The cerebellum, meaning "the little brain", sits at the base of the brain in the posterior cranial fossa below the tentorium and behind the brainstem.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The cerebellum has the following features:
three surfaces: anterior (petrosal), superior (tentorial), inferior (suboccipital)
three fissures: primary (tentorial), horizontal (petrosal), prebiventral/prepyramidal (suboccipital)
two hemispheres
single median vermis
Vermis
The cerebellar vermis is located in the midline, separating the two cerebellar hemispheres. Its organization mirrors that of the adjacent hemispheres divided into nine lobules.
Cerebellar hemisphere
Just like the vermis, each hemisphere is divided into nine lobules separated by fissures:
wing of lingula (lingula)
wing of central lobule (central lobule)
-
quadrangular lobule (culmen)
primary (tentorial) fissure
simple lobule (declive)
-
superior semilunar lobule (folium)
horizontal (petrosal) fissure
-
inferior semilunar lobule (tuber)
prebiventral/prepyramidal (suboccipital) fissure
biventral lobule (pyramid)
tonsil (uvula)
flocculus (nodulus)
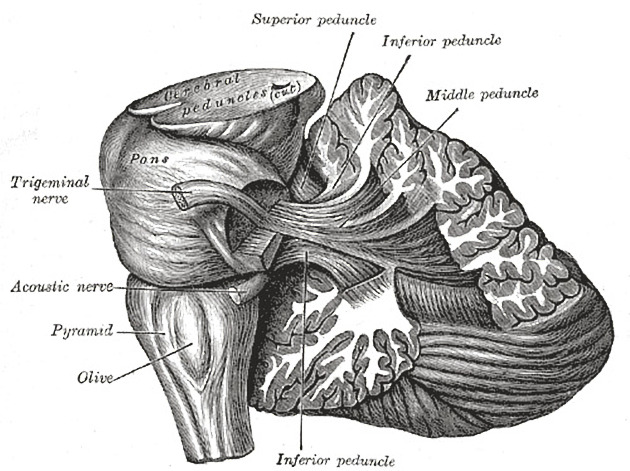
Connections to brainstem
to the midbrain via the superior cerebellar peduncles (brachia conjunctiva)
to the pons via the middle cerebellar peduncles (brachia pontis)
to the medulla via the inferior cerebellar peduncles (restiform bodies)
CSF cisterns
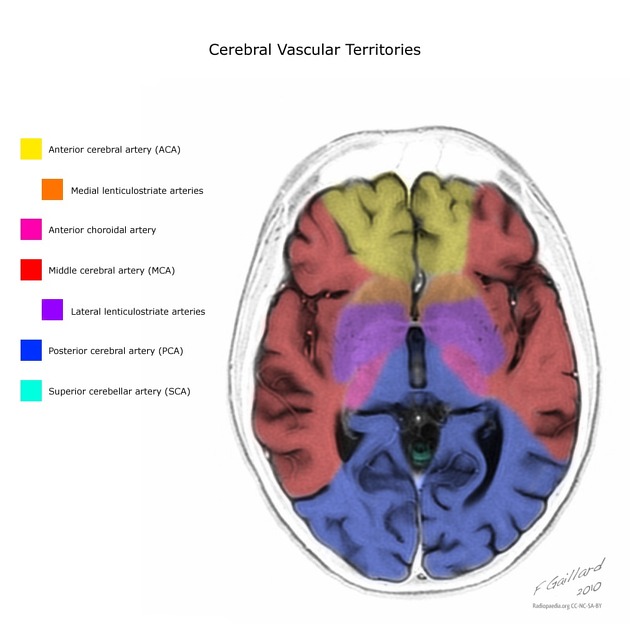
Arterial supply
The cerebellum is supplied by three bilateral arteries from the vertebrobasilar system:
superior cerebellar artery (SCA): branch of the distal basilar artery
anterior inferior cerebellar (AICA): branch of the proximal basilar artery
posterior inferior cerebellar (PICA): branch of the distal vertebral arteries
Superior cerebellar (SCA)
The SCA supplies:
whole superior surface of the cerebellar hemispheres down to the great horizontal fissure
the superior vermis
most of the cerebellar white matter
superior cerebellar peduncle
middle cerebellar peduncle
Anterior inferior cerebellar (AICA)
The AICA has a variable vascular territory depending on the size of the PICA (see AICA-PICA dominance) but usually supplies:
middle cerebellar peduncle
inferolateral portion of the pons
flocculus
anteroinferior surface of the cerebellum
Posterior inferior cerebellar (PICA)
The PICA has a variable vascular territory depending on the size of the AICA (see AICA-PICA dominance), but usually supplies:
posteroinferior cerebellar hemispheres (up to the great horizontal fissure)
inferior portion of the vermis
inferior cerebellar peduncle
It divides into lateral and medial branches that supply the inferior portion of the vermis and cerebellar hemispheres respectively.
