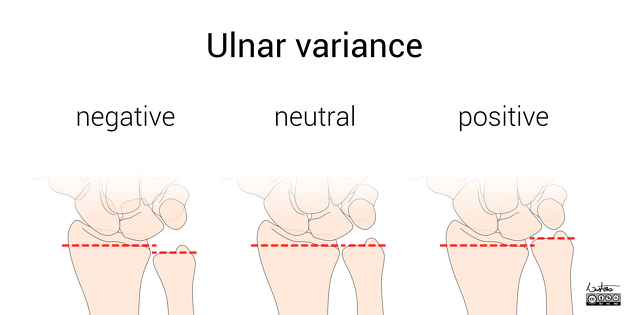
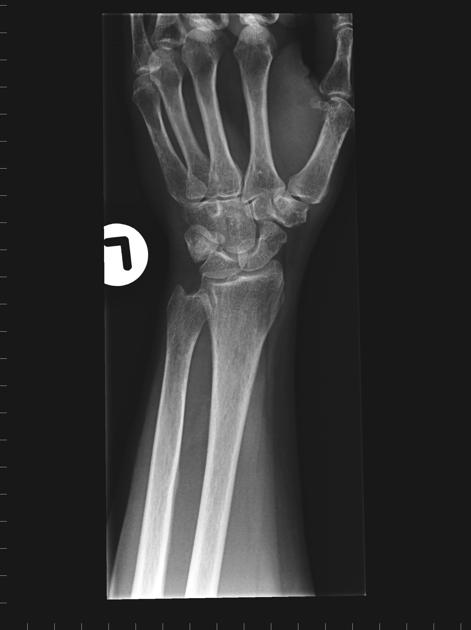
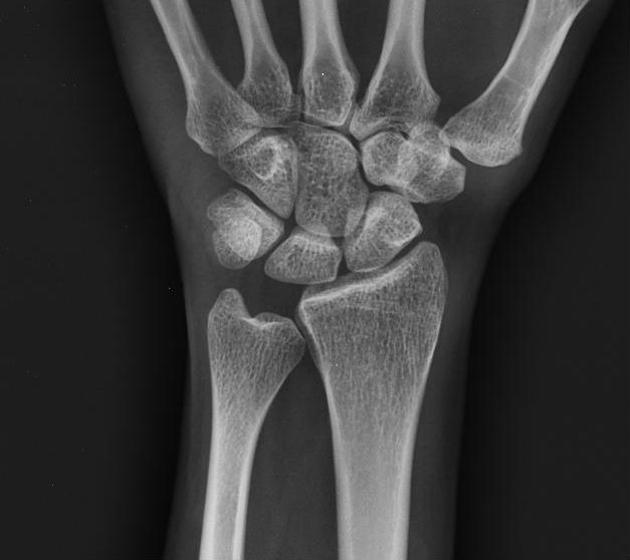
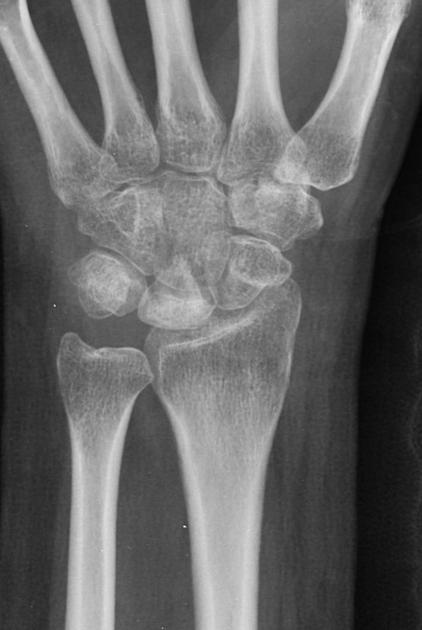
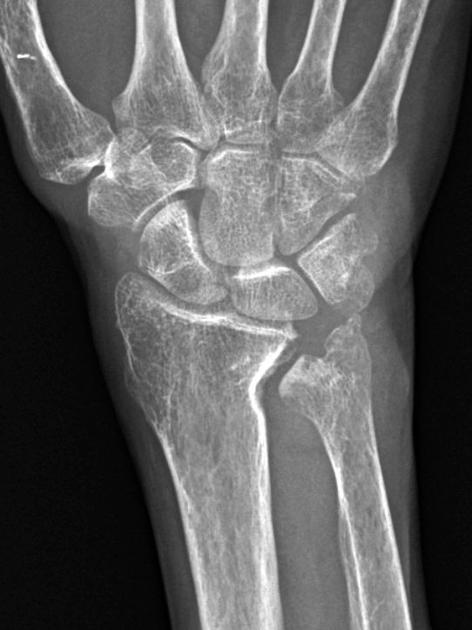
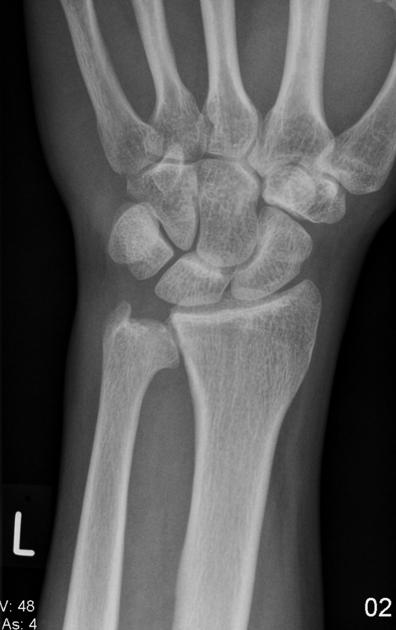
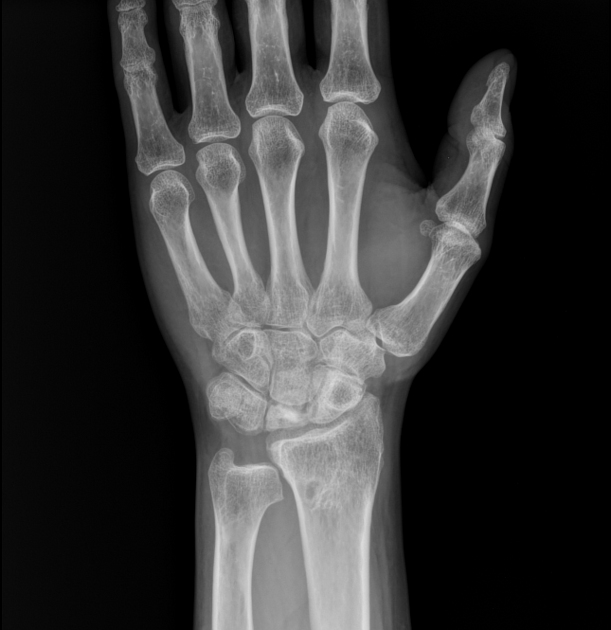
Negative ulnar variance
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Gagandeep Singh had no recorded disclosures.
View Gagandeep Singh's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Negative ulnar variances
Negative ulnar variance describes a state where the ulna is abnormally shortened (by more than 2.5 mm) compared to the radius and plays an important role in wrist pathology.
There is a significant association between negative ulnar variance and Kienböck disease, although the majority of people with negative ulnar variance do not have this condition. A causal association is difficult to prove, however the effectiveness of decompressive procedures such as radial shortening or ulnar lengthening in relieving pain and preventing further collapse of the lunate supports this 1.
Ulnar impingement syndrome, a wrist condition caused by a shortened distal ulna impinging on the distal radius proximal to the sigmoid notch of radius, is usually due to acquired ulnar shortening but can be due to de novo negative ulnar variance 2.
