Cerebral peduncles
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures- Crus cerebri
- Crura cerebri
- Cerebral crus
- Basis pedunculi
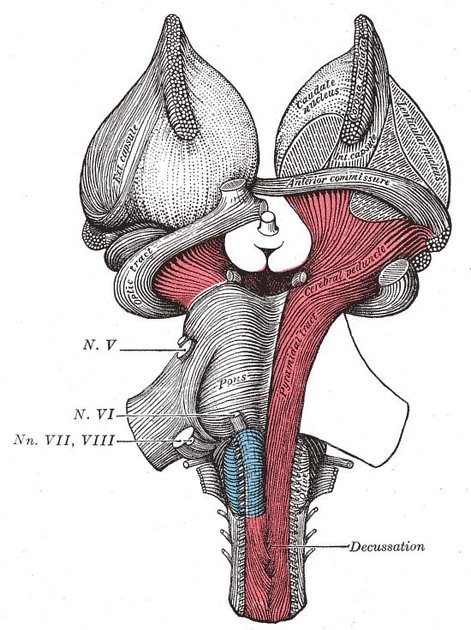
The cerebral peduncles are the anterior part of the midbrain that connects the brainstem to the thalami. They are paired, separated by the interpeduncular cistern, and contain the large white matter tracts that run to and from the cerebrum.
Terminology
The crus cerebri (cerebral crus) usually refers to the most anterior, semilunar shaped bundle of white matter fibers in the midbrain, including the corticospinal tract centrally (3/5 intermediates) as well as the corticopontine (fronto-pontine and temporo-pontine fibers) and corticobulbar tracts. Posterior to the crus cerebri is the substantia nigra, followed by the mesencephalic tegmentum.
"Cerebral peduncle" is commonly used synonymously with the crus cerebri alone 1,2, but traditionally this refers to the cylindrical shaped combination of the crus cerebri, substantia nigra, and tegmentum (i.e., the entire midbrain ventral to the tectum) 1-4.
The basis pedunculi or crusta traditionally refers to the combination of the crus cerebri and substantia nigra 3, but has also been used synonymously with the crus cerebri 2.
References
- 1. Hirsch WL, Kemp SS, Martinez AJ, Curtin H, Latchaw RE, Wolf G. Anatomy of the brainstem: correlation of in vitro MR images with histologic sections. (1989) AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology. 10 (5): 923-8. Pubmed
- 2. Vanderah TW, Gould DJ. Nolte's The Human Brain (7th edition). (2015) ISBN: 9781455728596
- 3. Standring S. Gray's Anatomy (40th edition). (2015) ISBN: 9780702052309
- 4. Crossman AR, Neary D. Neuroanatomy (6th edition). (2019) ISBN: 9780702074622
Incoming Links
- Trochlear nerve
- Anterior choroidal artery
- Lateral mesencephalic vein
- Red nucleus
- Crural cisterns
- CLCN2-related leukoencephalopathy
- Crus (disambiguation)
- Midbrain
- Weber syndrome
- Tegmentum
- Veins of the brainstem
- Posterior perforated substance
- Cerebrum
- Cavernous sinus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- Oculomotor nucleus
- Oculomotor nerve
- Kernohan phenomenon
- Peduncular vein
- Substantia nigra
- Guineafowl (Rorschach radiology)
- Incontinentia pigmenti (Bloch-Sulzberger syndrome)
- Embolic shower
- Huge periventricular nodular heterotopia and closed lip schizencephaly
- Posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistula
- Brain metastasis (large cystic mass)
- Suprasellar arachnoid cyst
- Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts
- Normal cranial nerves
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
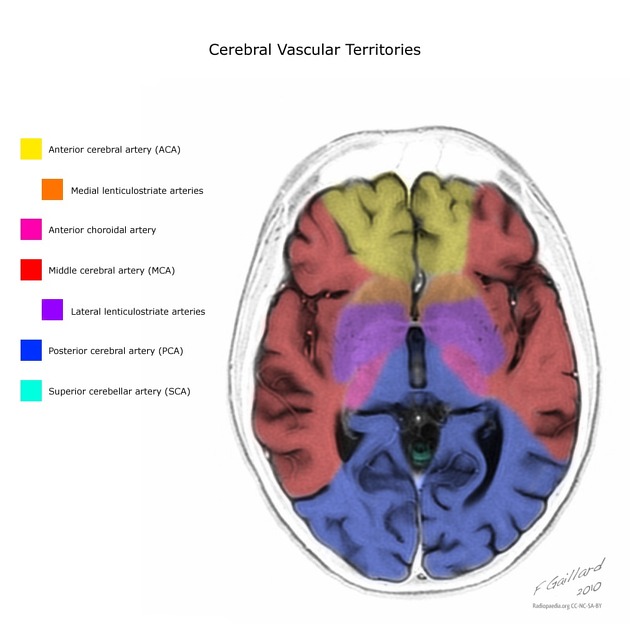
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
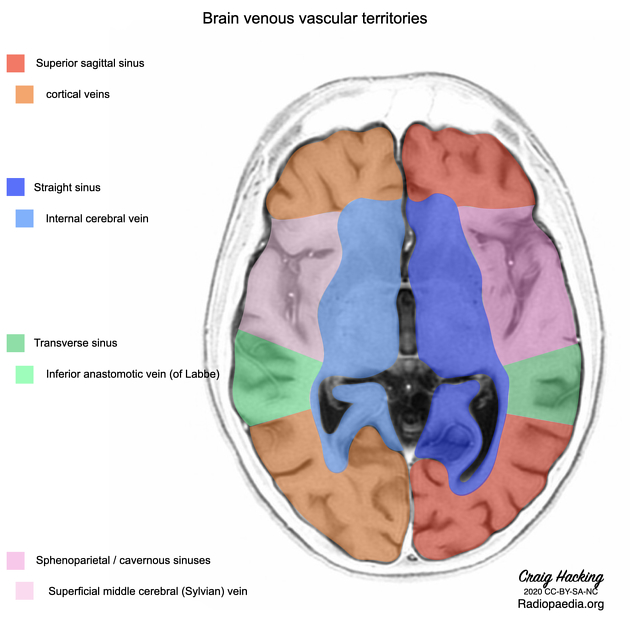
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.