There are some variations in the PICA:
18% arise extracranially, inferior to the foramen magnum
10% arise from the basilar rather than vertebral artery
2% bilaterally absent
occasionally loops around the cerebellar tonsil
occasionally a small vertebral artery will terminate into a common PICA/AICA trunk
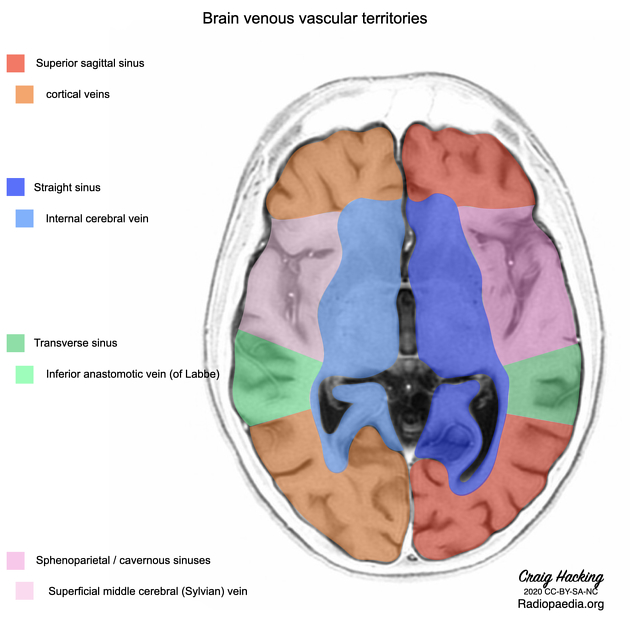
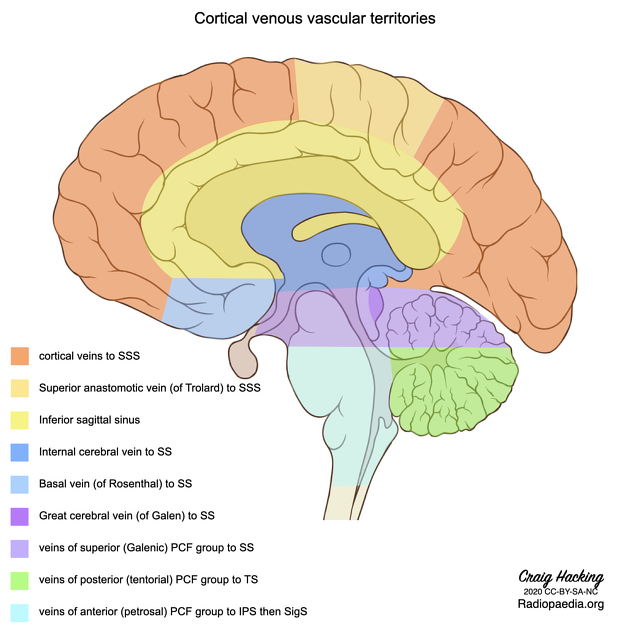
Venous drainage
There are three major groups of bilateral veins that drain the cerebellum along with other structures of the posterior cranial fossa. Not unsurprisingly there is significant variation between patients and also between the left and right in the same patient.
The three posterior fossa venous groups are:
-
superior (Galenic)
drains the midbrain, upper pons, superior vermis and the superior surface of the cerebellar hemispheres
-
drains into the vein of Galen and has three named veins
precentral cerebellar vein
superior vermian vein
anterior pontomesencephalic vein
-
anterior (petrosal)
drains the lateral pons, medulla and the anterior surface of the cerebellar hemispheres
drains into the inferior petrosal sinus and has a petrosal vein
-
posterior (tentorial)
drains the inferior vermis, tonsils and the posteroinferior surface of the cerebellar hemispheres
drains into the transverse sinus and has an inferior vermian vein
Variant anatomy
tonsillar ectopia: asymptomatic protrusion of the tonsils through the foramen magnum by no more than 3-5 mm
Related pathology
-
neoplastic
-
inflammatory
-
degenerative
-
congenital disease
-
intoxication
-
signs
-
others







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.