See also
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Chen W. Kienböck Disease and Negative Ulnar Variance. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(1):143-4. - Pubmed
- 2. Cerezal L, del Piñal F, Abascal F, García-Valtuille R, Pereda T, Canga A. Imaging Findings in Ulnar-Sided Wrist Impaction Syndromes. Radiographics. 2002;22(1):105-21. doi:10.1148/radiographics.22.1.g02ja01105 - Pubmed
- 3. Voorhees D, Daffner R, Nunley J, Gilula L. Carpal Ligamentous Disruptions and Negative Ulnar Variance. Skeletal Radiol. 1985;13(4):257-62. doi:10.1007/BF00355345 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Wrist
- Rett syndrome
- Wrist radiograph (checklist)
- Carpal instability
- Radiocarpal joint
- Ulnar variance
- Ulnar impingement syndrome
- Pseudo-Madelung deformity
- Causes of abnormal lunate signal on MRI
- Congenital radial head dislocation
- Kienböck disease
- Madelung deformity
- Triangular fibrocartilage complex
- Positive ulnar variance
- Kienbock disease (lunatomalacia)
- Non-union ulnar styloid fracture with negative ulnar variance
- Kienböck disease with negative ulnar variance
- Kienböck disease
- Kienbock disease
- Pseudo-Madelung deformity - hereditary multiple exostoses
- Pseudo-Madelung deformity
- Kienböck disease
- Fracture of the radial styloid process with scapholunate dissociation
- Kienböck disease
- Kienböck disease
- Kienböck disease
- Lunotriquetral coalition - complete osseous fusion
- Scapholunate advanced collapse (SLAC) & dorsal intercalated segment instability (DISI)
- Extensor carpi ulnaris subluxation
- Ulnar variance (illustration)
- Kienböck disease
- Kienbock disease
- Ulnar impingement with negative ulnar variance
- CT apperance of ulnar impingement syndrome secondary to negative ulna variance
Related articles: Anatomy: Upper limb
-
skeleton of the upper limb
- clavicle
- scapula
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- hand
- accessory ossicles of the upper limb
- accessory ossicles of the shoulder
- accessory ossicles of the elbow
-
accessory ossicles of the wrist (mnemonic)
- os centrale carpi
- os epilunate
- os epitriquetrum
- os styloideum
- os hamuli proprium
- lunula
- os triangulare
- trapezium secondarium
- os paratrapezium
- os radiostyloideum (persistent radial styloid)
- joints of the upper limb
-
pectoral girdle
-
shoulder joint
- articulations
- associated structures
- joint capsule
- bursae
- ligaments
- movements
- scapulothoracic joint
-
glenohumeral joint
- arm flexion
- arm extension
- arm abduction
- arm adduction
- arm internal rotation (medial rotation)
- arm external rotation (lateral rotation)
- circumduction
- arterial supply - scapular anastomosis
- ossification centers
-
shoulder joint
-
elbow joint
- proximal radioulnar joint
- ligaments
- associated structures
- movements
- alignment
- arterial supply - elbow anastomosis
- development
-
wrist joint
- articulations
-
ligaments
- intrinsic ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments
- radioscaphoid ligament
- dorsal intercarpal ligament
- dorsal radiotriquetral ligament
- dorsal radioulnar ligament
- volar radioulnar ligament
- radioscaphocapitate ligament
- long radiolunate ligament
- Vickers ligament
- short radiolunate ligament
- ulnolunate ligament
- ulnotriquetral ligament
- ulnocapitate ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- associated structures
- extensor retinaculum
- flexor retinaculum
- joint capsule
- movements
- alignment
- ossification centers
-
hand joints
- articulations
- carpometacarpal joint
-
metacarpophalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
-
interphalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
- movements
- ossification centers
- articulations
-
pectoral girdle
- spaces of the upper limb
- muscles of the upper limb
- shoulder girdle
- anterior compartment of the arm
- posterior compartment of the arm
-
anterior compartment of the forearm
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
-
posterior compartment of the forearm (extensors)
- superficial
- deep
- muscles of the hand
-
accessory muscles
- elbow
- volar wrist midline
- palmaris longus profundus
- aberrant palmaris longus
- volar wrist radial-side
- accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis
- flexor indicis profundus
- flexor carpi radialis vel profundus
- accessory head of the flexor pollicis longus (Gantzer muscle, common)
- volar wrist ulnar-side
- dorsal wrist
- blood supply to the upper limb
-
arteries
- subclavian artery (mnemonic)
- axillary artery
- brachial artery (proximal portion)
- ulnar artery
- radial artery
- veins
-
arteries
- innervation of the upper limb
- intercostobrachial nerve
-
brachial plexus (mnemonic)
- branches from the roots
- branches from the trunks
- branches from the cords
- lateral cord
- posterior cord
- medial cord
- terminal branches
- lymphatic drainage of the upper limb
Related articles: Wrist pathology
- alignment
- wrist fractures and dislocations
- distal radial fracture
- pediatric
- carpal bones
- Mayfield classification of carpal instability
- carpal instability
- osteonecrosis
- triangular fibrocartilaginous complex (TFCC) injuries
- ulnar-sided wrist impaction and impingement syndromes
- soft tissue and tendons
- arthritides





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.